
USING PUSH & PULL OPERATORS IN MONGODB
The $push and $pull operators are a part of array operators designed to modify arrays in MongoDB
documents. In this tutorial, I’ll show you how the push and pull operators work and how to use them
with additional modifiers and conditions.
(This article is part of our MongoDB Guide. Use the right-hand menu to navigate.)
What are push and pull operators?
Push and Pull are the two operations used to add and remove elements from arrays in MongoDB
documents. Pushing and pulling elements are done using the MongoDB $push and $pull operators,
respectively:
The $push operator appends a specified value to an array.
The $pull operator removes values from an array that matches a specified condition.
Basic syntax of $push operator
{ $push: { <field1>: <value1>, ... } }
Basic syntax of $pull operator
{ $pull: { <field1>: <value|condition>, ... } }
Let’s look at each in more detail, including how they work and how you can use them.

How MongoDB $push operator works
You can see the $push operator takes two arguments:
The array field
The value to be appended to the specified array field
If the array field is not present in the document, the $push operator will create a new array field.
However, if the specified field is not an array, MongoDB will return an error.
$push operator modifiers
The functionality of the $push operator can be further extended using the following modifiers.
$each. The $each modifier is used to append multiple values to an array. If the $each operator
is not specified, all values in the $push operator will be appended as a single item to the array
field in the document.
$slice. This limits the number of elements in the array. However, this must be used in
conjunction with the $each modifier.
$sort. The $sort modifiers orders the items in the array. This modifier also requires the use of
$each modifier.
$position. The $push operator appends a new item to the end of an array by default. Use the
$position modifier if you want to explicitly specify the location where the item should be
appended.
The $push operation is carried out in the following order, regardless of the order in which the
modifiers are defined:
Update the array to add elements in the specified positions.1.
Sort the array if $sort modifier is specified.2.
Slice the array if $slice modifier is specified.3.
Store the array.4.
Next, we will look at how we can use MongoDB $push operations to manipulate documents. I’ll
show a few examples, so jump to the one you need:
Append a single value to an array
Append multiple values to an array
Use the $sort and $slice modifiers
Use the $position modifier
For the base data set for these examples, I’ll use the “vehicledetails” collection.
db.vehicledetails.find().pretty()
Result:

Append a single value to an array
Let us see how we can append a single value to an array when an array field is present, and it's not
present. In all examples, the "_id" field is used to indicate which document the array should be
added.
Example: No Array Field
A new array field will be created with the field name specified in the $push operator.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52f05f9a62418038240d")},
{$push: {"vehicle_colours": "red"}})
Result:

Example: When the array Field is present
The new item will be appended at the end of the array.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52f05f9a62418038240d")},
{$push: {"vehicle_colours": "green"}})
Result:

If we try to use the $push operator for a non-array field, it will result in an error. The following code
returns an error as we are trying to append a value to the non-array field “make”.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52f05f9a62418038240d")},
{$push: {"make": "green"}})
Result:
Append Multiple Values to an Array
You can append multiple values to an array with or without $each modifier.
Example: Multiple Values without $each modifier
If the $each modifier is not present, MongoDB will append all the values as a single value to the
specified array field.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52f55f9a62418038240e")},
{$push: {"vehicle_colours": }})
Result:

Here, you can see "blue", "red", and "yellow" are elements of a newly created array. But that array is
just one element of the "vehical_colours" array.
Example: Multiple Values with $each modifier
When a $push operation is defined with the $each modifier, each element in the $push operation
will be added to the array as individual items.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52f55f9a62418038240e")},
{$push: {"vehicle_colours": { $each :}}})
Result:
Here, “vehicle_colours” has three elements after $push operation.

Using the $sort and $slice Modifiers
In this section, we will demonstrate how to use the $sort and $slice modifiers using the following
document in the “vehicledetails” collection.
Let us add the color "silver" to the "vehicle_colours" array field and sort the contents alphabetically
(ascending order).
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52fb5f9a62418038240f")},
{$push: {"vehicle_colours": { $each :, $sort: 1}}})
Result:
The above output shows us that the new colors were added, and the array has been sorted
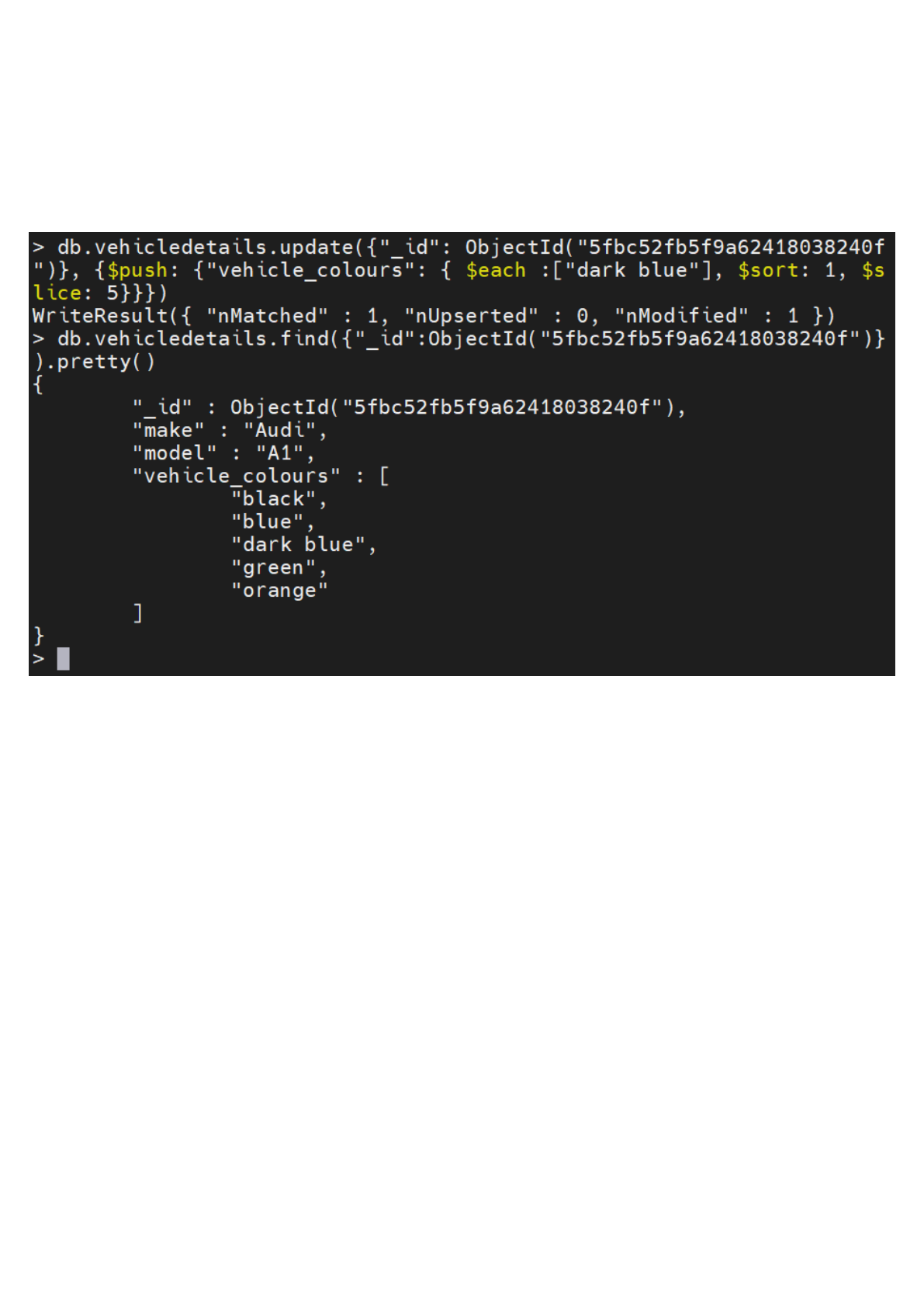
alphabetically. In the following example, we will add the color "dark blue" to the array field while
sorting alphabetically and using the $slice modifier to limit the array to 5 elements.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52fb5f9a62418038240f")},
{$push: {"vehicle_colours": { $each :, $sort: 1, $slice: 5}}})
Result:
Using the $position Modifier
The $position modifier is used to specify the location in the array where the new item should be
added. This will override the default behavior of appending the items to the end of the array.
In the following example, we will add the color "white" to the beginning of the array field
"vehicle_colours". In the "$position" modifier, zero (0) is used to indicate the first position (index 0) of
the array.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52fb5f9a62418038240f")},
{$push: {"vehicle_colours": { $each :, $position: 0}}})
Result:

How MongoDB $pull operator works
The $pull operator is used to remove all the instances of a value or values from a MongoDB
document that matches a specified condition. If an array contains embedded or nested documents,
the specified $pull operator condition will be applied to each array element as if each array element
were a document in a collection.
When the specified value to be removed is an array, the $pull operator only removes the elements
in the array that matches the exact value specified, including the order in which the elements are
defined. If the specified value to remove is a document, the $pull operator will remove elements
that match the fields and values specified. In this instance order of fields is discarded.
Now I’ll walk you through a few examples of the $pull operator. Jump to the ones you need:
Remove a single item from an array
Remove all items that equal a specific value
Remove items that match a specified $pull
Remove items from an array of documents
In these examples, we’ll use the following data set to demonstrate:

Remove a single item from an array
Here, we will remove the single value “2018” from the “model_year” array field. The “_id” field is used
to indicate the document on which the $pull operation should occur.
db.vehicledetails.update({"_id": ObjectId("5fbc52fb5f9a62418038240f")},
{$pull: {"model_year": 2018}})
Result:

Remove All Items that Equal a Specified Value
In this example, we will be using the “vehicledetails" collection to remove the colors "blue" and
"green" from the "vehicle_colours" array field and remove the model year 2020 from the
"model_year" array field.
db.vehicledetails.update({}, {$pull: {"vehicle_colours": { $in: },
"model_year": 2020}},{multi: true})
Result:

Remove Items that Match a Specified $pull Condition
Using the collection “student_grades”, let us create a condition to remove all grades that are less
than or equal to 50 from the following document.
Unmodified Document:

Modified Document:
db.student_grades.update({"_id" : ObjectId("5fbed0faa94306028d2d7520")},
{$pull: {"grades": {$lte: 50}}})
Result:
The specified condition ({$lte: 50}) removed any item that is less than or equal to 50 in the “grades”
array field.
Remove Items from an Array of Documents
In this example, we will use the “student_grades” collection to remove all the values that are less
than or equal to 50 in the “grades” array field in all the documents in the collection.
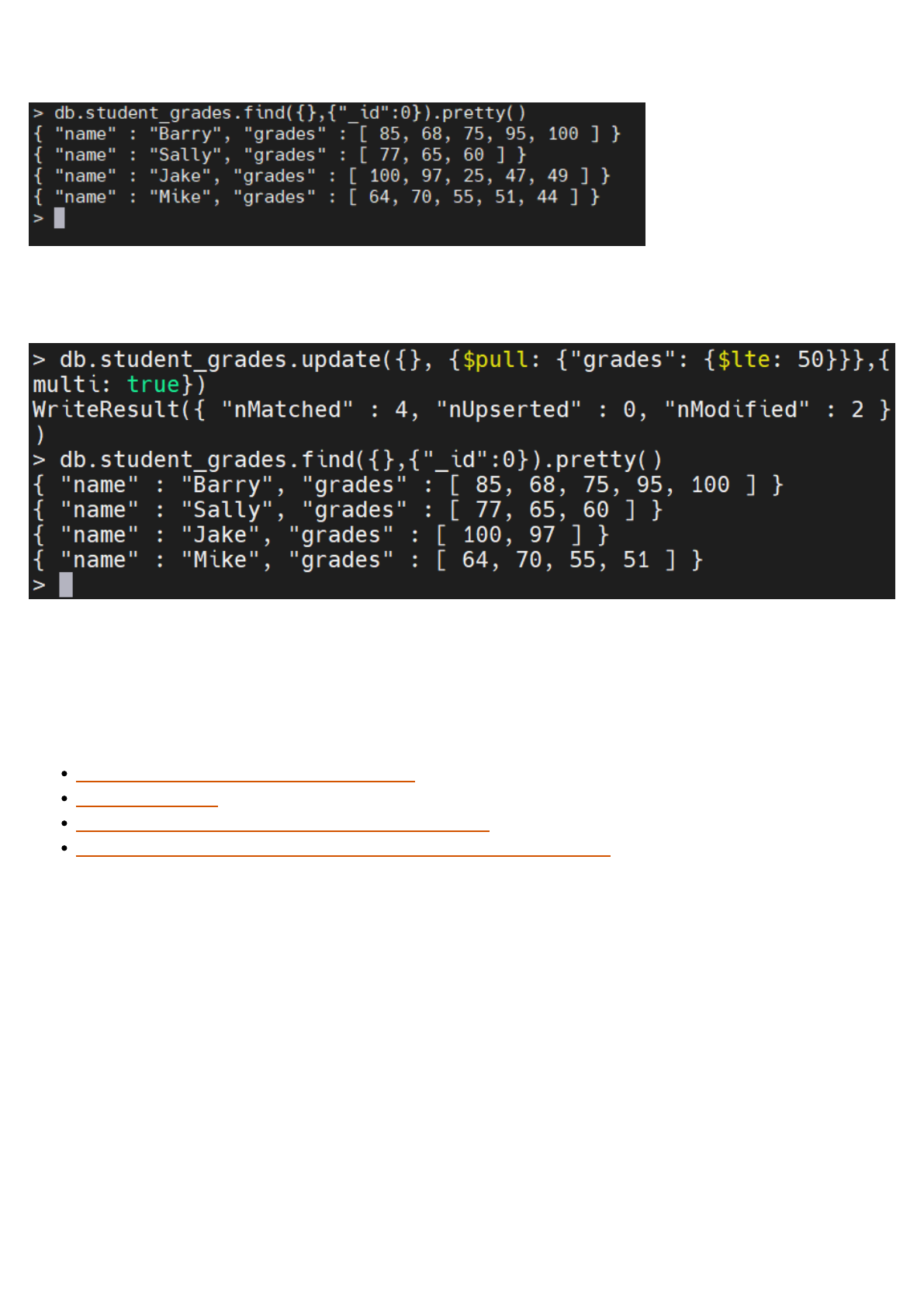
Unmodified Collection:
Modified Collection:
db.student_grades.update({}, {$pull: {"grades": {$lte: 50}}},{multi: true})
Result:
The above output demonstrates to us that any value that is less than or equal to 50 has been
removed from the “grades” array field in all documents in the “student_grades” collection.
That concludes this tutorial.
Related reading
BMC Machine Learning & Big Data Blog
MongoDB Guide, a series of articles and tutorials
MongoDB: The Mongo Shell & Basic Commands
Data Storage Explained: Data Lake vs Warehouse vs Database
