Billing and Coding Guidelines for Radiation Oncology Including Intensity
Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
LCD Determination ID Number
L34652
Guidelines
Reasons for Denial
Services performed for diagnoses not listed as covered in this policy or for excessive frequency will be
denied as not medically necessary. Frequency is considered excessive when services are performed more
frequently than generally accepted by peers and the reason for additional services is not justified by
documentation.
Indications not listed as covered under the Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity
section will be denied as not medically necessary.
When a hospital inpatient is transported to a freestanding facility for therapy, the technical component of
the radiation oncology services cannot be paid to the freestanding facility. Unless the patient is
discharged from the hospital and treated at the freestanding facility as an outpatient, this payment will be
denied.
Appeals for denied claims must be accompanied by that portion of the patient’s medical record that
documents the reason for the service. It is not necessary to provide the complete medical record.
Note: All documentation must be specific to the patient being treated or the claim will be denied.
Billing and Coding
A. Treatment planning is a one-time charge per course of therapy. Billing for multiple treatment plans for
a single course of treatment is not allowed. This is a professional service only and the physician is
responsible for all the technical aspects of the treatment planning process.
1. CPT code 77261 is used when the volume of interest to be treated is clearly defined and easily
encompasses the tumor while excluding normal tissue and structures. Simple planning requires a
single treatment area of interest encompassed in a single port or simple parallel opposed ports
with simple or no blocking.
2. CPT code 77262 is used when there is a moderate level of planning difficulty involved. It
requires three (3) or more converging ports, two (2) separate treatment areas, multiple blocks, or
special time dose constraints.
3. CPT code 77263 is uses when complex treatment planning is involved. Complex planning
requires highly complex blocking, custom shielding blocks, tangential ports, special wedges or
compensators, three (3) or more separate treatment areas, rotational or special beam
considerations, or combination of therapeutic modalities. Complex planning includes
interpretation of special testing, tumor localization, treatment volume determination, treatment
time/dosage determination, choice of treatment modality, determination of number and size of
treatment ports, selection of appropriate treatment devices, and other procedures.
B. Following treatment planning, simulation is used to actually direct the treatment beams to the specific
volume of interest. Simulation may be carried out on a dedicated conventional stimulator or CT
scanner, radiation therapy treatment unit (e.g., linear accelerator), or using diagnostic imaging
equipment (e.g., fluoroscopy, CT, MR). The complexity of the simulation is based on number of
ports, volumes of interest, and the inclusion and type of treatment devices. The number of films
taken per treatment, the modality from which the images for simulation are obtained, and the use of
fluoroscopy are not determinants of complexity. Portal changes based on unsatisfactory initial
simulation(s) are not reported as additional simulations. Additional simulations may be necessary
during a treatment in order to account for changes in port size, boost dose, or tumor volume.
However, minor changes in port size without changes in beam or without clinical justification do not
warrant an additional charge or a higher level of complexity.
Inclusion of treatment devices in the simulation process typically increases the complexity.
Simulation without the inclusion of devices or with any pre-made devices (e.g., blocks,
immobilization) is considered simple. The addition of custom immobilization devices or tangential
ports is an indicator of complex level of simulation. The typical course of radiation therapy will
require between one and three simulations. However, no more than one simulation should be
reported on any given day. Frequency in excess of three simulations should be supported by
documentation in the medical record.
1. Use CPT code 77280 to report simple simulation of a single treatment area. A treatment area is a
contiguous anatomic location that will be treated with radiation therapy. Generally, this includes
the primary tumor organ or the resection bed and the draining lymph node chains.
2. Use CPT code 77285 to report intermediate simulation for two (2) separate treatment areas.
3. Use CPT code 77290 to report complex simulation for three (3) or more treatment areas, or any
number of treatment areas if any of the following are involved: particle, rotation or arc therapy;
complex blocking; custom shielding blocks; brachytherapy simulation; hyperthermia probe,
verification; any use of contrast materials.
4. Use CPT code 77293 as an add-on code for respiratory motion management simulation. It
describes the physician work and resources involved in acquiring a respiratory correlated or 4-D
Ct simulation study for conformal planning. Add-on codes are never performed independently
and must be reported in addition to the primary procedure. This code must be reported with the
primary procedure of either 77295 or 77301 for the same date of service, even though the work
may take place over many days.
C. Use CPT code 77295 to report 3-dimensional radiothreapy plan, including dose-volume histogram.
This code also includes those procedures done in preparation for use of coplanar therapy beams and,
therefore, CPT codes 77280, 77285, and 77290 are not separately payable on the same date. It also
includes the work done for a teletherapy isodose plan (CPT codes 77306-77307) and accordingly,
codes 77306-77307 should not be billed separately. Code 77295 may be billed once per treatment
course per treatment volume. In those uncommon circumstances, where there is a substantial change
in either patient anatomy or tumor conformation and where a second CT dataset is required to
produce an accurate, efficacious and safe “cone-down” plan, a second 77295 charge may be
appropriate. When the physician deems this to be the case, the medical necessity for the second
77295 simulation must be documented.
D. Basic radiation dosimetry, calculation, central axis depth, TDF, NSD, gap calculation, off axis factor,
tissue inhomogeneity factors, as required during course of treatment but only when prescribed by the
treating physician. This service is considered to be medically necessary for each treatment port and if
a patient has off-axis calculations, calculations for different depth doses, different volumes of interest,
secondary film dosimetry, abutting volumes of interest, or any other situation requiring individual
point calculations of radiation dosage. Changes in a patient’s weight or girth during the course of
radiation treatment may necessitate dosimetry recalculation. This procedure need not be routinely
performed each time the patient is treated. Basic dosimetry calculations (CPT code 77300) may be
reported as many times as the calculations are performed. The typical course of radiation therapy will
require from one to six dosimetry calculations, depending on the complexity of the patient’s problem.
However, radiation treatments to the head/neck, prostate and Hodgkin’s disease may require eight or
more calculations.
E. Teletherapy isodose plan is considered medically necessary for a given course of radiation therapy to
a specific volume of interest. The typical course of radiation therapy will require from one to three
isodose plans. Usually only one plan per volume of interest will be sufficient, though some patients
may require multiple teletherapy plans during the course of therapy. Situations that may require an
extra teletherapy plan include the need to change the machine or volume of interest. Toward the end
of treatment, due to clinical variations of the patient, another plan may be required.
1. Use CPT code 77306 for a simple teletherapy isodose plan when there are one or two unmodified
ports directly at one volume of interest. This code includes basic dosimetry calculations.
2. Use CPT code 77307 for a complex teletherapy isodose plan when multiple treatment areas,
tangential ports, the use of wedges, blocking, rotational beams, or special beam considerations
will be used. This code includes basic dosimetry calculations.
3. Special teletherapy port plan, particles, hemi-body, total body uses CPT code 77321. Only one
plan should be billed per treatment course.
F. Special dosimetry (e.g., TLD, microdosimetry), CPT code 77331 is considered medically necessary
once per port when the physician determines that it is necessary to have a measurement of the amount
of radiation that a patient has actually received at a given point, with the final results being utilized to
accept or modify the current treatment plan. This procedure will generally be reimbursed one time
per port per course of treatment when prescribed by the treating physician. The monitoring devices
utilized for measuring and monitoring can include thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLD), solid state
diode probes, special dosimetry probes, or film dosimeters. The physician must specify the type of
special dosimetry. When special dosimetry is employed, the usual frequency will vary from one to
six, consistent with the number of dose calculations. Frequency in excess of the upper end of this
range will require appropriate documentation in the medical record. This code (CPT 77331) may be
used more than once per day per treatment course.
G. Treatment devices, designs, and construction may be charged during a course of therapy when
documentation substantiates multiple volumes of interest/ports, the use of custom-made devices,
and/or the necessity of replacement devices. Providers should bill for devices at the beginning of the
treatment course and then may bill again later in the course of treatment when additional or new
devices are required. Payment for one set of treatment devices may be allowed per separate port
when radiation therapy is started. However, a pair of mirror imaged opposing ports, ports that direct
parallel beams such as anterior-posterior or left lateral-right lateral pairs are considered, for billing
purposes, to be one port. This is true regardless of the level of complexity of the devices used to
create the ports. However, if these devices are significantly different from each other, then the
contractor may allow payment for each of the pair of devices. It is the responsibility of the provider to
determine the CPT code that most accurately describes the devices employed. At all levels of

complexity, the physician must be directly involved in the design, selection, and placement of any of
the devices.
A pair of devices for opposing ports, constructed from drawings made by a physician on a single film,
is considered for physician professional billing purposes to be one port. Each individual device
constructed may be billed separately by the facility. This is true regardless of the level of complexity
of the devices used to create these ports. The physician must be directly involved in the design,
selection, and placement of any of the devices.
When the patient has a combination of a wedge compensator (complex beam modification device)
and a bolus (simple beam modification device), covering the same treatment port, this would be billed
as a single complex treatment device rather than as a separate charge for each of the additional items
of lower complexity. If beam modification devices of two separate levels of complexity are utilized
for the same treatment port, only the one of highest complexity should be billed. Restraining devices
and beam modification devices may be billed separately for the same port, but only one restraining
device may be billed for each volume of interest treated.
The typical course of radiation therapy will justify from one to five charges for devices.
Treatment for prostate, head & neck and other complex therapy may require eight or more treatment
devices. Frequency in excess of the upper limit must be supported by documentation in the medical
record. These codes (CPT 77332-77334) may be used more than once per day per treatment course.
Code(s) 77332-77334 may be quantity billed on the same line of the 1500 claim form if a global
service is billed. When billing these codes with a 26 or a TC modifier each service has to be broken
out and billed per line.
It should be noted that when more than one volume of interest is being treated, it may be appropriate
to bill for devices for each volume of interest. The level of complexity of these devices will be
independent of each other. The number of different anatomic sites determines the number of sets or
ports involved except opposing fields (such as AP/PA) which represent one set. Each set must be
submitted on the claim, with the appropriate level of complexity at the onset of therapy or as
appropriate when additional devices are implemented during a course of treatment.
1. Use CPT code 77332 for simple treatment devices, design, and construction that include simple
port blocks that include one or two hand-positioned pre-made blocks; simple prefabricated bolus
that is capable of being shaped for an individual patient; or independent jaw motion or
asymmetrical collimation.
2. Use CPT code 77333 for intermediate treatment devices, design, and construction that include
multiple port blocks which include three or more pre-made blocks such as corner pelvis blocks,
beam splitter blocks, or midline spinal cord blocks; stents; bite blocks; or special multi-use bolus.
3. Use CPT code 77334 for complex treatment devices, design, and construction that include
customized, single-use bolus such as wax molds conformed to a particular patient body part;
customized blocks (low temperature alloy); customized compensators; wedges; molds or casts;
custom made immobilization devices, or eye-shields,. Custom made immobilization include
restraining devices such as aquaplast and alpha cradle. The use of passive restraints such as
straps, pillows, sandbags, etc. are not billable.
H. Medical radiation physics consultation are technical services only, and are payable only in a setting in
which the technical component is payable by Medicare such as freestanding radiation oncology center
that employs its own radiation physicist.
1. Use CPT code 77336 for continuing medical radiation physics consultation, including assessment
of treatment parameters, quality assurance of dose delivery, and review of patient treatment
documentation in support of the radiation oncologist, reported per week of therapy (once every
consecutive five treatments delivered). This frequency should match the weekly radiation
treatments billed. It is specific to the review of the weekly radiation treatment plan. This
consultation ensures that the treatment administered conforms the specifications of the
prescribing physician. It includes a documented review of the patient’s treatment chart and
record to verify that the patient received the prescribed radiation dosage, appropriate positioning
and beam orientation and radiation safety.
2. Use CPT code 77370 for special medical radiation physics consultation when a problem or
special situation arises during radiation therapy. This code requires a detailed written report
describing the problem to be given to the requesting physician.
Computation of dose to the fetus of a pregnant patient undergoing radiation therapy may be reported
using this code. Special brachytherapy equipment developed by the qualified medical physicist to
treat a particular patient can also be reported with this code. The qualified medical physicist will
spend a considerable amount of time and effort on behalf of a specific patient and will render a
customized written report (which will form part of the patient’s chart) to the radiation oncologist in
reference to the problem or service being addressed. Documentation of the physician’s request and
the physics report, as well as the physician review of that report, in the medical record is necessary.
Special physics consultations should not be charged when a qualified medical physicist verifies the
calculations performed by others or performs the duties of other members of the treatment team (e.g.
dosimetrists)
I. IMRT with simple technical guidance and tracking for CPT code 77385 is performed at any energy
including any of the following: prostate, beast, and all site using physical compensator based IMRT.
To report professional component of guidance and tracking, use CPT code 77387 with modifier 26.
This code is only used by OPPS.
J.IMRT with complex technical guidance and tracking for CPT code 77386 is performed at any energy
including all other sites if not using physical compensation based IMRT. To report professional
component of guidance and tracking, use CPT code 77387 with modifier 26. This code is only used
by OPPS.
K. Guidance for localization of target volume for delivery of radiation treatment delivery, includes
intrafraction tracking when performed should use CPT code 77387. This code is only used by OPPS.
L. Radiation treatment delivery codes are reported once per treatment session. These codes recognize
the technical component only and contain no physician work, the professional component. Treatment
management codes contain only the professional component. CMS Pub 100-04Medicare Claim
Processing Manual, Chapter 13 – Covered Medical and Other Health Services, Section 70.3 –
Radiation Treatment Delivery (CPT 77401-77417) (Rev. 1, 10-01-03). Carriers pay for these TC
services on a daily basis under CPT codes 77401-77416 for radiation treatment delivery. They do not
use local codes and RVUs in paying for the TC of radiation oncology services. Multiple treatment
sessions on the same day are payable as long as there has been a distinct break in therapy services,
and the individual sessions are of the character usually furnished on different days. When billing for
multiple treatments on the same day, the claim must document that there has been a distinct break
between therapy. Statements such as "A.M. and P.M. treatments" suffice.
When more than one treatment is performed on the same day, e.g., hyperfractionation, each treatment
should be billed on a separate detail line.
1. Use CPT code 77401 for radiation treatment delivery, superficial and/or ortho voltage per day.
Do not report clinical treatment planning (77261, 77262, 77263), treatment devices (77332,
77333, 77334), isodose planning (77306, 77307), physics consultation (77336), or treatment
management (77427, 77431, 77470) with 77401.
2. Use CPT code 77402 for simple radiation treatment delivery > 1 MeV which requires all of the
following to be met but none of the complex or intermediate criteria being met. This criteria
includes single treatment area, one or two ports, and two or fewer simple blocks. This code is
only used by OPPS.
3. Use CPT code 77407 for intermediate treatment delivery > 1 MeV which requires that any of the
following criteria are met but none of the complex criteria is being met. This criteria is 2
separate treatment areas, 3 or more ports on a single treatment area, or 3 or more simple blocks.
This code is only used by OPPS.
4. Use CPT code 77412 for complex treatment delivery > 1 MeV which requires any of the
following criteria are met : 3 or more separate treatment areas, custom blocking, tangential ports,
sedges, rotational beam, field-in-field or other tissue compensation that does not meet IMRT
guidelines, or electron beam. This code is only used by OPPS.
5. Radiation treatment delivery can be billed using a date range if the treatments are performed on
consecutive days and the energy and level of service are the same, the total number being
indicated in the CMS 1500 days or units field. If the dates of service are not consecutive or the
energy or level of service is not the same, each date of service must be billed in a separate detail
line.
The physician’s documentation within the patient’s medical record must support complexity of
treatment and the specific energy levels reported to Medicare.
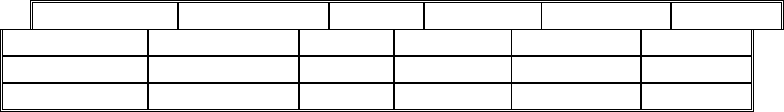
Two factors determine which treatment delivery code to choose:
• the energy level used in treatment, in megavolts (MV); and
• the complexity of treatment (defined as number of treatment sites, ports and devices).
These two selection criteria allow for the following matrix for determining which code to use:
Simple Treatment Delivery (77401, G6003, G6004, G6005, G6006)
Intermediate Treatment Delivery (G6007, G6008, G6009, G6010)
Complex Treatment Delivery (G6011, G6012, G6013, G6014)
Tier Kilo voltage ≤ 5 MV 6-10 MV 11-19 MV ≥ 20 MV
Simple
77401 G6003 G6004 G6005 G6006
Intermediate
77401 G6007 G6008 G6009 G6010
Complex
77401 G6011 G6012 G6013 G6014
Intensity Modulated Radiation Treatment (IMRT) CPT/HCPCS code G6015
Intensity modulated treatment delivery, single or multiple fields/arcs, via narrow spatially and
temporally modulated beams, binary, dynamic MLC, per treatment session. For intensity
modulated treatment planning, use 77301.
Code(s) 77401 and G6015 may be quantity billed on the same line of the 1500 claim form.
M. Portal verification film(s) CPT code 77417 is used to report port verification films or electronic
portal imaging for verification. Centers with electronic portal imaging technology may bill port film
verification when this technique is substituted for x-rays film. These films should agree with the
original simulation films and dosimetry. This is a technical component only procedure and does not
carry a professional physician component. No modifier is required for these services. The review
and interpretation of port films are considered part of the weekly clinical treatment management by
the physician. Port verification films should be reported as one charge per five fraction of therapy,
regardless of the number of films required during this time interval. CMS Pub 100-04Medicare
Claim Processing Manual, Chapter 13 – Covered Medical and Other Health Services, Section 70.3 –
Radiation Treatment Delivery (CPT 77401-77417) (Rev. 1, 10-01-03). Carriers pay for CPT code
77417 (Therapeutic radiology port film(s)) on a weekly (five fractions) basis. Portal verification
films should be reported as 1 charge per 5 fractions of therapy, per portal, one charge per port per
week, with additional charges as needed as the patient’s clinical status warrants. If at the end of a
treatment course, three or four fractions remain, then one unit of portal verification will be
reimbursed. If only one or two fractions remain, then no reimbursement will be made. This code
(CPT 77417) may be used more than once per day per treatment course.
N. Radiation treatment management, 5 treatments CPT code 77427 is reported once for every five
fractions or treatment sessions regardless of the actual time period in which the services are furnished.
The services need not be furnished on consecutive days. Multiple fractions representing two or more
treatment sessions furnished on the same day may be counted separately as long as there has been a
distinct break in therapy and the fractions are of the character usually furnished on different days. If
there are three (3) or four (4) fractions beyond a multiple of five at the end of a course of treatment,
then one unit of radiation therapy management may be billed. If one (1) or two (2) fractions beyond a
multiple of five at the end of a course of treatment are delivered, no separate reporting should be
made. The professional services furnished during treatment management typically consist of review
of port films; review of dosimetry, dose delivery and treatment parameters; review of patient
treatment set-up; and examination of patient for medical evaluation and management (e.g.,
assessment of the patient’s response to treatment, coordination of care and treatment, review of
imaging and/or lab results.) Claims should be clearly documented when a new course of therapy
begins. Payment should only be made after the fifth treatment has been delivered, not before unless
payment will be made for only one radiation therapy management service since the entire treatment
course consists of only three (3) or four (4) fractions.
CMS Pub 100-04 Medicare Claim Processing Manual, Chapter 13 – Medical and Other Health
Services, Section 70.1 – Weekly Radiation Therapy Management (CPT77419-77430) (Rev.1, 10-
01[03).
Carriers must pay for a physician’s weekly treatment management services under code 77427. Billing
entities must indicate on each claim the number of fractions for which payment is sought. A weekly
unit of treatment management is equal to five fractions or treatment sessions. A week for the purpose
of making payments under these codes is comprised of five fractions regardless of the actual time
period in which the services are furnished. It is not necessary that the radiation therapist personally
examine the patient during each fraction for the weekly treatment management code to be payable.
Multiple fractions representing two or more treatment sessions furnished on the same day may be
counted as long as there has been a distinct break in therapy sessions, and the fractions are of the
character usually furnished on different days. If, at the final billing of the treatment course, there are
three or four fractions beyond a multiple of five, those three or four fractions are paid for as a week.
If there are one or two fractions beyond a multiple of five, payment for these services is considered as
having been made through prior payments.
Instruct billing entities to indicate on each claim the number of fractions for which payment is sought.
A weekly unit of treatment management is equal to five fractions or treatment sessions. A week for
the purpose of making payments under these codes is comprised of five fractions regardless of the
actual time period in which the services are furnished. It is not necessary that the radiation therapist
personally examine the patient during each fraction for the weekly treatment management code to be
payable.
Multiple fractions representing two or more treatment sessions furnished on the same day may be
counted as long as there has been a distinct break in therapy sessions, and the fractions are of the
character usually furnished on different days.
Code 77427 is also reported if there are three or four fractions beyond a multiple of five at the end of
a course of treatment; one or two fractions beyond a multiple of five at the end of a course of
treatment are not reported separately. The professional services furnished during treatment
management typically consist of:
• review of port films;
• review of dosimetry, dose delivery, and treatment parameters;
• review of patient treatment set-ups;
• examination of patient for medical evaluation and management, (e.g., assessment of the
patient’s response to treatment, coordination of care and treatment, review of imaging
and/or lab test results).
EXAMPLE:
18 fractions = 4 weekly services
62 fractions = 12 weekly services
8 fractions = 2 weekly services
6 fractions = 1 weekly service
If billings have occurred which indicate that the treatment course has ended (and, therefore, the
number of residual fractions has been determined), but treatments resume, adjust your payments for
the additional services consistent with the above policy.
EXAMPLE:
8 fractions = payment for 2 weeks
2 additional fractions are furnished by the same physician. No additional Medicare payment is made
for the 2 additional fractions.
Each unit of service (5 treatment sessions/fractions) of radiation therapy management should be billed
on a separate claim line and should be billed with (1) one unit of service in Item 24G of the CMS-
1500 claim form or the electronic equivalent. The date of the last treatment session/fraction should be
entered as the date of service.
Documentation needs to include the date and the current treatment dose on the day of the weekly
management note, although the individual components of the service may occur throughout the
reporting period. A radiation oncologist must evaluate the clinical and technical aspects of the
treatment and document that evaluation and the resulting management decisions.
The number of treatment sessions/fractions being billed for must be indicated in Item 19 of the CMS-
1500 claim form or the electronic equivalent.
If more than one treatment session/fraction is performed on the same date of service (AM and PM),
place this information in Item 19 of the CMS-1500 claim form or the electronic equivalent.
A. SNF Treatment Management Delivery Services
A SNF may not bill weekly treatment management services for its outpatients (codes 77419, 77420,
77425, 77430, and 77431). Instead, the SNF should bill for radiation treatment delivery (codes 77401
- 77404, 77406 - 77409, 77411 - 77414, and 77416). Also, SNFs bill for therapeutic radiology port
film (code 77417), which was previously a part of the weekly services. They enter the number of
services in the units field.
O. Radiation therapy management with complete course of therapy consisting of one (1) or two (2)
fractions only uses CPT code 77431. If the entire treatment course consists of only one (1) or two (2)
fractions, the physician should bill this code and report the number of fractions in the units/days field
on the claim. This code should not be used for reimbursement of the remaining treatments at the end
of a longer course of therapy. CMS Pub 100-04 Medicare Claim Processing Manual, Chapter 13 –
Covered Medical and Other Health Services, Section 70.5 –Radiation Physics Services ( CPT Codes
77300-77399) (Rev.1, 10-01-03). Carriers pay for the PC and TC of CPT codes 77300-77334 and
77399 on the same basis as they pay for radiologic services generally. For professional component
billings in all settings, carriers presume that the radiologist participated in the provision of the
service, e.g., reviewed/validated the physicist’s calculation. CPT codes 77336 and 77370 are
technical services only codes that are payable by carriers in settings in which only technical
component is are payable.
P. Special treatment procedures (e.g., total body irradiation, hemibody radiation, per oral or endocavitary
irradiation CPT code 77470 is used to cover the additional physician effort and work for the special
procedure of hyper-fractionation, total body irradiation, per oral, endocavitary, or intraoperative cone
use, or when other modalities are being managed in combination with external beam therapy, such as
brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and any other special time consuming treatment plan. This
code is not intended to be used because a patient has another ongoing medical diagnosis like diabetes,
COPD, or hypertension.
CPT code 77470 (Special radiation treatment) covers the additional physician effort and work
required for the special procedures of:
• hyperfractionation
• total body irradiation
• brachytherapy
• hyperthermia
• planned combination with chemotherapy; or
• other combined modality therapy
• stereotactic radiosurgery
• intra-operative radiation therapy, and
• hemibody irradiation
• intracavitary cone use

• radiation response modifiers
• heavy particles (e.g. protons/neutrons)
• 3-D CRT
• IMRT
• any other special time consuming treatment plan.
It is considered an acceptable standard of practice for this code to be reported only once during a
treatment course and may be billed with the weekly management codes.
For the remaining treatment course, a physician should use the appropriate weekly radiation therapy
management codes (CPT codes 77427 and 77431) for the management of the patient.
If the treatment course is modified for any reason, the physician should use the appropriate CPT
code for the simulation field setting and dosimetry. CPT code 77470 should not be used for this
reason.
Q. In radiation oncology, evaluation and management CPT codes are not separately reportable except
for an initial visit at which time a decision is made whether to proceed with the treatment.
Subsequent evaluation and management services are included in the radiation treatment management
CPT codes. National Correct Coding Initiative Policy Manual for Medicare Services, Chapter 9 –
Radiology Services (CPT codes 70000 – 79999). F. Radiation Oncology 1. Except for an initial visit
evaluation and management (E&M) service at which the decision to perform radiation therapy is
made, E&M services are not separately reportable with radiation oncology services with one
exception as noted below. Effective January 1, 2010, CMS eliminated payment for consultation
E&M CPT codes 99241-99255. The initial E&M visit for radiation oncology services may be
reported with office/outpatient E&M CPT codes 99201-99215, initial hospital care E&M CPT codes
99221-99223, subsequent hospital care E&M CPT codes 99231-99233, or observation/inpatient
hospital care with same day admission and discharge E&M CPT codes 99234-99236.
The only radiation oncology services that may be reported with E&M services in addition to an
initial visit E&M service are CPT codes 77785-77787 (remote afterloading high dose rate
radionuclide brachytherapy...). E&M services reported with these brachytherapy codes must be
significant, separate and distinct from radiation treatment management services.
R. Radiation physics services (CPT codes 77300-77334, 77399) include a professional component (PC)
and a technical component (TC). These services are covered following the same logic as other
radiologic services that include PC and TC components.
1. The physician’s professional component is covered in all settings when the billed service
represents the physician’s (e.g., radiologist, radiation oncologist) involvement in the care.
Radiation dosimetry calculations are payable by Medicare Part B only when the physician
personally performs the service described in the code, or when the physician participated in the
provision of the service (e.g., reviewed or validated the physicist's calculation).
2. The technical component is covered only in settings where the TC is payable (e.g., freestanding
clinic). The services provided by a Radiation Physicist are considered a part of the TC.
3. When the radiation physics service is provided in a hospital setting, it is considered a Part A
service, therefore, is not billable to Part B. This is true whether the physicist is employed by a
radiologist, or is employed by, or under contract with, the hospital. Therefore, Physicists may not:
direct bill for their services,
submit "incident to" billing for services furnished to hospital inpatients or
outpatients, or
receive duplicate payment for the same services furnished by a radiation
oncologist.
4. When the radiation physics service is provided in a freestanding clinic, the physicist’s services
are included in the global service billed by the physician.
5. This code (77300) is not reported with the teletherapy isodose plan (77306, 77307),
brachytherapy isodose plan (77316, 77317, 77318), or special teletherapy port plan (77321) as
indicated in CPT coding guidelines.
S. CMS Pub 100-04 Medicare Claim Processing Manual, Chapter 13 – Covered Medical and Other
Health Services, Section 70.2 - Services Bundled Into Treatment Management Codes (Rev. 1, 10-
01-03). Carriers do not make separate payment for services rendered by the radiation oncologists
or in conjunction with radiation therapy.
The following services are bundled into the treatment management codes:
11920, 11921, 16000, 16010, 16015, 16020, 16025, 16030, 36000, 36410, 36425, 51701, 51703,
96360-96368, 90832-90838, 90846, 90847, 90863, M0064, 97802-97804, 99185, 99201-99215,
99217-99239, 99281-99480
Anesthesia (whatever code billed)
Care of infected skin (whatever code billed)
Checking of treatment charts,
Verification of dosage, as needed (whatever code billed)
Continued patient evaluation, examination, written progress notes, as needed (whatever code
billed)
Final physical examination (whatever code billed)
Medical prescription writing (whatever code billed)
Nutritional counseling (whatever code billed)
Pain management (whatever code billed)
Review & revision of treatment plan (whatever code billed)
Routine medical management of unrelated problem (whatever code billed)
Special care of ostomy (whatever code billed)
Written reports, progress notes (whatever code billed)
Follow-up examination and care for 90 days after last treatment (whatever code billed)
Please consult the latest version of Correct Coding Initiative (CCI) for rebundling combinations.
U. Place of Service:
Payment is limited to services furnished in office (POS 11), inpatient hospital (POS 21), and
outpatient hospital (POS 22). A freestanding radiation oncology center is considered, for billing
purposes, an office.
IMRT
A. Medical Radiation Physics, Dosimetry and Treatment Devices for use with IMRT
1. Basic Radiation Dosimetry
Basic radiation dosimetry is a separate and distinct service from IMRT planning and should be
reported accordingly. The radiation dose delivered by each IMRT beam must be individually
calculated and verified before the course of radiation treatment begins. Thus, multiple basic
dosimetry calculations (up to 10) are typically performed and reported on in a single day.
Supporting documentation should accompany a claim for more than ten (10) calculations in a
single day.
2. IMRT Dosimetry
CPT code 77300 basic radiation dosimetry calculation, central axis depth dose calculation,
TDF, NDS, gap calculation, off axis factor, tissue inhomogeneity factors, calculation of non-
ionizing radiation surface and depth dose, as required during course of treatment, only when
prescribed by the treating physician.
3. CPT code 77301 Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) plan, including dose-volume
histograms for target and critical structure partial tolerance specifications.
(Dose plan is optimized using inverse or forward planning technique for modulated beam
delivery (e.g., binary dynamic MLC) to create highly conformal dose distribution. Computer plan
distribution must be verified for positional accuracy based on dosimetry verification of the
intensity map with verification of treatment set-up and interpretation of verification methodology)
This code is typically reported only once per course of IMRT.
B. IMRT Treatment Delivery
1. Collimator-based IMRT Treatment Delivery
CPT/HCPCS code G6015 Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) delivery, single or
multiple fields/arcs, via narrow spatially and temporally modulated beams, binary, dynamic
MLC, per treatment session
2. Compensator-based IMRT Treatment Delivery
CPT/HCPCS code G6016 Compensator-based beam modulation treatment delivery of inverse
planned treatment using three or more high resolution (milled or cast) compensator convergent
beam modulated fields, per treatment session
C. Treatment Devices
There are several categories of treatment devices used in conjunction with the delivery of IMRT
radiotherapy. Immobilization treatment devices are commonly employed to ensure that the beam is
accurately on target. In addition, the radiation oncologist is responsible for the design of the series of
treatment devices that define the beam geometry. The beam aperture, the dose constraints per beam,
the couch and gantry angles for each portal, and the coverage requirements all must be evaluated in
order to guide the generation of the multi-leaf collimator segments. It is appropriate to report a
treatment device CPT code for each complex IMRT field (i.e., gantry/table angle for step and shoot
and sliding windows). It should not be billed for each segment within the field. CPT code 77334 is
typically billed multiple times (often on the same day of service), once for each of the separate IMRT
fields as required by the plan during the course of IMRT treatment. The typical case will require up to
ten (10) devices. A claim for the use of more than ten (10) should be submitted with supporting
documentation.
1. CPT codes for IMRT Treatment Devices
a. 77332 treatment devices, design and construction; simple (simple block, simple bolus)
b. 77333 treatment devices, design and construction; intermediate (multiple blocks, stents, bite
blocks, special bolus)
c. 77334 treatment devices, design and construction; complex (irregular blocks, special
shields, compensators, sedges, molds or casts)

2. Devices
a. CPT code 77338 Multi-Leaf Collimator (Mlc) device(s) for Intensity Modulated Radiation
Therapy (IMRT), design and construction per IMRT plan. Do not report 77338 more than
once per IMRT plan. Do not report 77338 in conjunction with G6016, compensator based
IMRT.
b. G6016 Compensator-based beam modulation treatment delivery of inverse planned treatment
using 3 or more high resolution (milled or cast) compensator convergent beam modulated
fields, per treatment session. For treatment planning, use 77301. Do not report G6016 in
conjunction with 77401, G6003-G6014 or G6015.
D. Image Guided Radiation Therapy
Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) utilizes imaging technology to modify treatment delivery to
account for changes in the position of the intended target. IGRT is used in conjunction with IMRT in
patients whose tumors are located near or within critical structures and/or in tissue with inherent setup
variation. Although an IGRT is a distinct service, it may be used and documented along with IMRT
treatment delivery (G6015) when necessary.
CPT codes for IGRT
G6001
Ultrasonic guidance for placement of radiation therapy fields
77014
Computed tomography guidance for placement of radiation therapy fields
G6002
Stereoscopic X-ray guidance for localization of target volume for the delivery of
radiation therapy
G6017
Intra-fraction localization and tracking of target or patient motion during delivery of
radiation therapy(e.g.,3-D positional tracking, gating, 3-D surface tracking), each fraction
of treatment
Bundling
CMS CCI edits will apply to radiation codes and may include the following:
The following CPT codes were used as building blocks during the development of the IMRT planning
CPT code. They are components of CPT code 77301 and therefore should not be separately coded or
billed on the same day of service.
CPT Code CPT Code Descriptor
76370 / 77014
(deleted/current)
Computerized axial tomography guidance for placement of radiation therapy fields
76375/ 76376
(deleted/current)
Coronal, sagittal, multiplanar, oblique, three-dimensional and/or holographic reconstruction
of computerized axial tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or other tomography
modality
77295 Therapeutic radiology simulation-aided field setting; Three-dimensional simulation
77331 Special radiation dosimetry
The following list of codes should not be reported on the same date of service as IMRT planning (77301).
They may, however, correctly be used, as needed, for medically necessary simulation and treatment
planning during the course of IMRT treatment (i.e. with code G6015).
CPT Code CPT Code Descriptor

77280 Therapeutic radiology simulation-aided field setting, simple
77285 Therapeutic radiology simulation-aided field setting, intermediate
77290 Therapeutic radiology simulation-aided field setting, complex
Summary of 2015 coding changes:
CMS established HCPCS level II “G” codes for use in 2015. The G codes are recognized under the
Medicare Physicians Fee Schedule (MPFS) but are not recognized under OPPS.
Radiation treatment delivery: G codes G6003-G6014 will be used in the MPFS and CPT codes 77402,
77407, and 77412 will be used in OPPS.
IMRT: G codes G6015 and G6016 are used for payment under the MPFS and CPT codes 77385 and
77386 will be used in OPPS.
Isodose Planning codes: CPT codes 77305-77315 were deleted and replaced by codes 77306 and 77307
CPT code 77300 should not be reported with these codes.
Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT): CPT codes 76950, 77421 and 0197T were deleted and
replaced with G6001, G6002 and G6017 for MPFS and CPT 77387 for OPPS, the details of the bundling
of the TC or PC can be found in the CPT manual.
Submitting Documentation:
Part A
Do not attach information to the original claim. Below is the list from the Part A website of what
documentation is requested when reviewing radiation therapy:
• A detailed itemization and supporting documentation for all services billed
• Documentation of history of illness being treated
• Documentation of physician involvement
• Physician order(s) for treatment including current dosage
• Documentation to support all services billed were provided
o Dosimetry reports
o Physicist reports
o Simulation reports
o Oncology reports
• Documentation of each treatment billed
• Copy of radiological report or physician's interpretation
• Documentation of any contrast material provided
Part B.
Do not attach information to the original claim.
Additional information can be placed in Item 19 on the 1500 form or its electronic equivalent when
needed.
Revision Effective Date
Revision History
11/01/2015 Annual Review completed 10/08/2015. Billing and Coding information moved from LCD
into Billing and Coding Guidelines. Updated resources and CPT coding definitions.
02/01/2015 CPT/HCPCS code update effective 01/01/2015: added codes 77385 and 77386. This was
missed in the revision history below dated 01/01/2015.
01/01/2015 CPT/HCPCS code update effective 01/01/ 2015: removed codes 77305, 77310, 77315,
77326, 77327, 77328, 77402-77416, 77418, 77421, 76950, 0197T, 0073T and associated instructions,
Added codes 77306, 77307, G6001-G6017.
11/01/2014 Annual review completed 10/09/14.
