
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
First Published: 2019-12-15
Last Modified: 2024-04-30
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH
THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY,
CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version of
the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright
©
1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS.
CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network
topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional
and coincidental.
All printed copies and duplicate soft copies of this document are considered uncontrolled. See the current online version for the latest version.
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses and phone numbers are listed on the Cisco website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/legal/trademarks.html. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a
partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1721R)
©
2024 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

CONTENTS
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit 1
CHAPTER 1
area authentication 3
area authentication (key-chain) 5
area default-cost 6
area filter-list 8
area nssa 10
area nssa translate 12
area range 15
area sham-link 17
area sham-link (OSPFv3) 20
area stub 22
area transit 24
area virtual-link 25
authentication mode (OSPF) 28
auto-cost 29
BFD Deterministic Offload 30
capability lls 31
capability transit 32
capability vrf-lite 34
capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3) 36
clear proximity ip ospf 38
clear ip ospf force-spf 39
clear ip ospf traffic 40
clear ipv6 ospf traffic 41
compatible rfc1583 42
compatible rfc1587 43
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
iii

compatible rfc5243 44
default-information originate (OSPF) 45
default-metric (OSPF) 47
discard-route 49
distance ospf 52
distance ospf 54
domain-id (OSPF) 56
domain-id (OSPFv3) 57
domain-tag 58
fast-reroute keep-all-paths 60
fast-reroute per-prefix enable (OSPF) 62
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa maximum-cost 64
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa tunnel 65
fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF) 66
ignore lsa mospf 69
interface-id snmp-if-index 70
ip ospf area 72
ip ospf authentication 74
ip ospf authentication-key 76
ip ospf bfd 78
ip ospf cost 79
ip ospf database-filter all out 81
ip ospf dead-interval 83
ip ospf demand-circuit 85
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R 87
CHAPTER 2
ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix 89
ip ospf flood-reduction 91
ip ospf hello-interval 93
ip ospf lls 94
ip ospf message-digest-key md5 96
ip ospf mtu-ignore 98
ip ospf multi-area 100
ip ospf multi-area cost 101
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
iv
Contents

ip ospf name-lookup 102
ip ospf network 103
ip ospf prefix-suppression 105
ip ospf priority 106
ip ospf resync-timeout 107
ip ospf retransmit-interval 109
ip ospf shutdown 110
ip ospf transmit-delay 112
ip ospf ttl-security 113
limit retransmissions 115
local-rib-criteria 118
log-adjacency-changes 120
max-lsa 121
max-metric router-lsa 123
neighbor (OSPF) 126
neighbor database-filter all out 129
network area 130
nsf (OSPF) 133
nsf cisco 135
nsf cisco helper disable 137
nsf ietf 139
nsf ietf helper disable 141
nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking 143
nsr 145
ospfv3 authentication (key-chain) 146
ospfv3 multi-area 147
ospfv3 multi-area cost 148
prefix-suppression 149
process-min-time percent 150
redistribute maximum-prefix 152
router ospf 155
router-id 157
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T 159
CHAPTER 3
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
v
Contents

show ip ospf 161
show ip ospf border-routers 169
show ip ospf database 170
show ip ospf events 180
show ip ospf fast-reroute 182
show ip ospf flood-list 185
show ip ospf interface 187
show ip ospf max-metric 191
show ip ospf multi–area 192
show ip ospf neighbor 194
show ip ospf nsf 200
show ip ospf nsr 201
show ip ospf request-list 202
show ip ospf retransmission-list 204
show ip ospf rib 206
show ip ospf sham-links 208
show ip ospf statistics 209
show ip ospf summary-address 212
show ip ospf timers rate-limit 213
show ip ospf traffic 214
show ip ospf virtual-links 219
show ipv6 ospf 221
show ipv6 ospf traffic 225
show ospfv3 multi-area 229
show ospfv3 sham-links 230
show tech-support ospf 232
shutdown (router OSPF) 236
snmp-server enable traps ospf 237
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors 239
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error 241
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink 243
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa 245
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit 247
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change 249
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
vi
Contents

snmp-server enable traps ospf errors 251
snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa 253
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit 255
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit 257
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change 259
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 errors 261
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 rate-limit 263
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 state-change 264
summary-address (OSPF) 266
timers lsa arrival 268
timers pacing flood 270
timers pacing lsa-group 272
timers pacing retransmission 274
timers throttle lsa all 276
timers throttle spf 278
ttl-security all-interfaces 280
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
vii
Contents

Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
viii
Contents

OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf
demand-circuit
• area authentication, on page 3
• area authentication (key-chain), on page 5
• area default-cost, on page 6
• area filter-list, on page 8
• area nssa, on page 10
• area nssa translate, on page 12
• area range, on page 15
• area sham-link, on page 17
• area sham-link (OSPFv3), on page 20
• area stub, on page 22
• area transit, on page 24
• area virtual-link, on page 25
• authentication mode (OSPF), on page 28
• auto-cost, on page 29
• BFD Deterministic Offload, on page 30
• capability lls, on page 31
• capability transit, on page 32
• capability vrf-lite, on page 34
• capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), on page 36
• clear proximity ip ospf, on page 38
• clear ip ospf force-spf, on page 39
• clear ip ospf traffic, on page 40
• clear ipv6 ospf traffic, on page 41
• compatible rfc1583, on page 42
• compatible rfc1587, on page 43
• compatible rfc5243, on page 44
• default-information originate (OSPF), on page 45
• default-metric (OSPF), on page 47
• discard-route, on page 49
• distance ospf, on page 52
• distance ospf, on page 54
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
1

• domain-id (OSPF), on page 56
• domain-id (OSPFv3), on page 57
• domain-tag, on page 58
• fast-reroute keep-all-paths, on page 60
• fast-reroute per-prefix enable (OSPF), on page 62
• fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa maximum-cost, on page 64
• fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa tunnel, on page 65
• fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF), on page 66
• ignore lsa mospf, on page 69
• interface-id snmp-if-index, on page 70
• ip ospf area, on page 72
• ip ospf authentication, on page 74
• ip ospf authentication-key, on page 76
• ip ospf bfd, on page 78
• ip ospf cost, on page 79
• ip ospf database-filter all out, on page 81
• ip ospf dead-interval, on page 83
• ip ospf demand-circuit, on page 85
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
2
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit

area authentication
To enable authentication for an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area, use the area authentication command
in router configuration mode. To remove an authentication specification of an area or a specified area from
the configuration, use the no form of this command.
area authentication commandarea area-id authentication [message-digest]
no area area-id authentication [message-digest]
Syntax Description
Identifier of the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be
specified as either a decimal value or an IP address.
area-id
(Optional) Enables Message Digest 5 (MD5) authentication on the area specified by the
area-id argument.
message-digest
Command Default
Type 0 authentication (no authentication)
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
The message-digest keyword was added.11.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
Specifying authentication for an area sets the authentication to Type 1 (simple password) as specified in RFC
1247. If this command is not included in the configuration file, authentication of Type 0 (no authentication)
is assumed.
The authentication type must be the same for all routers and access servers in an area. The authentication
password for all OSPF routers on a network must be the same if they are to communicate with each other via
OSPF. Use the ip ospf authentication-key interface command to specify this password.
If you enable MD5 authentication with the message-digest keyword, you must configure a password with
the ip ospf message-digest-key interface command.
To remove the authentication specification for an area, use the noform of this command with the authentication
keyword.
To remove the specified area from the software configuration, use the no area area-idcommand (with no
other keywords). That is, the no area ar ea-id command removes all area options, such as area authentication,
area default-cost, area nssa, area range, area stub, and area virtual-link.
Note
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
3
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area authentication

Examples
The following example mandates authentication for areas 0 and 10.0.0.0 of OSPF routing process
201. Authentication keys are also provided.
interface ethernet 0
ip address 192.168.251.201 255.255.255.0
ip ospf authentication-key adcdefgh
!
interface ethernet 1
ip address 10.56.0.201 255.255.0.0
ip ospf authentication-key ijklmnop
!
router ospf 201
network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 10.0.0.0
network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
area 10.0.0.0 authentication
area 0 authentication
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Specifies a cost for the default summary route sent into a stub area.area default-cost
Defines an area as a stub area.area stub
Assigns a password to be used by neighboring routers that are using the simple
password authentication of OSPF.
ip ospf authentication-key
Enables OSPF MD5 authentication.ip ospf message-digest-key
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
4
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area authentication

area authentication (key-chain)
To enable authentication trailer for an Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) area, use the area
authentication command in router configuration mode or in address-family configuration mode. To disable
the authentication trailer, use theno form of this command.
area area-id authentication {key-chain chain-name | null}
no area area-id authentication {key-chain | null}
Syntax Description
Area ID assigned to the OSPFv3 area. This can be either a decimal value or a valid IPv6
prefix. There is no default.
area-id
Enables area authentication.authentication
Configures a key chain for cryptographic authentication keys.key-chain
Name of the authentication key that is valid..chain-name
(Optional) Enables Message Digest 5 (MD5) authentication on the area specified by the
area-id argument.
null
Command Default
No authentication trailer is enabled for an OSPFv3 area.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Router address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S
Usage Guidelines
Use the area authenticationcommand to enable authentication trailer on all interfaces in the area.
Examples
The following example enables the authentication trailer for an OSPFv3 area:
Device(config-router-af)# area 1 authentication key-chain ospf-1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Specifies the cryptographic authentication keys for an OSPFv3
instance.
ospfv3 authentication (key-chain)
Specifies the authentication mode used in OSPFv3.authentication mode (OSPF)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
5
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area authentication (key-chain)

area default-cost
To specify a cost for the default summary route that is sent into a stub area or not-so-stubby area (NSSA),
use the ar eadefault-cost command in router address family topology or router configuration mode. To remove
the assigned default route cost, use the no form of this command.
area default-cost commandarea area-id default-cost cost
no area area-id default-cost cost
Syntax Description
Identifier for the stub area or NSSA. The identifier can be specified as either a decimal value or
an IP address.
area-id
Cost for the default summary route used for a stub or NSSA. The acceptable value is a 24-bit
number.
cost
Command Default
cost: 1
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
This command is used only on an Area Border Router (ABR) attached to a stub area or NSSA.
There are two stub area router configuration commands: the stub and default-cost options of the area
command. In all routers and access servers attached to the stub area, the area should be configured as a stub
area using the stub option of the area command. Use the default-cost option only on an ABR attached to the
stub area. The default-cost option provides the metric for the summary default route generated by the ABR
into the stub area.
To remove the specified area from the software configuration, use the no area area-id command (with no
other keywords). That is, the no area ar ea-id command removes all area options, such as area authentication,
area default-cost, area nssa, area range, area stub, and area virtual-link.
Note
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the area
default-costcommand in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router
configuration command to become topology-aware.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
6
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area default-cost

Examples
The following example assigns a default cost of 20 to stub network 10.0.0.0:
interface ethernet 0
ip address 10.56.0.201 255.255.0.0
!
router ospf 201
network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 10.0.0.0
area 10.0.0.0 stub
area 10.0.0.0 default-cost 20
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables authentication for an OSPF area.area authentication
Defines an area as a stub area.area stub
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
7
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area default-cost

area filter-list
To filter prefixes advertised in type 3 link-state advertisements (LSAs) between Open Shortest Path First
(OSPF) areas of an Area Border Router (ABR), use the area filter-list command in router address family
topology or router configuration mode. To change or cancel the filter, use the no form of this command.
area area-id filter-list prefix prefix-list-name {in | out}
no area area-id filter-list prefix prefix-list-name {in | out}
Syntax Description
Identifier of the area for which filtering is configured. The identifier can be specified as
either a decimal value or an IP address.
area-id
Indicates that a prefix list is used.prefix
Name of a prefix list.prefix-list-name
The prefix list is applied to prefixes advertised to the specified area from other areas.in
The prefix list is applied to prefixes advertised out of the specified area to other areas.out
Command Default
This command is disabled by default. The router will not filter prefixes.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(15)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)T.12.2(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
Usage Guidelines
With this feature enabled in the “in” direction, all type 3 LSAs originated by the ABR to this area, based on
information from all other areas, are filtered by the prefix list. Type 3 LSAs that were originated as a result
of the area range command in another area are treated like any other type 3 LSA that was originated
individually. Any prefix that does not match an entry in the prefix list is implicitly denied.
With this feature enabled in the “out” direction, all type 3 LSAs advertised by the ABR, based on information
from this area to all other areas, are filtered by the prefix list. If the area range command has been configured
for this area, type 3 LSAs that correspond to the area range are sent to all other areas, only if at least one prefix
in the area range matches an entry in the prefix list.
If all specific prefixes are denied by the prefix list, type 3 LSAs that correspond to the area range command
will not be sent to any other area. Prefixes that are not permitted by the prefix list are implicitly denied.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the area
filter-listcommand in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router
configuration command to become topology-aware.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
8
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area filter-list

Examples
The following example filters prefixes that are sent from all other areas to area 1:
area 1 filter-list prefix AREA_1 in
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Consolidates and summarizes routes at an area boundary.area range
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
9
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area filter-list

area nssa
To configure a not-so-stubby area ( NSSA), use the area nssa command in router address family topology
or router configuration mode. To remove the NSSA distinction from the area, use the no form of this command.
area nssa commandarea area-id nssa [no-redistribution] [default-information-originate [metric]
[metric-type]] [no-summary] [nssa-only]
no area area-id nssa [no-redistribution] [default-information-originate [metric] [metric-type]]
[no-summary] [nssa-only]
Syntax Description
Identifier for the stub area or NSSA. The identifier can be specified as either
a decimal value or an IP address.
area-id
(Optional) Used when the router is an NSSA Area Border Router (ABR) and
you want the redistribute command to import routes only into the normal
areas, but not into the NSSA area.
no-redistribution
(Optional) Used to generate a Type 7 default into the NSSA area. This
keyword takes effect only on the NSSA ABR or the NSSA Autonomous
System Boundary Router (ASBR).
default-information-
originate
(Optional) Specifies the OSPF default metric.metric
(Optional) Specifies the OSPF metric type for default routes.metric-type
(Optional) Allows an area to be an NSSA but not have summary routes
injected into it.
no-summary
(Optional) Limits the default advertisement to this NSSA area by setting the
propagate (P) bit in the type-7 LSA to zero.
nssa-only
Command Default
No NSSA area is defined.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. The nssa-only keyword was added.15.0(1)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.15.2(1)E
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
10
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area nssa

Usage Guidelines
To remove the specified area from the software configuration, use the no area area-idcommand (with no
other keywords). That is, the no area area-id command removes all area options, including area
authentication, area default-cost, area nssa, area range, area stub, and area virtual-link.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the area nssacommand
in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration command
to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example makes area 1 an NSSA area:
router ospf 1
redistribute rip subnets
network 172.19.92.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
area 1 nssa
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Redistributes routes from one routing domain into another routing domain.redistribute
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
11
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area nssa

area nssa translate
To configure a not-so-stubby area ( NSSA) and to configure the OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in
Translated Type-5 LSAs feature, use the area nssa translatecommand in router address family topology or
router configuration mode. To remove the NSSA distinction from the area, use the no form of this command.
area nssa translate commandarea area-id nssa translate type7 [always] [suppress-fa]
[default-information-originate [metric ospf-metric] [metric-type ospf-link-state-type] [nssa-only]]
[no-ext-capability] [no-redistribution] [no-summary]
no area area-id nssa translate type7 [always] [suppress-fa] [default-information-originate [metric
ospf-metric] [metric-type ospf-link-state-type] [nssa-only]] [no-ext-capability] [no-redistribution]
[no-summary]
Syntax Description
Identifier for the stub area or NSSA. The identifier can be specified as either
a decimal value or an IP address.
area-id
Translates one type of link-state advertisement (LSA) to another type of
LSA. This keyword takes effect only on an NSSA Area Border Router (ABR)
or an NSSA Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR).
translate
(Required) Translates a Type-7 LSA to a Type-5 LSA. This keyword takes
effect only on an NSSA ABR or an NSSA ASBR.
type7
(Optional) Configures an NSSA ABR router as a forced NSSA LSA
translator. The NSSA ABR router unconditionally translates Type-7 LSAs
to Type-5 LSAs. You can configure the always keyword only in router
configuration mode, not in router address family topology configuration
mode.
always
(Optional) Suppresses the forwarding address of the Type-7 LSAs from
being placed in the Type-5 LSAs. This keyword takes effect only on an
NSSA ABR or an NSSA ASBR.
suppress-fa
(Optional) Used to generate a Type 7 default into the NSSA area. This
keyword takes effect only on the NSSA ABR or the NSSA Autonomous
System Boundary Router (ASBR).
default-information-originate
(Optional) Configures the OSPF default metric.metric
Specifies the OSPF default metric in the range from 0 to 16777214.ospf-metric
(Optional) Configures the OSPF metric type for default routes.metric-type
Specifies OSPF metric type in the range from 1 to 2.ospf-link-state-type
(Optional) Limits the default advertisement to this NSSA area by setting the
propagate (P) bit in the type-7 LSA to zero..
nssa-only
(Optional) Specifies that domain-specific capabilities are not sent to NSSA.no-ext-capability
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
12
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area nssa translate

(Optional) Specifies that the redistribute command will import routes only
into the normal areas, not into the NSSA area. Used when the router is an
NSSA ABR.
no-redistribution
(Optional) Allows an area to be an NSSA but not have summary routes
injected into it.
no-summary
Command Default
The ABRs connecting an NSSA and the backbone areas elect one of them to translate LSAs, which means
that a router might be elected as translator.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support for the always keyword was added.15.1(2)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.15.2(1)E
Usage Guidelines
To configure the OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs feature, configure the
translate type7 suppress-fa keywords. Consider the following caution.
Configuring the OSPF Forwarding Address Suppression in Translated Type-5 LSAs feature causes the router
to be noncompliant with RFC 1587. Also, suboptimal routing might result because there might be better paths
to reach the destination’s forwarding address. This feature should not be configured without careful
consideration and not until the network topology is understood.
Caution
If the the no-redistribution or default-information-originate keywords are used, two separate lines for the
area nssa command appear in the configuration file for ease of readability. For example, if the area 6 nssa
translate type7 suppress-fa no-redistributioncommand is configured, the following lines would appear in
the configuration file:
router ospf 1
area 6 nssa no-redistribution
area 6 nssa translate type7 suppress-fa
Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)S and later releases support RFC 3101 and include the always keyword, which
allows you to configure an NSSA ABR router as a forced NSSA LSA translator. This means that the NSSA
ABR router will unconditionally assume the role of LSA translator, preempting the default behavior, which
would only include it among the candidates to be elected as translator.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
13
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area nssa translate

Even a forced translator might not translate all LSAs; translation depends on the contents of each LSA.
Note
You can configure the alwayskeyword only in router configuration mode, not in router address family topology
configuration mode.
To remove the specified area from the software configuration, use the no area area-idcommand (with no
other keywords). That is, the no area ar ea-id command removes all area options, such as area authentication,
area default-cost, area nssa, area range, area stub, and area virtual-link.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature with this command, you you must do so
in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration command
to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example causes OSPF to translate Type-7 LSAs from area 1 to Type-5 LSAs, but not
place the Type-7 forwarding address into the Type-5 LSAs. OSPF places 0.0.0.0 as the forwarding
address in the Type-5 LSAs.
router ospf 2
network 172.19.92.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
area 1 nssa translate type7 suppress-fa
The following example configures an NSSA ABR as a forced LSA translator.
Router(config-router)# area 10 nssa translate type7 always
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Redistributes routes from one routing domain into another routing domain.redistribute
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
14
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area nssa translate

area range
To consolidate and summarize routes at an area boundary, use the a rea range command in router configuration
mode. To disable this function, use the noform of this command.
area area-id range ipv6-prefix /prefix-length [{advertise | not-advertise}] [cost cost]
no area area-id range ipv6-prefix /prefix-length [{advertise | not-advertise}] [cost cost]
Syntax Description
Identifier of the area about which routes are to be summarized. It can be specified as either
a decimal value or as an IPv6 prefix.
area-id
IPv6 prefix.ipv6-prefix
IPv6 prefix length./ prefix-length
(Optional) Sets the address range status to advertise and generates a Type 3 summary
link-state advertisement (LSA).
advertise
(Optional) Sets the address range status to DoNotAdvertise. The Type 3 summary LSA
is suppressed, and the component networks remain hidden from other networks.
not-advertise
(Optional) Metric or cost for this summary route, which is used during OSPF SPF
calculation to determine the shortest paths to the destination. The value can be 0 to
16777215.
cost cost
Command Default
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
Support for IPv6 was added. The cost keyword and cost argument were added.12.0(24)S
Support for IPv6 was added. The cost keyword and cost argument were added.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)S.12.2(18)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)SG.12.2(25)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
This command was introduced on Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1
Usage Guidelines
The area range command is used only with Area Border Routers (ABRs). It is used to consolidate or summarize
routes for an area. The result is that a single summary route is advertised to other areas by the ABR. Routing
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
15
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area range

information is condensed at area boundaries. External to the area, a single route is advertised for each address
range. This behavior is called route summarization
Multiple area router configuration commands specifying the range option can be configured. Thus, OSPF
can summarize addresses for many different sets of address ranges.
This command has been modified for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) for IPv6. Users can now enter the IPv6
address syntax.
To remove the specified area from the software configuration, use the no area area-idcommand (with no
other keywords). That is, the no area area-id command removes all area options, such as area default-cost,
area nssa, area range, area stub, and area virtual-link.
Note
Examples
The following example specifies one summary route to be advertised by the ABR to other areas for
all subnets on network 10.0.0.0 and for all hosts on network 192.168.110.0:
interface Ethernet0/0
no ip address
ipv6 enable
ipv6 ospf 1 area 1
!
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 192.168.255.5
log-adjacency-changes
area 1 range 2001:0DB8:0:1::/64
The following example shows the IPv6 address syntax:
Router(config-rtr)# area 1 range ?
X:X:X:X::X/<0-128> IPv6 prefix x:x::y/z
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
16
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area range

area sham-link
To configure a sham-link interface on a provider edge (PE) router in a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
VPN backbone, use the area sham-link command in router configuration or address family configuration
mode. To remove the sham link, use the no form of this command.
area area-id sham-link source-address destination-address authentication key-chain chain-name
[cost number] [ttl-security hops hop-count]
no area area-id sham-link source-address destination-address authentication key-chain chain-name
Syntax Description
ID number of the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area assigned to the sham
link. Valid values: numeric value from 1 to 4294967295 or valid IP address,
in A.B.C.D format. There is no default.
area-id
IP address associated with the sham-link source.source-address
IP address associated with the destination router.destination-address
Enables sham link authentication.authentication
Configures a key-chain for cryptographic authentication keys.key-chain
Name of the authentication key that is valid.chain-name
(Optional) Specifies the OSPF cost to send IP packets over the sham-link
interface. The number argument range is from 1 to 65535.
cost number
(Optional) Configures Time-to-Live (TTL) security on a sham link. The
hop-count argument range is from 1 to 254.
ttl-security hops hop-count
Command Default
A sham link interface is not configured on the router. The default cost is 1.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(8)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(21)ST, and support
for Cisco 12000 series Internet routers was added.
12.0(21)ST
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S, and support
for Cisco 10000 series Internet routers was added.
12.0(22)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
17
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area sham-link

ModificationRelease
The ttl-security hops hop-count keywords and argument were added.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was modified. Support for Cisco ASR 1000 series routers was
added.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)S. This command
was made available in the address family configuration mode.
15.2(4)S
This command was modified. The command was made available in the address
family configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S
The authentication key-chain keywords were added.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S
Usage Guidelines
In the MPLS VPN environment, several VPN client sites can be connected in the same OSPF area. If these
sites are connected over a backdoor link in addition to the VPN backbone, all traffic passes over the backdoor
link instead of over the VPN backbone. OSPF always selects intra-area routes over inter-area (external) routes.
To correct this default OSPF behavior in an MPLS VPN, use the area sham-link command to configure a
sham link between two PEs to connect the sites through the MPLS VPN backbone. A sham link represents
an intra-area (unnumbered point-to-point) connection between PEs. All other routers in the area use the sham
link to calculate intra-area shortest path first (SPF) routes to the remote site.
Configure the source and destination addresses of the sham link as a host route mask (255.255.255.255) on
the PE routers that serve as the endpoints of the sham link. The source and destination IP addresses must
belong to the VPN routing and forwarding instance (VRF) and be advertised by Border Gateway Protocol
(BGP) to remote PE routers. The sham-link endpoint addresses should not be advertised by OSPF.
In an IPv6 environment, the source and destination must be global scope IPv6 addresses in the correct VRF.
The source address should be a local interface address, typically a loopback. The destination address should
be learned from BGP, not OSPFv3.
Use the ttl-security hops hop-count keywords and argument to enable checking of TTL values on OSPF
packets from neighbors or to set TTL values sent to neighbors. This feature adds an extra layer of protection
to OSPF. This option is not configurable for OSPFv3.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure a sham link between two PE routers in an MPLS
VPN backbone by using the area sham-link command on each router:
Router1(config)# interface loopback 55
Router1(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding v1
Router1(config-if)# ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255
!
Router1(config)# router ospf 2 vrf v1
Router1(config-router)# log-adjacency-changes
Router1(config-router)# area 120 sham-link 10.0.0.1 172.16.0.1 cost 1
Router1(config-router)# redistribute bgp 1 subnets
Router1(config-router)# network 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.255 area 1
Router1(config-router)# network 10.120.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
Router1(config-router)# network 10.140.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
!
Router2(config)# interface loopback 44
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
18
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area sham-link

Router2(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding v1
Router2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.255
!
Router2(config)# router ospf 2 vrf v1
Router2(config-router)# log-adjacency-changes
Router2(config-router)# area 120 sham-link 172.16.0.1 10.0.0.1 cost 1
Router2(config-router)# redistribute bgp 1 subnets
Router2(config-router)# network 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.255 area 1
Router2(config-router)# network 10.120.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
Router2(config-router)# network 10.140.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 120
!
The following example shows how to configure TTL security for a sham link in OSPFv3 for IPv6:
Device(config)# router ospfv3 1
Device(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast vrf vrf1
Device(config-router-af)#area 1 sham-link 2001:DB8:1::1 2001:DB8:0:A222::2 ttl-security
hops 10
The following example shows how to configure the authentication using a key chain for sham-links:
area 1 sham-link 1.1.1.1 authentication key-chain ospf-chain-1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables checking of TTL values on OSPF packets from neighbors or setting TTL values
sent to neighbors.
ttl-security hops
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
19
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area sham-link

area sham-link (OSPFv3)
To configure a sham-link interface on a provider edge (PE) router in a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
VPN backbone, use the area sham-link command in address family configuration mode. To remove the sham
link, use the no form of this command.
area area-id sham-link sour ce-address destination-address [cost number] [ttl-security hops hop-count]
no area area-id sham-link source-address destination-address
Syntax Description
OSPFv3 area assigned to the sham link. The range is from 1 to 4294967295.
The area number may be configured in IPv4 address format A.B.C.D There
is no default.
area-id
IPv6 address associated with the sham-link source.source-address
IPv6 address associated with the destination router.destination-address
(Optional) Specifies the OSPFv3 cost to send IP packets over the sham-link
interface. The range is from 1 to 65535.
cost number
(Optional) Configures Time-to-Live (TTL) security on a sham link. The range
is from 1 to 254.
ttl-security hops hop-count
Command Default
A sham link interface is not configured on the router. The default cost is 1.
Command Modes
Address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.2(2)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SY.15.1(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M.15.2(4)M
Usage Guidelines
In the MPLS VPN environment, several VPN client sites can be connected in the same OSPFv3 area. If these
sites are connected over a backdoor link in addition to the VPN backbone, all traffic passes over the backdoor
link instead of over the VPN backbone. OSPFv3 always selects intra-area routes over inter-area (external)
routes.
To correct this default OSPFv3 behavior in an MPLS VPN, use the area sham-link command to configure
a sham link between two PEs to connect the sites through the MPLS VPN backbone. A sham link represents
an intra-area (unnumbered point-to-point) connection between PEs. All other routers in the area use the sham
link to calculate intra-area shortest path first (SPF) routes to the remote site.
Configure the source and destination addresses of the sham link as an IPv6 host route mask (/128) on the PE
routers that serve as the endpoints of the sham link. The source and destination IP addresses must belong to
the VPN routing and forwarding instance (VRF) and be advertised by Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to
remote PE routers. The sham-link endpoint addresses should not be advertised by OSPFv3.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
20
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area sham-link (OSPFv3)

The source and destination must be global scope IPv6 addresses in the correct VRF. The source address should
be a local interface address, typically a loopback. The destination address should be learned from BGP, not
OSPFv3.
Use the ttl-security hops hop-count keywords and argument to enable checking of TTL values on OSPFv3
packets from neighbors or to set TTL values sent to neighbors. This option adds an extra layer of protection
to OSPFv3. This option is not configurable for OSPFv3.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure an OSPFv3 sham link between two PE routers in
an MPLS VPN backbone by using the area sham-link command on each router:
Device(config-vrf)# interface loopback 0
Device(config-if)# description Sham-link endpoint
Device(config-if)# vrf forwarding vrf1
Device(config-if)# ipv6 address 0:0:0:7272::72/128
Device(config-if)# ipv6 enable
Device(config-if)# router ospfv3 1
Device(config router)# address-family ipv6 unicast vrf vrf1
Device(config router-af)# redistribute bgp 2
Device(config router-af)# area 0 sham-link 0:0:0:7272::72 0:0:0:7373::73 cost 100
The following example shows how to configure TTL security for a sham link in OSPFv3 for IPv6:
Device(config)# router ospfv3 1
Device(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast vrf vrf1
Device(config-router-af)# area 1 sham-link 2001:DB8:1::1 2001:DB8:0:A222::2 ttl-security
hops 10
Related Commands
Enters address family configuration mode for configuring routing sessions, such as
BGP, that use standard IPv6 address prefixes.
address-family ipv6
Redistributes IPv6 and IPv4 routes from one routing domain into another routing
domain.
redistribute OSPFv3
Enters OSPFv3 router configuration mode for the IPv4 or IPv6 address family.router ospfv3
Associates a VRF instance or a virtual network with an interface or subinterface.vrf forwarding
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
21
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area sham-link (OSPFv3)

area stub
To define an area as a stub area, use the area stub command in router address family topology or router
configuration mode. To disable this function, use the no form of this command.
area stub commandarea area-id stub [no-summary]
no area area-id stub [no-summary]
Syntax Description
Identifier for the stub area; either a decimal value or an IP address.area-id
(Optional) Prevents an Area Border Router (ABR) from sending summary link advertisements
into the stub area.
no-summary
Command Default
No stub area is defined.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
You must configure the area stub command on all routers and access servers in the stub area. Use the area
router configuration command with the default-cost keyword to specify the cost of a default internal route
sent into a stub area by an ABR.
There are two stub area router configuration commands: the stub and default-cost options of the area router
configuration command. In all routers attached to the stub area, the area should be configured as a stub area
using the stub keyword of the area command. Use the default-cost keyword only on an ABR attached to the
stub area. The default-cost keyword provides the metric for the summary default route generated by the ABR
into the stub area.
To further reduce the number of link-state advertisements (LSAs) sent into a stub area, you can configure the
no-summary keyword on the ABR to prevent it from sending summary LSAs (LSA type 3) into the stub
area.
To remove the specified area from the software configuration, use the no area area-idcommand (with no
other keywords). That is, the no area ar ea-id command removes all area options, such as area authentication,
area default-cost, area nssa, area range, area stub, and area virtual-link.
Note
Release 12.2(33)SRB
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
22
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area stub

If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the area stubcommand
in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration command
to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example assigns a default cost of 20 to stub network 10.0.0.0:
interface ethernet 0
ip address 10.56.0.201 255.255.0.0
!
router ospf 201
network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 10.0.0.0
area 10.0.0.0 stub
area 10.0.0.0 default-cost 20
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables authentication for an OSPF area.area authentication
Specifies a cost for the default summary route sent into a stub area.area default-cost
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
23
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area stub

area transit
To transit data in type 3 link-state advertisements (LSAs) between Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) areas of
an Area Border Router (ABR), use the area transit command in IPv6 address family configuration mode.
To remove the transit, use the area no-transit form of this command.
area area-id {transit | no-transit}
Syntax Description
Identifier of the area for which filtering is configured. The identifier can be specified as either
a decimal value or an IP address.
area-id
Enables the device to transit data.transit
Disables the device to transit data.no-transit
Command Default
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
IPv6 address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(3)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)T.15.2(1)T
Examples
The following example shows how to configure a device so that it does not transit data between
OSPF areas of an ABR:
Device (config-router-af)#area 0 no-transit
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Consolidates and summarizes routes at an area boundary.area range
Filter prefixes advertised in type 3 LSAs between OSPF areas of an ABR.area fitler-list
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
24
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area transit

area virtual-link
To define an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) virtual link, use the area virtual-link command in router
address family topology, router configuration, or address family configuration mode. To remove a virtual
link, use the no form of this command.
area area-id virtual-link router-id authentication key-chain chain-name [hello-interval seconds]
[retransmit-interval seconds] [transmit-delay seconds] [dead-interval seconds] [ttl-security hops
hop-count]
no area area-id virtual-link router-id authentication key-chain chain-name
Syntax Description
Area ID assigned to the virtual link. This can be either a decimal value or a valid
IPv6 prefix. There is no default.
area-id
Router ID associated with the virtual link neighbor. The router ID appears in the
show ip ospf or show ipv6 display command. There is no default.
router-id
Enables virtual link authentication.authentication
Configures a key-chain for cryptographic authentication keys.key-chain
Name of the authentication key that is valid.chain-name
(Optional) Specifies the time (in seconds) between the hello packets that the
Cisco IOS software sends on an interface. The hello interval is an unsigned
integer value to be advertised in the hello packets. The value must be the same
for all routers and access servers attached to a common network. The range is
from 1 to 8192. The default is 10.
hello-interval seconds
(Optional) Specifies the time (in seconds) between link-state advertisement
(LSA) retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to the interface. The retransmit
interval is the expected round-trip delay between any two routers on the attached
network. The value must be greater than the expected round-trip delay. The range
is from 1 to 8192. The default is 5.
retransmit-interval
seconds
(Optional) Specifies the estimated time (in seconds) required to send a link-state
update packet on the interface. The integer value that must be greater than zero.
LSAs in the update packet have their age incremented by this amount before
transmission. The range is from 1 to 8192. The default value is 1.
transmit-delay seconds
(Optional) Specifies the time (in seconds) that hello packets are not seen before
a neighbor declares the router down. The dead interval is an unsigned integer
value. The default is four times the hello interval, or 40 seconds. As with the
hello interval, this value must be the same for all routers and access servers
attached to a common network.
dead-interval seconds
(Optional) Configures Time-to-Live (TTL) security on a virtual link. The
hop-count argument range is from 1 to 254.
ttl-security hops
hop-count
Command Default
No OSPF virtual link is defined.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
25
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area virtual-link

Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology)
Router configuration (config-router)
Address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
Support for IPv6 was added.12.0(24)S
Support for IPv6 was added.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)S.12.2(18)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology
configuration mode.
12.2(33)SRB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
The ttl-security hops hop-count keywords and argument were added.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)S. This command
was made available in the address family configuration mode.
15.2(4)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S. This command
was made available in the OSPFv3 address family configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SY.15.1(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S. The
authentication key-chain keywords were added.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S
Usage Guidelines
In OSPF, all areas must be connected to a backbone area. A lost connection to the backbone can be repaired
by establishing a virtual link.
The shorter the hello interval, the faster topological changes will be detected, but more routing traffic will
ensue. The setting of the retransmit interval should be conservative, or needless retransmissions will result.
The value should be larger for serial lines and virtual links.
You should choose a transmit delay value that considers the transmission and propagation delays for the
interface.
To configure a virtual link in OSPF for IPv6, you must use a router ID instead of an address. In OSPF for
IPv6, the virtual link takes the router ID rather than the IPv6 prefix of the remote router.
Use the ttl-security hops hop-count keywords and argument to enable checking of TTL values on OSPF
packets from neighbors or to set TTL values sent to neighbors. This feature adds an extra layer of protection
to OSPF.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
26
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area virtual-link

In order for a virtual link to be properly configured, each virtual link neighbor must include the transit area
ID and the corresponding virtual link neighbor router ID. To display the router ID, use the show ip ospf or
the show ipv6 ospf command in privileged EXEC mode.
Note
To remove the specified area from the software configuration, use the no area area-id command (with no
other keywords). That is, the no area area-id command removes all area options, such as area default-cost,
area nssa, area range, area stub, and area virtual-link.
Note
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multitopology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the area virtual-link
command in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration
command to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example establishes a virtual link with default values for all optional parameters:
ipv6 router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
area 1 virtual-link 192.168.255.1
The following example establishes a virtual link in OSPF for IPv6:
ipv6 router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
area 1 virtual-link 192.168.255.1 hello-interval 5
The following example shows how to configure TTL security for a virtual link in OSPFv3 for IPv6:
Device(config)# router ospfv3 1
Device(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast vrf vrf1
Device(config-router-af)# area 1 virtual-link 10.1.1.1 ttl-security hops 10
The following example shows how to configure the authentication using a key chain for virtual-links:
area 1 virtual-link 1.1.1.1 authentication key-chain ospf-chain-1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures OSPFv3 area parameters.area
Enables the display of general information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Enables the display of general information about OSPF routing processes.show ipv6 ospf
Enables checking of TTL values on OSPF packets from neighbors or setting TTL values
sent to neighbors.
ttl-security hops
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
27
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
area virtual-link

authentication mode (OSPF)
To specify authentication mode used in Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) , use the authentication
mode command in router configuration mode or in address-family configuration mode. To restore
defaultnormal authentication mode, use theno form of this command.
authentication mode {deployment | normal}
no authentication mode {deployment | normal}
Syntax Description
Provides seamless deployment by allowing maintaining adjacency between authentication
trailer enabled and not-yet-enabled devices.
deployment
Restores to default mode of authentication in the address family.normal
Command Default
The default mode of authentication is strict mode.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Router address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S
This command was modified. The strict keyword was removed.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.14S
Usage Guidelines
The authentication mode is strict by default. See section-3 of RFC 6506 for details on the normal mode
behavior.
OSPFv3 in deployment mode sends packets with both authentication trailer and checksums. While receiving
packets, authentication trailer is verified but does not affect adjacency. These changes allows the device in
deployment mode to maintain neighborship with both non-enabled and authentication trailer enabled devices.
While in deployment mode, the show ospfv3 neighbor detail command displays an additional line that
shows whether last packet was successfully authenticated.
Examples
The following example shows how to specify the authentication type for an OSPFv3 instance using
the deployment mode of operation:
Device(config-router-af)# authentication mode deployment
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Specifies the cryptographic authentication keys for an OSPFv3
instance.
ospfv3 authentication (key-chain)
Enables authentication trailer for an OSPFv3 area.area authentication (key-chain)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
28
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
authentication mode (OSPF)

auto-cost
To control how Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) calculates default metrics for the interface, use the
auto-costcommand in router configuration mode. To assign cost based only on the interface type, use the no
form of this command.
auto-cost commandauto-cost reference-bandwidth mbps
no auto-cost reference-bandwidth
Syntax Description
Rate in Mbps (bandwidth). The range is from 1 to 4294967; the default is
100.
reference-bandwidth mbps
Command Default
100 Mbps
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
In Cisco IOS Release 10.3 and later releases, by default OSPF will calculate the OSPF metric for an interface
according to the bandwidth of the interface. For example, a 64K link will get a metric of 1562, and a T1 link
will have a metric of 64.
The OSPF metric is calculated as the ref-bw value divided by the bandwidth, with mbps equal to 108 by
default, and bandwidth determined by the bandwidth (interface)command. The calculation gives FDDI a
metric of 1.
If you have multiple links with high bandwidth (such as FDDI or ATM), you might want to use a larger
number to differentiate the cost on those links.
The value set by the ip ospf cost command overrides the cost resulting from the auto-cost command.
Examples
The following example changes the cost of the FDDI link to 10, while the gigabit Ethernet link
remains at a cost of 1. Thus, the link costs are differentiated.
router ospf 1
auto-cost reference-bandwidth 1000
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Explicitly specifies the cost of sending a packet on an interface.ip ospf cost
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
29
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
auto-cost

BFD Deterministic Offload
To host a BFD session either in hardware or software on ES + line cards for Cisco 7600 routers, use the
platformbfd offload-timer command in the global configuration mode. Set the Tx timer lower than, or equal
to the offload-timer limit, to host the BFD session in hardware, if resources are available. Set the Tx timer
that is higher than the offload timer limit to host the BFD session in software.
platform bfd offload-timer offload timer
Syntax Description
Indicates the platform specific BFD commands.bfd
Specifies the tx-timer limit, which if exceeded by any interface session, denies hardware offload
for that session. It specifies the rate, in milliseconds, at which BFD packets will be offloaded.
The valid range for the milliseconds argument is from 50 to 999.
timer-limit
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced on the Cisco 7600 series routers.15.3(3)S
Usage Guidelines
None
Sample Configuration
The following shows a sample configuration for the command:
Router# enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#platform bfd offload-timer 450
Router(config)#end
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
30
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
BFD Deterministic Offload

capability lls
To enable the use of the Link-Local Signalling (LLS) data block in originated Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
packets and reenable OSPF nonstop forwarding (NSF) awareness, use the capability llscommand in router
configuration mode. To disable LLS and OSPF NSF awareness, use the no form of this command.
capability lls
no capability lls
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
LLS is enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Usage Guidelines
You might want to disable NSF awareness by disabling the use of the LLS data block in originated OSPF
packets. You might want to disable NSF awareness if the router has no applications using LLS.
If NSF is configured and you try to disable LLS, you will receive the error message, “OSPF Non-Stop
Forwarding (NSF) must be disabled first.”
If LLS is disabled and you try to configure NSF, you will receive the error message, “OSPF Link-Local
Signaling (LLS) capability must be enabled first.”
Examples
The following example disables LLS support and OSPF NSF awareness:
router ospf 2
no capability lls
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
31
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
capability lls

capability transit
To reenable Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area capability transit after it has been disabled, use the capability
transit command in router configuration mode. To disable OSPF area capability transit on all areas for a
router process, use the no form of this command.
capability transit
no capability transit
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
OSPF area capability transit is enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(27)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(7)T.12.3(7)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33) SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Usage Guidelines
OSPF area capability transit is enabled by default, allowing the OSPF Area Border Router to install better-cost
routes to the backbone area through the transit area instead of the virtual links. If you want to retain a traffic
pattern through the virtual-link path, you can disable capability transit by entering the no capability transit
command. If paths through the transit area are discovered, they are most likely to be more optimal paths, or
at least equal to, the virtual-link path. To reenable capability transit, enter the capability transit command.
If you need to verify whether OSPF area capability transit is enabled for a specific routing process, enter the
show ip ospf command.
Examples
The following example shows how to disable OSPF area capability transit on all areas for a router
process named ospf 1. A show ip ospf command is issued first to display the current areas that have
area capability transit enabled. The no capability transit command is then entered to disable OSPF
area capability transit on all areas for the router process ospf 1.
Router# show ip ospf
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 10.1.1.1
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
!Supports area transit capability
It is an area border router
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
32
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
capability transit

Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs. Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Number of external LSA 8. Checksum Sum 0x02853F
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 2. 2 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
!Number of areas transit capable is 1
External flood list length 0
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 3
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:02:21.524 ago
SPF algorithm executed 11 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 49. Checksum Sum 0x19B5FA
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 38
Flood list length 0
Area 1
Number of interfaces in this area is 3
!This area has transit capability: Virtual Link Endpoint
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:02:36.544 ago
SPF algorithm executed 9 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 42. Checksum Sum 0x1756D5
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(router-config)# no capability transit
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays general information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
33
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
capability transit

capability vrf-lite
To suppress the provider edge (PE) specific checks on a router when the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
process is associated with the VPN routing and forwarding instance (VRF), use the capabilityvrf-lite command
in router configuration mode. To restore the checks, use the no form of this command.
capability vrf-lite
no capability vrf-lite
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Disabled. PE specific checks are performed if the process is associated with VRF command modes.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(21)ST
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S.12.0(22)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(8)B.12.2(8)B
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T.12.2(13)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S.12.2(14)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
This command works only if the OSPF process is associated with the VRF.
When the OSPF process is associated with the VRF, several checks are performed when link-state
advertisements (LSAs) are received. PE checks are needed to prevent loops when the PE is performing a
mutual redistribution between OSPF and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) interfaces.
The table below describes the PE checks performed when Type-3, Type-5, and Type-7 LSAs are received.
Table 1: PE Checks Performed
The OSPF VRF process acts as an Area Border Router (ABR) when you configure an OSPF
process that is associated with a VRF without the capability vrf-lite.
Note
The DN bit is checked. If the DN bit is set, the Type-3 LSA is
not considered during the shortest path first (SPF) calculation.
Type-3 LSA received
If the Tag in the LSA is equal to the VPN-tag, the Type-5 or-7
LSA is not considered during the SPF calculation.
Type-5 or -7 LSA received
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
34
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
capability vrf-lite

In some situations, performing PE checks might not be desirable. The concept of VRFs can be used on a router
that is not a PE router (that is, a router that is not running BGP). With the capabilityvrf-lite command, the
checks can be turned off to allow correct population of the VRF routing table with routes to IP prefixes.
Examples
This example shows a router configured with multi-VRF:
router ospf 100 vrf grc
capability vrf-lite
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
35
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
capability vrf-lite

capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3)
To suppress the provider edge (PE)-specific checks on a router when the Open Shortest Path First version 3
(OSPFv3) process is associated with the VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance, use the capability
vrf-lite command in address family configuration mode. To restore the checks, use the no form of this
command.
capability vrf-lite
no capability vrf-lite
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Disabled. PE-specific checks are performed if the process is associated with VRF command modes.
Command Modes
Address family configuration (config-router-af)#
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.2(2)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SY.15.1(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M.15.2(4)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.15.2(1)E
Usage Guidelines
This command works only if the OSPFv3 process is associated with the VRF.
When the OSPFv3 process is associated with the VRF, several checks are performed when link-state
advertisements (LSAs) are received. PE checks are needed to prevent loops when the PE is performing a
mutual redistribution between OSPF and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) interfaces.
The table below describes the PE checks performed when inter-area-prefix LSAs, AS-External LSAs, or
not-so-stubby area (NSSA) LSAs are received.
Table 2: PE Checks Performed
CheckLSA Received
The down bit (DN) is checked. If the DN bit is set, the inter-area-prefix
LSAs, AS-External LSAs or NSSA LSAs is not considered during the
SPF calculation.
Inter-area-prefix LSAs,
AS-External LSAs or NSSA
LSAs received
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
36
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3)

The OSPFv3 VRF process acts as an Area Border Router (ABR) and the
PE router does ABR-specific checks. Most noticeably, the router does
not consider during shortest path first (SPF) calculation inter-area-prefix
LSAs received from a nonbackbone (nonzero) area. The capability vrf-lite
command disconnects the OSPFv3 process from the Multiprotocol Label
Switching (MPLS) VPN super-backbone and the router loses ABR status
(unless the OSPFv3 process is configured with active backbone and
nonbackbone areas).
Inter-Area-Prefix-LSAs LSA
received from nonbackbone area
Examples
The following example shows a router in IPv6 address-family configuration mode reconfigured with
multi-VRF:
router ospfv3 1
!
address-family ipv6 unicast vrf v2
capability vrf-lite
exit-address-family
Related Commands
Enters address family configuration mode for configuring routing sessions, such as
BGP, that use standard IPv6 address prefixes.
address-family ipv6
Enters OSPFv3 router configuration mode for the IPv4 or IPv6 address family.router ospfv3
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
37
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3)

clear proximity ip ospf
To clear redistribution based on the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing process ID, use the clear
proximity ip ospf command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear proximity ip ospf [pid] {process | redistribution | counters [neighbor [neighbor-interface]
[neighbor-id]]}
Syntax Description
(Optional) Process ID.pid
Reset OSPF process.process
Clear OSPF route redistribution.redistribution
OSPF counters.counters
(Optional) Neighbor statistics per interface.neighbor
(Optional) Neighbor interface.neighbor-interface
(Optional) Neighbor ID.neighbor-id
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.1
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. The proximitykeyword was added.15.2(1)S
Usage Guidelines
Use the pidargument to clear only one OSPFprocess. If the pid argumentis not specified,all OSPF processesare
cleared.
Examples
The following example shows how to clear all OSPF processes:
Device# clear proximity ip ospf process
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
38
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
clear proximity ip ospf

clear ip ospf force-spf
To start the shortest path first (SPF) algorithm without clearing the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) database,
use the clear ip ospf force-spf command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear ip ospf [process-id] force-spf
Syntax Description
(Optional) Process identifier (ID). The range is from 1 to 65535.process-id
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.0(1)M
The command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRE.12.2(33)SRE
The command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)XNE.12.2(33)XNE
Usage Guidelines
The clear ip ospf force-spf command is used in troubleshooting and for testing purposes. This command is
used to verify if the currently computed routes are correct, to generate debug messages, and so on.
Examples
The following example shows how to start the SPF algorithm without first clearing the OSPF database:
Router# clear ip ospf 1000 force-spf
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Clears redistribution based on the OSPF routing process ID.clear ip ospf redistribution
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
39
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
clear ip ospf force-spf

clear ip ospf traffic
To clear Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) traffic statistics, use the clear ip ospf traffic command in user
EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
clear ip ospf [process-id] traffic [interface-type interface-number]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Process ID. If the process-id argument is included, only traffic statistics for
the specified routing process are cleared.
process-id
(Optional) Interface type.interface-type
(Optional) interface number.interface-number
Command Modes
User EXEC Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(11)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(28)S.12.0(28)S
Examples
The following example clears OSPF traffic statistics for the OSPF process 100:
Router# clear ip ospf 100 traffic
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays OSPF traffic statistics.show ip ospf traffic statistics
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
40
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
clear ip ospf traffic

clear ipv6 ospf traffic
To reset counters and clear IPv6 OSPFv3 traffic statistics, use the clear ipv6 ospf traffic command privileged
EXEC mode.
clear ipv6 ospf traffic
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.4(6)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.12.2(33)SRB
Examples
The following example resets the counters and clears the OSPFv3 traffics statistics:
Router# clear ipv6 ospf traffic
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Clears OSPFv2 traffic statistics.clear ip ospf traffic
Displays OSPFv2 traffic statistics.show ip ospf traffic
Displays OSPFv3 traffic statistics.show ipv6 ospf traffic
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
41
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
clear ipv6 ospf traffic

compatible rfc1583
To restore the method used to calculate summary route costs per RFC 1583, use the compatible
rfc1583command in router configuration mode. To disable RFC 1583 compatibility, use the no form of this
command.
compatible rfc1583
no compatible rfc1583
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Compatible with RFC 1583.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.1(2)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
This command is backward compatible with Cisco IOS Release 12.0.
To minimize the chance of routing loops, all Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routers in an OSPF routing
domain should have RFC compatibility set identically.
Because of the introduction of RFC 2328, OSPF Version 2, the method used to calculate summary route costs
has changed. Use the no compatible rfc1583 command to enable the calculation method used per RFC 2328.
Examples
The following example specifies that the router process is compatible with RFC 1583:
router ospf 1
compatible rfc1583
!
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
42
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
compatible rfc1583

compatible rfc1587
To replace RFC 3101 compatibility with RFC 1587 compatibility for route selection in not-so-stubby area
(NSSA) Area Border Routers (ABRs), use the compatible rfc1587command in router configuration mode
or address family configuration mode. To restore RFC 3101 compatibility, use the no form of this command.
compatible rfc1587
no compatible rfc1587
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Route selection is compatible with RFC 3101.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(2)S
This command was modified. Support for OSPFv3 was added.15.2(4)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S
Usage Guidelines
In Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)S and later releases, RFC 3101 replaces RFC 1587, and RFC 3101 behavior is
automatically enabled. You can choose the route selection behavior by configuring a router to run as RFC
3101 or RFC 1587 compatible.
See Appendix F of RFC3101 The OSPF Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) Option for a detailed list of differences
between RFC1587 and RFC3101.
Examples
The following example specifies that the router process is compatible with RFC 1587:
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospfv3 1
Router(config-router)# compatible rfc1587
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
43
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
compatible rfc1587

compatible rfc5243
To optimize the database description (DBD) packet exchange between two OSPF neighbors, use the compatible
rfc5243 in router configuration mode or address family configuration mode. To disable RFC5243 optimization,
use the no form of this command.
compatible rfc5243
no compatible rfc5243
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
RFC5243 optimization is enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Address family configuration (config-router-af)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.14S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.5(2)T.15.5(2)T
Usage Guidelines
The compatible rfc5243command optimizes the DBD packet exchange between two OSPF neighbors forming
adjacency. This optimization helps to avoid announcing the DBD packets to neighbor link state advertisements
(LSA) that have already received the announcements. This ensures that the neighbor's link state database
(LSDB) receives only the newer instance of the LSA.
The compatible rfc5243 command can be used only in the router configuration mode for OSPFv2. For
OSPFv3, this command can be used in both the router configuration and address-family configuration modes.
Examples
The following example shows how to disable the default RFC 5243 optimization for OSPFv3:
Device(config-router-af)# no compatible rfc5243
The following example shows how to disable the default RFC 5243 optimization for OSPFv2:
Device(config-router)# no compatible rfc5243
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays general information about OSPFv2 routing instances.show ip ospf
Displays general information about OSPFv3 routing processes.show ospfv3
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
44
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
compatible rfc5243

default-information originate (OSPF)
To generate a default external route into an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing domain, use the
default-inf ormation originate command in router configuration or router address family topology configuration
mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command.
default-information originate [always] [metric metric-value] [metric-type type-value] [route-map
map-name]
no default-inf ormation originate [always] [metric metric-value] [metric-type type-value] [route-map
map-name]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Always advertises the default route regardless of whether the software
has a default route.
The always keyword includes the following exception when the
route map is used. When a route map is used, the origination of the
default route by OSPF is not bound to the existence of a default route
in the routing table and the always keyword is ignored.
Note
always
(Optional) Metric used for generating the default route. If you omit a value and
do not specify a value using the default-metric router configuration command,
the default metric value is 10. The value used is specific to the protocol.
metric metric-value
(Optional) External link type associated with the default route that is advertised
into the OSPF routing domain. It can be one of the following values:
• Type 1 external route.
• Type 2 external route.
The default is type 2 external route.
metric-type
type-value
(Optional) The routing process will generate the default route if the route map is
satisfied.
route-map map-name
Command Default
This command is disabled by default. No default external route is generated into the OSPF routing domain.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router) Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
45
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
default-information originate (OSPF)

Usage Guidelines
Whenever you use the redistribute or the default-information router configuration command to redistribute
routes into an OSPF routing domain, the Cisco IOS software automatically becomes an Autonomous System
Boundary Router (ASBR). However, an ASBR does not, by default, generate a default route into the OSPF
routing domain. The software must still have a default route for itself before it generates one, except when
you have specified the always keyword.
When a route map is used, the origination of the default route by OSPF is not bound to the existence of a
default route in the routing table.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the default-information
originatecommand in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router
configuration command to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example specifies a metric of 100 for the default route that is redistributed into the
OSPF routing domain and specifies an external metric type of 1:
router ospf 109
redistribute eigrp 108 metric 100 subnets
default-information originate metric 100 metric-type 1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Accepts exterior or default information into Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
Protocol (EIGRP) processes.
default-information
Sets default metric values for routes.default-metric
Redistributes routes from one routing domain into another routing domain.redistribute (IP)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
46
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
default-information originate (OSPF)

default-metric (OSPF)
To set default metric values for the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol, use the default-metric
command in router address family topology or router configuration mode. To r eturn to the default state, use
the no form of this command.
default-metric metric-value
no default-metric metric-value
Syntax Description
Default metric value appropriate for the specified routing protocol.metric-value
Command Default
Built-in, automatic metric translations, as appropriate for each routing protocol. The metric of redistributed
connected and static routes is set to 0.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
T he default-metric command is used in conjunction with the redistribute router configuration command
to cause the current routing protocol to use the same metric value for all redistributed routes. A default metric
helps solve the problem of redistributing routes with incompatible metrics. Whenever metrics do not convert,
using a default metric provides a reasonable substitute and enables the redistribution to proceed.
When enabled, the default-metric command applies a metric value of 0 to redistributed connected routes.
The default-metric command does not override metric values that are applied with the redistrib utecommand.
Note
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the default-metric
command in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration
command to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example shows a router in autonomous system 109 using both the Routing Information
Protocol (RIP) and the OSPF routing protocols. The example advertises OSPF-derived routes using
RIP and assigns the OSPF-derived routes a RIP metric of 10.
router rip
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
47
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
default-metric (OSPF)

default-metric 10
redistribute ospf 109
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Redistributes routes from one routing domain into another routing domain.redistribute (IP)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
48
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
default-metric (OSPF)

discard-route
To reinstall an external or internal discard route that was previously removed, use the discard-route command
in router address family topology configuration or router configuration mode. To remove an external or internal
discard route, use the no form of this command.
discard-route [external [distance]] [internal [distance]]
no discard-route [external [distance]] [internal [distance]]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies the discard-route entry for redistributed summarized routes on an Autonomous
System Boundary Router (ASBR).
external
(Optional) Specifies the discard-route entry for summarized internal routes on the Area Border
Router (ABR).
internal
(Optional) Administrative distance. A value between 1 and 254. The default administrative
distance for external and internal discard routes is 254 and 110, respectively.
distance
Command Default
External and internal discard-route entries are installed.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.1(1)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
The distance argument was added.12.4(15)T
The distance argument was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SB.12.2(33)SB
Usage Guidelines
External and internal discard-route entries are installed in routing tables by default. During route summarization,
routing loops may occur when data is sent to a nonexisting network that appears to be a part of the summary,
and the router that is performing the summarization has a less specific route (pointing back to the sending
router) for this network in its routing table. To prevent the routing loop, a discard route entry is installed in
the routing table of the ABR or ASBR.
If for any reason you do not want to use the external or internal discard route, remove the discard route by
entering the no discard-route command with the external or internal keyword.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
49
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
discard-route

If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the
discard-routecommand in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router
configuration command to become topology-aware.
Release 12.4(15)T
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T, both external and internal discard routes were installed using the default
OSPF intra-area administrative distance 110. You can now modify this default distance for discard routes by
entering a new administrative distance for the distance argument of the discard-route command.
Examples
The following display shows the discard-route functionality installed by default. When external or
internal routes are summarized, a summary route to Null0 will appear in the router output from the
show ip route command. See the router output lines that refer to Null0:
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.16.0.128/25 is directly connected, Loopback1
O 172.16.0.0/24 is a summary, 00:00:14, Null0
C 172.16.0.0/25 is directly connected, Loopback0
172.31.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.31.0.128/25 is directly connected, Loopback3
O 172.31.0.0/24 is a summary, 00:00:02, Null0
C 172.31.0.0/25 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
Router# show ip route ospf
172.16.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
O 172.16.0.0/24 is a summary, 00:00:29, Null0
172.16.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
O 172.16.0.0/24 is a summary, 00:00:17, Null0
When the no discard-route command with the internal keyword is entered, notice the following
route change, indicated by the router output lines that that refer to Null0:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# no discard-route internal
Router(config-router)# end
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.16.0.128/25 is directly connected, Loopback1
C 172.16.0.0/25 is directly connected, Loopback0
172.31.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.31.0.128/25 is directly connected, Loopback3
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
50
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
discard-route

O 172.31.0.0/24 is a summary, 00:00:02, Null0
C 172.31.0.0/25 is directly connected, Loopback2
C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
Router# show ip route ospf
172.31.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
O 172.16.0.0/24 is a summary, 00:04:14, Null0
Next, the no discard-route command with the external keyword is entered to remove the external
discard route entry:
Router# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# no discard-route external
Router(config-router)# end
The following router output from the show running-config command confirms that both the external
and internal discard routes have been removed from the routing table of the router. See the router
output lines that that refer to discard routes.
Router# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 1114 bytes
!
version 12.2
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router
.
.
.
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
no discard-route external
no discard-route internal
area 1 range 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.0
summary-address 172.31.0.0 255.255.255.0
redistribute rip subnets
network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
!
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays the current state of the routing table.show ip route
Displays the contents of the currently running configuration file, the configuration
for a specific interface, or map class information.
show running-config
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
51
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
discard-route

distance ospf
To define Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) route administrative distances based on route type, use the distance
ospf command in router address family topology or router configuration mode. To restore the default value,
use the no form of this command.
distance ospf commanddistance ospf {external dist1 | inter-area dist2 | intra-area dist3}
no distance ospf
Syntax Description
(Optional) Sets the distance for routes from other routing domains, learned by
redistribution. Range is 1 to 255. The default value is 110.
external dist1
(Optional) Sets the distance for all routes from one area to another area. Range is 1 to
255. The default value is 110.
inter-area dist2
(Optional) Sets the distance for all routes within an area. Range is 1 to 255. The default
value is 110.
intra-area dist3
Command Default
dist1 : 110
dist2 : 110
dist3 : 110
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.1(14)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
You must specify at least one of the keywords.
This command performs the same function as the distance command used with an access list. However, the
distance ospfcommand allows you to set a distance for an entire group of routes, rather than a specific route
that passes an access list.
A common reason to use the distance ospf command is when you have multiple OSPF processes with mutual
redistribution, and you want to prefer internal routes from one over external routes from the other.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the distance
ospfcommand in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration
command to become topology-aware.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
52
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
distance ospf

Examples
The following example changes the external distance to 200, making the route less reliable:
Router A Configuration
router ospf 1
redistribute ospf 2 subnet
distance ospf external 200
!
router ospf 2
redistribute ospf 1 subnet
distance ospf external 200
Router B Configuration
router ospf 1
redistribute ospf 2 subnet
distance ospf external 200
!
router ospf 2
redistribute ospf 1 subnet
distance ospf external 200
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Defines an administrative distance.distance (IP)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
53
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
distance ospf

distance ospf
To define Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) route administrative distances based on route type, use the distance
ospf command in router address family topology or router configuration mode. To restore the default value,
use the no form of this command.
distance ospf commanddistance ospf {external dist1 | inter-area dist2 | intra-area dist3}
no distance ospf
Syntax Description
(Optional) Sets the distance for routes from other routing domains, learned by
redistribution. Range is 1 to 255. The default value is 110.
external dist1
(Optional) Sets the distance for all routes from one area to another area. Range is 1 to
255. The default value is 110.
inter-area dist2
(Optional) Sets the distance for all routes within an area. Range is 1 to 255. The default
value is 110.
intra-area dist3
Command Default
dist1 : 110
dist2 : 110
dist3 : 110
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.1(14)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
You must specify at least one of the keywords.
This command performs the same function as the distance command used with an access list. However, the
distance ospfcommand allows you to set a distance for an entire group of routes, rather than a specific route
that passes an access list.
A common reason to use the distance ospf command is when you have multiple OSPF processes with mutual
redistribution, and you want to prefer internal routes from one over external routes from the other.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the distance
ospfcommand in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration
command to become topology-aware.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
54
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
distance ospf

Examples
The following example changes the external distance to 200, making the route less reliable:
Router A Configuration
router ospf 1
redistribute ospf 2 subnet
distance ospf external 200
!
router ospf 2
redistribute ospf 1 subnet
distance ospf external 200
Router B Configuration
router ospf 1
redistribute ospf 2 subnet
distance ospf external 200
!
router ospf 2
redistribute ospf 1 subnet
distance ospf external 200
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Defines an administrative distance.distance (IP)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
55
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
distance ospf

domain-id (OSPF)
To change the OSPF domain ID that is used during the redistribution of BGP VPNv4 routes to OSPF, use the
domain-id command in router configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this
command.
domain-id {ip-address [secondary] | null | type type-value value hex-value [secondary]}
no domain-id [{ip-address [secondary] | null | type type-value value hex-value
[secondary]}]
Syntax Description
OSPF domain ID in IP address format.ip-address
(Optional) Specifies the secondary domain ID in IP address format.secondary
No domain ID is associated with the process.null
OSPF domain ID type in hexadecimal format.type type-value
OSPF domain ID value in hexadecimal format.value hex-value
(Optional) Specifies the secondary domain ID type in hexadecimal format.secondary
Command Default
The default value for the domain-id command is equal to the OSPF process ID.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(2)
Usage Guidelines
The domain ID is an 8-byte value that identifies the OSPF domain of the prefix. When the OSPF route is
redistributed to the BGP VPNv4 route in the MPLS VPN context, the domain ID extended community is
attached to the BGP update. The domain ID is used on the egress provider-edge (PE) router, when the BGP
VPNv4 route is redistributed to OSPF to decide what type of link-state advertisement (LSA) to generate as a
result of the redistribution of the BGP VPNv4 route.
Examples
The following example shows how to change the OSPF domain ID using the domain-id command
where the primary domain ID is a valid IP address and the secondary domain ID is a valid hexadecimal
value:
Router(config)# router ospf 100 vrf abcd
Router(config-router)# domain-id 10.2.3.4
Router(config-router)# domain-id type 0005 value CAFECAFECAFE secondary
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
56
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
domain-id (OSPF)

domain-id (OSPFv3)
To configure the BGP/MPLS VPN domain ID, use the domain-id command in address-family configuration
mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
domain-id type type-value value hex-value
no domain-id type type-value value hex-value
Syntax Description
BGP extended community used to carry the domain-id.type type-value
An arbitrary 48-bit number encoded as 12 hexadecimal digits.value hex-value
Command Default
The default value for the domain-id command is NULL.
Command Modes
address-family configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)S.15.2(4)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M.15.2(4)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SY
.
15.1(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.15.2(1)E
Usage Guidelines
The value of the BGP extended community used to carry the domain-id can be one of 0005, 0105, 0205, or
8005. In OSPFv2, a default non-NULL domain-id is provided by using the process-id of the router instance.
In OSPFv3, the default value is NULL.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
57
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
domain-id (OSPFv3)

domain-tag
To s et the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) domain tag value for Type-5 or Type-7 link-state advertisements
(LSAs) when OSPF is used as a protocol between a provider edge (PE) router and customer edge (CE) router,
use the domain-tag command in router configuration mode. To reinstate the default tag value, use the no
form of this command.
domain-tag tag-value
no domain-tag tag-value
Syntax Description
Tag value. A 32-bit value entered in decimal format. The default value is calculated based on
the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) autonomous system number of the Multiprotocol Label
Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) backbone. The four highest bits are set to
1101 according to RFC 1745. The lowest 16 bits map the BGP autonomous system (AS) number
of the MPLS VPN backbone. If a user specifies the tag-value, the value does not have to follow
any particular format.
tag-value
Command Default
The default value is calculated based on the BGP autonomous system number of the MPLS VPN backbone.
The four highest bits are set to 1101 according to RFC 1745. The lowest 16 bits map the BGP autonomous
system number of the MPLS VPN backbone.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.1(7)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.1(7)E.12.1(7)E
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.1(7)EC.12.1(7)EC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(17)ST.12.0(17)ST
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)B.12.2(2)B
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S.12.2(14)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
When OSPF is used between a PE router and a CE router, BGP routes that come from the MPLS backbone
are redistributed to OSPF. These redistributed routes can be announced in Type-3, Type-5, or Type-7 LSAs.
If the redistribution of the BGP routes results in Type-5 or Type-7 LSAs, the External Route Tag will be set
to the value of the tag. If another PE router receives a Type-5 or Type-7 LSA with an External Route Tag
equal to the set tag value, it will ignore the LSA, therefore preventing the redistributed routes that originated
from the MPLS backbone from returning via some other location on the MPLS backbone.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
58
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
domain-tag

Examples
The following example configures the tag value 777:
Router(config)# router ospf 10 vrf grc
Router(config-router)# domain-tag 777
The show ip ospf database command is entered to verify that the tag value 777 has been applied to
the External Route Tag:
Router# show ospf database external 192.168.50.1
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.239.66) (Process ID 10)
Type-5 AS External Link States
LS age: 18
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
S Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.168.238.1 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 192.168.239.66
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0xDAB0
Length: 36
Network Mask: /32
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
TOS: 0
Metric: 1
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 777
.
.
.
OSPF Router with ID (198.168.237.56) (Process ID 1)
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays lists of information related to the OSPF database for a specific router.show ospf database
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
59
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
domain-tag

fast-reroute keep-all-paths
To create a list of all the candidate repair paths considered when a per-prefix loop-free alternate (LFA) Fast
Reroute (FRR) route is computed, use the fast-reroute keep-all-paths command in router configuration
mode. To disable prefix priority, use the no form of this command.
fast-reroute keep-all-paths
no fast-reroute keep-all-paths
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
A list of candidate repair paths is not created.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)#
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(3)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S
Usage Guidelines
You can use the fast-reroute keep-all-paths command to display all the candidate repair paths that are
considered when an LFA FRR repair path is computed. You can use this list to troubleshoot repair paths
without having to enable debugs, but it greatly increases memory consumption so it should be reserved for
testing.
Examples
The following example shows how to create a list of all the candidate LFA FRR repair paths
considered:
Router(config-router)# fast-reroute keep-all-paths
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays debugging information for per-prefix LFA FRR paths.debug ip ospf fast-reroute
Configures a per-prefix LFA FRR path that redirects traffic to an
alternative next hop other than the primary neighbor.
fast-reroute per-prefix enable (OSPF)
Configures the tiebreaking policy in selecting an LFA FRR repair
path.
fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)
Configures an interface as either protecting or protected.ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix
Configures a set of prefixes to have high priority for protection in
an OSPF local RIB.
prefix-priority
Displays information about prefixes protected by LFA FRR repair
paths.
show ip ospf fast-reroute
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
60
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute keep-all-paths

DescriptionCommand
Displays OSPF interface information.show ip ospf interface
Displays OSPF neighbor information on a per-interface basis.show ip ospf neighbor
Displays information for the OSPF local RIB or locally redistributed
routes.
show ip ospf rib
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
61
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute keep-all-paths

fast-reroute per-prefix enable (OSPF)
To configure a per-prefix loop-free alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR) path that redirects traffic to an
alternative next hop other than the primary neighbor, use the fast-reroute per-prefix enable command in
router configuration mode. To disable prefix priority, use the no form of this command.
fast-reroute per-prefix enable [area area-id] prefix-priority {high | low}
no fast-reroute per-prefix enable [area area-id] prefix-priority {high | low}
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies an area in which to enable LFA FRR.area
OSPF area ID expressed as a decimal value or in IP address format.area-id
Specifies the priority of prefixes to be protected.pref ix-priority
Sets the prefix priority to high.high
Sets the prefix priority to low.low
Command Default
LFA is enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)#
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(3)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S
Examples
The command in the following example configures an LFA and specifies the prefix priority for
protection:
Router(config-router)# fast-reroute per-prefix enable prefix-priority low
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays debugging information for per-prefix LFA FRR paths.debug ip ospf fast-reroute
Creates a list of all the candidate repair paths that were considered when
a per-prefix LFA FRR route was computed.
fast-reroute keep-all-paths
Configures the FRR tiebreaking priority.fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)
Configures an interface as either protecting or protected.ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix
Configures a set of prefixes to have high priority for protection in an OSPF
local RIB.
prefix-priority
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
62
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute per-prefix enable (OSPF)

DescriptionCommand
Displays information about prefixes protected by LFA FRR repair paths.show ip ospf fast-reroute
Displays OSPF interface information.show ip ospf interface
Displays OSPF neighbor information on a per-interface basis.show ip ospf neighbor
Displays information for the OSPF local RIB or locally redistributed routes.show ip ospf rib
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
63
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute per-prefix enable (OSPF)

fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa maximum-cost
To configure the maximum distance to the tunnel endpoint in a per-prefix loop-free alternate (LFA) fast reroute
(FRR) path that redirects traffic to a remote LFA, use the fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa maximum-cost
command in router configuration mode. To disable the configuration, use the no form of this command.
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa [{area area-id}] maximum-cost distance
no fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa [{area area-id}] maximum-cost distance
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies an area in which to enable LFA FRR.area
(Optional) OSPF area ID expressed as a decimal value or in IP address format.area-id
Specifies the value of the maximum distance to the tunnel endpoint.distance
Command Default
The maximum distance to the remote LFA is not enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.2(2)S
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to limit routers to which remote LFA can create an automatic tunnel to the vicinity of the
calculating router.
Examples
The following example shows how to set a maximum cost of 30 in area 2:
Router(config-router)# fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa area 2 maximum-cost 30
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures a per-prefix LFA FRR
path that redirects traffic to a
remote LFA tunnel.
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-id tunnel
Displays a list of tunnel interfaces
created by the FRR manager on
behalf of OSPF.
show ip ospf fast-reroute remote-lfa tunnels
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
64
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa maximum-cost

fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa tunnel
To configure a per-prefix loop-free alternate (LFA) fast reroute (FRR) path that redirects traffic to a remote
LFA tunnel, use the fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa tunnel command in router configuration mode. To
disable remote LFA, use the no form of this command.
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa [{area area-id}] tunnel mpls-ldp
no fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa [{area area-id}] tunnel mpls-ldp
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies an area in which to enable LFA FRR.area
(Optional) OSPF area ID expressed as a decimal value or in IP address format.area-id
Enables remote LFA tunneling via Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)-Label Distribution
Protocol (LDP).
mpls-ldp
Command Default
A remote LFA is not enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)#
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.2(2)S
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to enable the remote LFA feature and to configure the type of an automatically created
tunnel.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure a remote per-prefix LFA FRR in area 2. The remote
tunnel type is specified as MPLS-LDP:
Router(config-router)# fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa area 2 tunnel mpls-ldp
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures the maximum distance
to the tunnel endpoint.
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa maximum-cost
Displays a list of tunnel interfaces
created by the FRR manager on
behalf of OSPF.
show ip ospf fast-reroute remote-lfa tunnels
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
65
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa tunnel

fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)
To configure the tiebreaking policy in selecting in a loop-free alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR) repair path,
use the fast-reroute tie-break command in router configuration mode. To disable the configuration, use the
no form of this command.
fast-reroute tie-break {broadcast-interface-disjoint | downstream | interface-disjoint | linecard-disjoint
| node-protecting | primary-path | secondary-path | srlg} [required] {index attribute-priority |
lowest-metric index attribute-priority}
no fast-reroute tie-break {broadcast-interface-disjoint | downstream | interface-disjoint |
linecard-disjoint | node-protecting | primary-path | secondary-path | srlg} [required] {index
attribute-priority | lowest-metric index attribute-priority}
Syntax Description
Configures the interface protection attribute.broadcast-interface-disjoint
Configures LFAs whose metric to the protected destination is lower than the
metric of the protecting node to the destination.
downstream
Configures the interface protection attribute.interface-disjoint
Configures the linecard protection attribute.linecard-disjoint
Configures the node-protecting repair path attribute.node-protecting
Configures the equal-cost multipath attribute.primary-path
Configures the not-equal-cost multipath attribute.secondary-path
Configures the shared risk link group (SRLG) attribute.srlg
(Optional) Specifies that the tiebreaker is required.required
Specifies the tiebreak attribute priority.index
The tiebreak attribute priority number. Valid values are from 1 to 255.attribute-priority
(Configures the lowest metric repair path attribute.lowest-metric
Command Default
If you do not configure a tiebreaker policy, repair path attributes are assigned in the following priority order:
1. SRLG
2. Primary path
3. Interface disjoint
4. Lowest metric
5. Line-card disjoint
6. Node protecting
7. Broadcast-interface disjoint
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
66
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)

Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)#
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(3)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S
Usage Guidelines
You must configure the router ospf command before you can configure the fast-reroute tie-break command.
You can use the show ip ospf fast-reroute command to display the default, or the current, tiebreak
configuration.
The tiebreaker policy is evaluated in the configured or the default order. If the evaluation does not select any
candidate, the repair path is selected by implicit load balancing. This means that repair path selection varies
depending on the prefix.
The primary-path and secondary-path keywords configure the same attribute: configuring one automatically
deletes the other from the tiebreaker policy.
You can configure the required keyword for all attributes except lowest metric. To be selected as the LFA
repair path, a candidate must have all the tiebreaker attributes that are configured as “required.”
Examples
The commands in the following example configures a tiebreaking policy that prioritizes SRLG as a
required tiebreaker and sets the priority index for it and for the lower-priority tiebreaking attributes:
Router(config-router)# fast-reroute tie-break
srlg required index
10
Router(config-router)# fast-reroute tie-break
linecard-disjoint index 15
Router(config-router)# fast-reroute tie-break downstream index 20
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays debugging information for per-prefix LFA FRR paths.debug ip ospf fast-reroute
Creates a list of all the candidate repair paths that were considered
when a per-prefix LFA FRR route was computed.
fast-reroute keep-all-paths
Configures a per-prefix loop-free alternative (LFA) route that
redirects traffic to an alternative next hop other than the primary
neighbor.
fast-reroute per -pref ixenable (OSPF)
Configures an interface as either protecting or protected.ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix
Configures a set of prefixes to have high priority for protection in
an OSPF local RIB.
prefix-priority
Configures an OSPF routing process.router ospf
Displays information about prefixes protected by LFA FRR repair
paths.
show ip ospf fast-reroute
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
67
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)

DescriptionCommand
Displays OSPF interface information.show ip ospf interface
Displays OSPF neighbor information on a per-interface basis.show ip ospf neighbor
Displays information for the OSPF local RIB or locally redistributed
routes.
show ip ospf rib
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
68
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)

ignore lsa mospf
To suppress the sending of syslog messages when the router receives link-state advertisement (LSA) Type 6
Multicast OSPF ( MOSPF) packets, which are unsupported, use the ignore lsa mospfcommand in router
configuration mode. To restore the sending of syslog messages, use the no form of this command.
ignore lsa mospf commandignore lsa mospf
no ignore lsa mospf
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
This command is disabled by default. Each MOSPF packet causes the router to send a syslog message.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.1
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
Cisco routers do not support LSA Type 6 MOSPF packets, and they generate syslog messages if they receive
such packets. If the router is receiving many MOSPF packets, you might want to configure the router to ignore
the packets and thus prevent a large number of syslog messages.
Examples
The following example configures the router to suppress the sending of syslog messages when it
receives MOSPF packets:
router ospf 109
ignore lsa mospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
69
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ignore lsa mospf

interface-id snmp-if-index
To configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) interfaces with Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
MIB-II interface Index (ifIndex) identification numbers, use the interface-id snmp-if-indexcommand in
router configuration mode. To revert to the original interface numbering, use the no form of this command.
interface-id snmp-if-index
no interface-id snmp-if-index
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
SNMP MIB-II ifIndex numbering for interfaces is disabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.4(6)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.12.2(33)SRB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6
Usage Guidelines
The advantage to using SNMP MIB-II ifIndex numbers to identify OSPF interfaces is that the ifIndex number
corresponds to the number that a user will see reported by SNMP. Using the SNMP MIB-II ifIndex is also
suggested, but not required, by RFC 2328 for OSPFv2 and by RFC 2740 for OSPFv3.
If you want to use the SNMP MIB-II ifIndex numbers, all interfaces that have OSPF enabled must have an
SNMP ifIndex number assigned or else OSPF will not be enabled on those interfaces.
A user may choose not to configure SNMP MIB-II ifIndex numbers in order to maintain consistent behavior
across upgrades and among routers that may not have the functionality offered with Cisco IOS Release 12.4(6)T
and later releases.
Note
Examples
The following example configures the OSPF interfaces to use SNMP MIB-II ifIndex ID numbers.
The output from the show snmp mib ifmib ifindex command verifies the configuration.
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# interface-id snmp-if-index
Router(config-router)# end
Router# show snmp mib ifmib ifindex serial13/0
Serial13/0: Ifindex = 53
Router# show ip ospf 1 1 data router self-originate
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.3.1) (Process ID 1)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
70
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
interface-id snmp-if-index

Router Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 66
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 192.168.3.1
Advertising Router: 192.168.3.1
LS Seq Number: 80000003
Checksum: 0xE38F
Length: 36
Number of Links: 1
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 192.168.3.7
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 0.0.0.49
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 64
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays SNMP interface index identification numbers (ifIndex values)
for all the system interfaces or the specified system interface.
show snmp mib ifmib ifindex
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
71
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
interface-id snmp-if-index

ip ospf area
To enable Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) on an interface, use the ip ospf area command in
interface configuration mode. To disable OSPFv2 on the interface, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf process-id area area-id [secondaries none]
no ip ospf process-id area [secondaries none]
Syntax Description
A decimal value in the range from 1 to 65535 that identifies the process ID.process-id
A decimal value in the range from 0 to 4294967295, or an IP address.area-id
(Optional) Prevents secondary IP addresses on the interface from being advertised.secondaries none
Command Default
If the secondaries nonekeywords are entered in the no form of this command, the secondary IP addresses
will be advertised. If the secondaries nonekeywords are not present, OSPFv2 will be disabled.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(29)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(11)T.12.3(11)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(1)SB.12.2(1)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.12.2(33)SRB
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation
Services Routers.
15.2(2)SNI
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.15.2(1)E
Usage Guidelines
OSPF is enabled on an interface when the network address for the interface matches the range of addresses
that is specified by the network area command that is entered in router configuration mode. You can enable
OSPFv2 explicitly on an interface with the ip ospf area command that is entered in interface configuration
mode. This capability simplifies the configuration of unnumbered interfaces with different areas.
The ip ospf areacommand that is entered in interface configuration mode will supersede the effects of the
network areacommand. Therefore, an interface that is configured with the ip ospfareacommand in interface
configuration mode will not be affected by the network areacommand.
If you later disable the ip ospf area command, the interface will still run OSPFv2 as long as its network
address matches the range of addresses that is specified by the network areacommand.
Note
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
72
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf area

Examples
The following example enables OSPFv2 on Ethernet interface 0/0/2 and prevents secondary IP
addresses from being advertised:
Router(config)# interface Ethernet0/0/2
Router(config-if)# ip ospf 10 area 0 secondaries none
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode.interface
Defines the interfaces on which OSPF runs and defines the area ID for those
interfaces.
network area
Displays OSPF-related interface information.show ip ospf interface
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
73
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf area

ip ospf authentication
To specify the authentication type for an interface, use the ip ospf authentication command in interface or
virtual network interface configuration mode. To remove the authentication for an interface, use the no form
of this command.
ip ospf authentication [{key-chain name | message-digest | null}]
no ip ospf authentication
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies key chain name for cryptographic authentication keys.key-chain name
(Optional) Specifies that message-digest authentication is used.message-digest
(Optional) Specifies that no authentication is used. Use this keyword to override password
or message-digest authentication if the keyword is configured for an area.
null
Command Default
The authentication type for an interface is not configured.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Virtual network interface configuration (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation
Services Routers.
15.2(2)SNI
This command was modified. The key-chain keyword and name argument
were added.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.10S
Usage Guidelines
Before using the ip ospf authentication key-chain command, for the key to be operational, configure a
password for the interface using the ip ospfauthentication-key command. If you use the ipospf authentication
message-digest command, configure the message-digest key for the interface using the ip ospf
message-digest-key command.
Before using the ip ospf authentication key-chain command for cryptographic authentication on an
interface, define a key chain, a key ID, and a key string, and configure the key with the cryptographic algorithm.
If the authentication type is not specified for an interface, the authentication type for the area is used (the area
default is null authentication).
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
74
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf authentication

Examples
The following example shows how to enable message-digest authentication:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Device (config-if)# ip ospf authentication message-digest
Device (config-if)# end
The following example shows how to enable cryptographic authentication:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Device (config-if)# ip ospf authentication key-chain samplekeychain
Device (config-if)# end
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables authentication for an OSPF area.area authentication
Assigns a password to be used by neighboring routers that are using the simple
password authentication of OSPF.
ip ospf authentication-key
Enables OSPF MD5 authentication.ip ospf message-digest-key
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
75
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf authentication
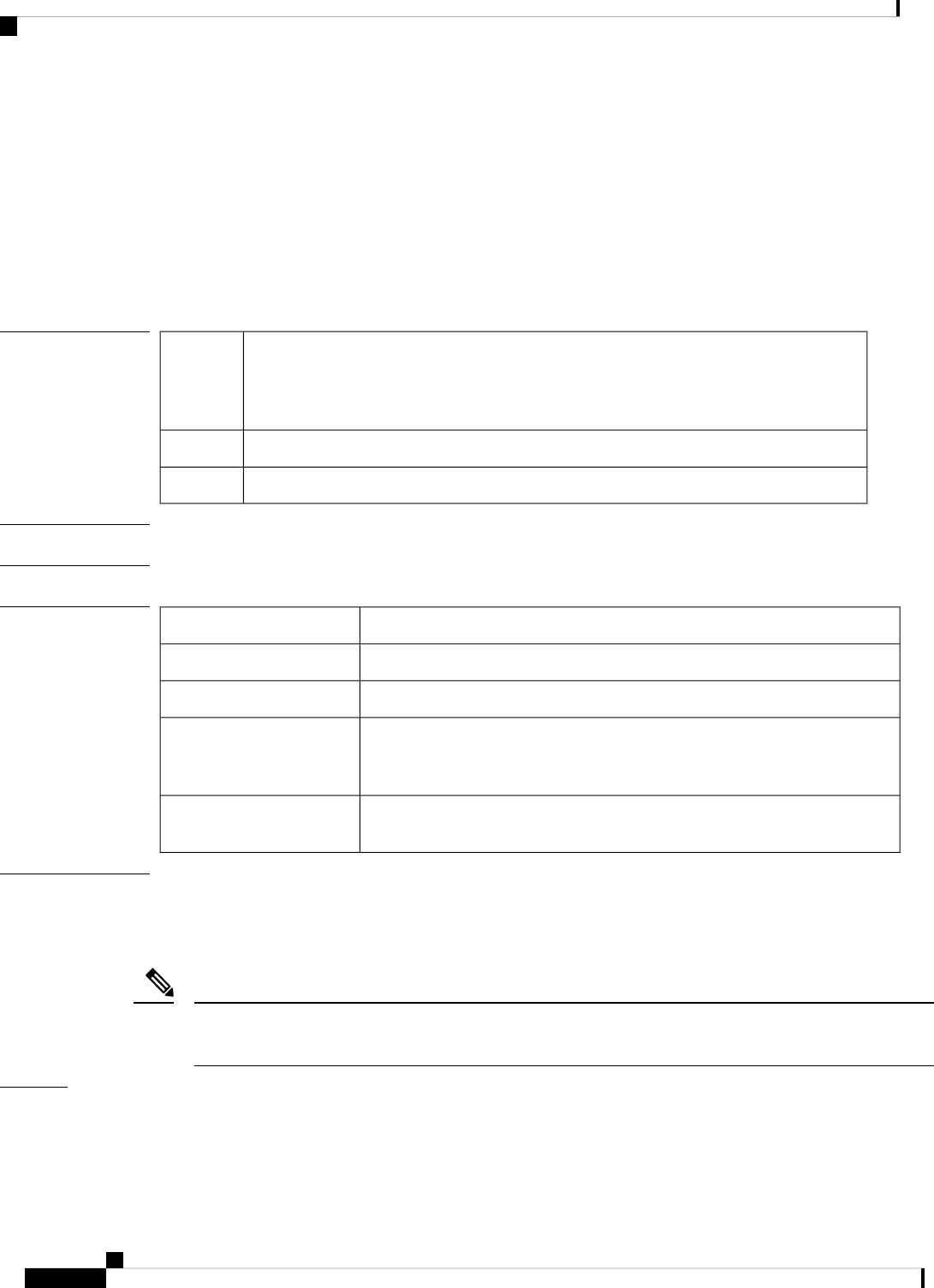
ip ospf authentication-key
To assign a password to be used by neighboring routers that are using the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
simple password authentication, use the ip ospf authentication-key command in interface configuration
mode. To remove a previously assigned OSPF password, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf authentication-key [{ 0 | 7 }] password
no ip ospf authentication-key
Syntax Description
Authentication key of type 0. The password length must be up to 8 bytes in length.
If no authentication key type is specified, then type 0 is the default
authentication key type.
Note
0
Authentication key of type 7. The password length must be up to 18 bytes in length.7
Any continuous string of characters that can be entered from the keyboard.password
Command Default
No password is specified.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
The password created by this command is used as a “key” that is inserted directly into the OSPF header when
the Cisco IOS software originates routing protocol packets. A separate password can be assigned to each
network on a per-interface basis. All neighboring routers on the same network must have the same password
to be able to exchange OSPF information.
The Cisco IOS software will use this key only when authentication is enabled for an area with the area
authentication router configuration command.
Note
Examples
The following example enables the authentication key with the string yourpass:
ip ospf authentication-key yourpass
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
76
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf authentication-key

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables authentication for an OSPF area.area authentication
Specifies authentication type for an interface.ip ospf authentication
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
77
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf authentication-key

ip ospf bfd
To enable Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) on a specific interface configured for Open Shortest
Path First (OSPF), use the ip ospfbfdcommand in interface configuration mode. To disable BFD on the OSPF
interface, use the disable keyword. To remove the ospf bfd command, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf bfd [disable]
no ip ospf bfd
Syntax Description
(Optional) Disables BFD for OSPF on a specified interface.disable
Command Default
When the disable keyword is not used, the default behavior is to enable BFD support for OSPF on the interface.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(18)SXE
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(31)S.12.0(31)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(4)T.12.4(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation
Services Routers.
15.1(2)SNG
Usage Guidelines
Enter the ip ospf bfd command to configure an OSPF interface to use BFD for failure detection. If you have
used the bfd-all interfaces command in router configuration mode to globally configure all OSPF interfaces
for an OSPF process to use BFD, you can enter the ip ospf bfd command in interface configuration mode
with the disable keyword to disable BFD for a specific OSPF interface.
Examples
In the following example, the interface associated with OSPF, Fast Ethernet interface 3/0, is configured
for BFD:
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface fastethernet 3/0
Router(config-if)# ip ospf bfd
Router(config-if)# end
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables BFD for all interfaces for a BFD peer.bfd all-interfaces
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
78
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf bfd

ip ospf cost
To explicitly specify the cost of sending a packet on an interface, use the ip ospf cost command in interface
configuration mode. To reset the path cost to the default value, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf costinterface-cost
no ip ospf cost interface-cost
Syntax Description
Unsigned integer value expressed as the link-state metric. It can be a value in the range from
1 to 65535.
interface-cost
Command Default
No default cost is predefined.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
You can set the metric manually using this command, if you need to change the default. Using the bandwidth
command changes the link cost as long as this command is not used.
The link-state metric is advertised as the link cost in the router link advertisement. We do not support type of
service (ToS), so you can assign only one cost per interface.
In general, the path cost is calculated using the following formula:
108 / bandwidth
Using this formula, the default path costs were calculated as noted in the following list. If these values do not
suit your network, you can use your own method of calculating path costs.
• 56-kbps serial link--Default cost is 1785
• 64-kbps serial link--Default cost is 1562
• T1 (1.544-Mbps serial link)--Default cost is 64
• E1 (2.048-Mbps serial link)--Default cost is 48
• 4-Mbps Token Ring--Default cost is 25
• Ethernet--Default cost is 10
• 16-Mbps Token Ring--Default cost is 6
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
79
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf cost

• FDDI--Default cost is 1
• X25--Default cost is 5208
• Asynchronous--Default cost is 10,000
• ATM-- Default cost is 1
Examples
The following example sets the interface cost value to 65:
ip ospf cost 65
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
80
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf cost

ip ospf database-filter all out
To filter outgoing link-state advertisements (LSAs) to an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) interface, use the
ip ospf database-filter all out command in interface or virtual network interface configuration modes. To
restore the forwarding of LSAs to the interface, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf database-filter all out [disable]
no ip ospf database-filter all out
Syntax Description
(Optional) Disables the filtering of outgoing LSAs to an OSPF interface; all outgoing LSAs are
flooded to the interface.
This keyword is available only in virtual network interface mode.
Note
disable
Command Default
This command is disabled by default. All outgoing LSAs are flooded to the interface.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
15.0(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SG.15.1(1)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG
Usage Guidelines
This command performs the same function that the neighbor database-filter command performs on a neighbor
basis.
If the ip ospf database-filter all out command is enabled for a virtual network and you want to disable it,
use the disable keyword in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Examples
The following example prevents filtering of OSPF LSAs to broadcast, nonbroadcast, or point-to-point
networks reachable through Ethernet interface 0:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
81
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf database-filter all out

interface ethernet 0
ip ospf database-filter all out
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Filters outgoing LSAs to an OSPF neighbor.neighbor database-filter
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
82
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf database-filter all out

ip ospf dead-interval
To set the interval during which at least one hello packet must be received from a neighbor before the router
declares that neighbor down, use the ip ospf dead-interval command in interface configuration mode. To
restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf dead-interval {seconds | minimal hello-multiplier multiplier}
no ip ospf dead-interval
Syntax Description
Interval (in seconds) during which the router must receive at least one hello packet
from a neighbor or else that neighbor is removed from the peer list and does not
participate in routing. The range is 1 to 65535. The value must be the same for
all nodes on the network.
seconds
Sets the dead interval to 1 second. Using this keyword requires that the
hello-multiplierkeyword and multiplier argument are also configured.
minimal
Integer value in the range from 3 to 20, representing the number of hello packets
sent during 1 second.
hello-multiplier
multiplier
Command Default
seconds : Four times the interval set by the ip ospf hello-interval command.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
The minimal keyword, hello-multiplier keyword and multiplier argument
were added to allow Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) support for fast hello
packets.
12.0(23)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
The dead interval is advertised in OSPF hello packets. This value must be the same for all networking devices
on a specific network.
Specifying a smaller dead interval (seconds) will give faster detection of a neighbor being down and improve
convergence, but might cause more routing instability.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
83
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf dead-interval

When the ip ospf dead-interval minimalcommand is configured, there is no guarantee that the OSPF hello
process will get the CPU cycles that are needed to maintain routing stability when the CPU is temporarily
busy. Hence this configuration should be used with caution.
Note
OSPF Support for Fast Hello Packets
By specifying the minimal and hello-multiplier keywords with a multiplier argument, you are enabling OSPF
fast hello packets. The minimalkeyword sets the dead interval to 1 second, and the hello-multiplier value sets
the number of hello packets sent during that 1 second, thus providing subsecond or “fast” hello packets.
When fast hello packets are configured on the interface, the hello interval advertised in the hello packets that
are sent out this interface is set to 0. The hello interval in the hello packets received over this interface is
ignored.
The dead interval must be consistent on a segment, whether it is set to 1 second (for fast hello packets) or set
to any other value. The hello multiplier need not be the same for the entire segment as long as at least one
hello packet is sent within the dead interval.
Use the show ip ospf interface command to verify the dead interval and fast hello interval.
Examples
The following example sets the OSPF dead interval to 20 seconds:
interface ethernet 1
ip ospf dead-interval 20
The following example configures OSPF fast hello packets; the dead interval is 1 second and there
are five hello packets sent every second:
interface ethernet 1
ip ospf dead-interval minimal hello-multiplier 5
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Interval between hello packets that the Cisco IOS software sends on the interface.ip ospf hello-interval
Displays OSPF-related information.show ip ospf interface
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
84
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf dead-interval

ip ospf demand-circuit
To configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) to treat the interface as an OSPF demand circuit, use the ip
ospf demand-circuit command in interface configuration mode or virtual network interface configuration
mode. To remove the OSPF demand circuit functionality from the interface, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf demand-circuit[disable] [ignore]
no ip ospf demand-circuit
Syntax Description
(Optional) Disables OSPF from treating the interface as an OSPF demand circuit.
This keyword is available only in virtual network interface mode.
Note
disable
(Optional) Ignores requests from other routers to operate the link in demand-circuit mode.ignore
Command Default
The circuit is not an OSPF demand circuit.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. The disable and ignore keywords were added.
Support was added for this command in virtual network interface configuration
mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release15.1(4)M.15.1(4)M
This command was modified. The disable and ignore keywords were added.
Support was added for this command in virtual network interface configuration
mode.
15.0(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SG.15.1(1)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOSXE Release 3.3SG.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG
Usage Guidelines
On point-to-point interfaces, only one end of the demand circuit must be configured with the ip ospf
demand-circuit command. Periodic hello messages are suppressed and periodic refreshes of link-state
advertisements (LSAs) do not flood the demand circuit. This command allows the underlying data-link layer
to be closed when the topology is stable. In point-to-multipoint topology, only the multipoint end must be
configured with this command.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
85
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf demand-circuit

If the ip ospf demand-circuit command is enabled for a virtual network and you want to disable it, use the
disable keyword in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure an OSPF demand circuit for an ISDN on-demand
circuit:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# network 10.0.3.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Router(config-router)# exit
Router(config)# interface BRI0
Router(config-if)# ip ospf demand-circuit
The following example shows how to prevent OSPF demand circuit operation on a multipoint hub
interface:
outer# configure terminal
Router(config)# interface Dialer0
Router(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-multipoint
Router(config-if)# ip ospf demand-circuit ignore
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures the OSPF network type to point-to-multipoint.ip ospf network point-to-multipoint
Defines the OSPF interfaces and area ID.network area
Configures the OSPF routing process.router ospf
Displays information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
86
OSPF Commands: A through ip ospf demand-circuit
ip ospf demand-circuit

OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix
through R
• ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix, on page 89
• ip ospf flood-reduction, on page 91
• ip ospf hello-interval, on page 93
• ip ospf lls, on page 94
• ip ospf message-digest-key md5, on page 96
• ip ospf mtu-ignore, on page 98
• ip ospf multi-area, on page 100
• ip ospf multi-area cost, on page 101
• ip ospf name-lookup, on page 102
• ip ospf network, on page 103
• ip ospf prefix-suppression, on page 105
• ip ospf priority, on page 106
• ip ospf resync-timeout, on page 107
• ip ospf retransmit-interval, on page 109
• ip ospf shutdown, on page 110
• ip ospf transmit-delay, on page 112
• ip ospf ttl-security, on page 113
• limit retransmissions, on page 115
• local-rib-criteria, on page 118
• log-adjacency-changes, on page 120
• max-lsa, on page 121
• max-metric router-lsa, on page 123
• neighbor (OSPF), on page 126
• neighbor database-filter all out, on page 129
• network area, on page 130
• nsf (OSPF), on page 133
• nsf cisco, on page 135
• nsf cisco helper disable, on page 137
• nsf ietf, on page 139
• nsf ietf helper disable, on page 141
• nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking, on page 143
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
87

• nsr, on page 145
• ospfv3 authentication (key-chain), on page 146
• ospfv3 multi-area, on page 147
• ospfv3 multi-area cost, on page 148
• prefix-suppression, on page 149
• process-min-time percent, on page 150
• redistribute maximum-prefix, on page 152
• router ospf, on page 155
• router-id, on page 157
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
88
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R

ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix
To configure an interface as a protecting or a protected interface in a per-prefix loop-free alternative (LFA)
repair path, use the ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix command in interface configuration mode.
ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix {candidate | protection} [disable]
Syntax Description
Specifies that the interface is protecting, that is, it can be used as the next hop in a repair path.candidate
Specifies that the interface is protected, that is, routes pointing to this interface can have a repair
path.
protection
(Optional) Specifies that the interface is either protecting or protected.disable
Command Default
All interfaces are protected and protecting.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)#
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(3)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S
Usage Guidelines
If you know from the network topology that an interface cannot be used to reroute traffic (for example, if it
goes to a customer site), you can use the ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix command to disable it from being
protecting interface.
Examples
The following example shows how to prohibit an interface from being a protecting interface:
Router(config)# interface Ethernet 0/0
ip address 192.0.2.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix candidate disable
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays debugging information for per-prefix LFA FRR paths.debug ip ospf fast-reroute
Configures a per-prefix l LFA route that redirects traffic to an alternative
next hop other than the primary neighbor.
fast-reroute per-prefix (OSPF)
Creates a list of all the candidate repair paths that were considered when
a per-prefix LFA FRR oute was computed.
fast-reroute keep-all-paths
Configures the tiebreaking policy in selecting in an LFA FRR repair path.fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)
Configures a set of prefixes to have high priority for protection in an OSPF
local RIB.
prefix-priority
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
89
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix

DescriptionCommand
Displays information about prefixes protected by LFA and IP FRR repair
paths.
show ip ospf fast-reroute
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
90
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix

ip ospf flood-reduction
To suppress the unnecessary flooding of link-state advertisements (LSAs) in stable topologies, use the ip ospf
flood-reduction command in interface configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this
command.
ip ospf flood-reductionflood-reduction [disable]
no ip ospf flood-reduction
Syntax Description
(Optional) Disables the suppressing of unnecessary flooding of LSAs in stable topologies.
This keyword is available only in virtual network interface mode.
Note
disable
Command Default
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.1(2)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
15.0(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SG.15.1(1)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG
Usage Guidelines
All routers supporting the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) demand circuit are compatible and can interact
with routers supporting flooding reduction.
If the ip ospf flood-reduction command is enabled for a virtual network and you want to disable it, use the
disable keyword in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Examples
The following example suppresses the flooding of unnecessary LSAs on serial interface 0:
interface serial 0
ip ospf flood-reduction
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
91
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf flood-reduction

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays OSPF-related interface information.show ip ospf interface
Displays OSPF-neighbor information on a per-interface basis.show ip ospf neighbor
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
92
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf flood-reduction

ip ospf hello-interval
To specify the interval between hello packets that the Cisco IOS software sends on the interface, use the ip
ospf hello-interval command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default time, use the no form
of this command.
ip ospf hello-intervalseconds
no ip ospf hello-interval
Syntax Description
Specifies the interval (in seconds). The value must be the same for all nodes on a specific network.
The range is from 1 to 65535.
seconds
Command Default
10 seconds (Ethernet)
30 seconds (nonbroadcast)
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
This value is advertised in the hello packets. The smaller the hello interval, the faster topological changes will
be detected, but more routing traffic will ensue. This value must be the same for all routers and access servers
on a specific network.
Examples
The following example sets the interval between hello packets to 15 seconds:
interface ethernet 1
ip ospf hello-interval 15
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Sets the time period for which hello packets must not have been seen before
neighbors declare the router down.
ip ospf dead-interval
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
93
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf hello-interval

ip ospf lls
To enable Link-Local Signaling (LLS) on an interface, regardless of the router-level LLS setting, use the ip
ospf llscommand in interface configuration mode. To reconfigure the router-level LLS setting on the specific
interface, use the no or defaultversion of this command.
ip ospf lls [disable]
{no | default} ip ospf lls [disable]
Syntax Description
Restores the default LLS setting for the interface that has been configured at the router level.no
Inherits the global (router level) LLS settings for the interface that has been specified.default
(Optional) Disables LLS on a specified interface regardless of the global (router level) setting.disable
Command Default
LLS is enabled.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(27)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(7)T.12.3(7)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SXE.12.2(18)SXE
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
By default, each Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) interface inherits the LLS setting from the router level. The
ip ospf lls interface-level command takes precedence over the capability lls router-level command. For
example, if you have entered the no capability lls command to disable LLS at the router level, you can use
the ip ospf lls command to selectively enable LLS for specific interfaces, in order to allow the router to enable
OSPF nonstop forwarding (NSF) awareness only for these specified interfaces.
To unconfigure the interface LLS setting, enter either the default ip ospf lls command or the no ip ospf lls
command to restore the default LLS setting for the interface that has been configured at the router level. For
example, if the capability lls command is enabled (by default) at the router level, you can use either the
default ip ospf lls command or the no ip ospf lls command to disable LLS on specific interfaces, for instance,
to interoperate on network segments where there are routers that do not properly handle LLS.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
94
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf lls

If the network is running OSPF with the LLS feature enabled by default, LLS is globally enabled for all
interfaces. If a router in the network is connected to a non-Cisco device that is not in compliance with RFC
2328, there may be network difficulties involving the forming of OSPF neighbors. In this situation, we
recommend that you use the ip ospf lls command with the disable keyword to disable LLS on the router that
is connected to the non-Cisco device.
Note
Examples
In following example, LLS is disabled on Ethernet interface 2/0:
Router(config)# interface Ethernet2/0
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.1.145.2 255.255.0.0
Router(config-if)# no ip directed-broadcast
Router(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 testing
Router(config-if)# ip ospf lls disable
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables the use of the LLS data block in originated OSPF packets and reenables
OSPF NSF awareness.
capability lls
Displays OSPF-related interface information.show ip ospf interface
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
95
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf lls

ip ospf message-digest-key md5
To enable Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Digest 5 (MD5) authentication, use the ip ospf
message-digest-key md5command in interface configuration mode. To remove an old MD5 key, use the no
form of this command.
ip ospf message-digest-keykey-idencryption-typemd5key
no ipospfmessage-digest-keykey-id
Syntax Description
An identifier in the range from 1 to 255.key-id
Specifies the encryption level. The range is from 0 to 7. 0 specifies no encryption. 7
specifies a proprietary level of encryption.
encryption-type
Alphanumeric password of up to 16 bytes.key
Command Default
OSPF MD5 authentication is disabled.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
Usually, one key per interface is used to generate authentication information when sending packets and to
authenticate incoming packets. The same key identifier on the neighbor router must have the same key value.
The process of changing keys is as follows. Suppose the current configuration is as follows:
interface ethernet 1
ip ospf message-digest-key 100 md5 OLD
You change the configuration to the following:
interface ethernet 1
ip ospf message-digest-key 101 md5 NEW
The system assumes its neighbors do not have the new key yet, so it begins a rollover process. It sends multiple
copies of the same packet, each authenticated by different keys. In this example, the system sends out two
copies of the same packet--the first one authenticated by key 100 and the second one authenticated by key
101.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
96
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf message-digest-key md5

Rollover allows neighboring routers to continue communication while the network administrator is updating
them with the new key. Rollover stops once the local system finds that all its neighbors know the new key.
The system detects that a neighbor has the new key when it receives packets from the neighbor authenticated
by the new key.
After all neighbors have been updated with the new key, the old key should be removed. In this example, you
would enter the following:
interface ethernet 1
no ip ospf message-digest-key 100
Then, only key 101 is used for authentication on Ethernet interface 1.
We recommend that you not keep more than one key per interface. Every time you add a new key, you should
remove the old key to prevent the local system from continuing to communicate with a hostile system that
knows the old key. Removing the old key also reduces overhead during rollover.
If the service password-encryption command is not used when implementing OSPF MD5 authentication,
the MD5 secret will be stored as plain text in NVRAM.
Note
Examples
The following example sets a new key 19 with the password 8ry4222:
interface ethernet 1
ip ospf message-digest-key 10 md5 xvv560qle
ip ospf message-digest-key 19 md5 8ry4222
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables authentication for an OSPF area.area authentication
Specifies authentication type for an interface.ip ospf authentication
Encrypts a password.service password-encryption
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
97
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf message-digest-key md5

ip ospf mtu-ignore
To disable Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) maximum transmission unit (MTU) mismatch detection on
receiving database descriptor (DBD) packets, use the ip ospf mtu-ignore command in interface configuration
mode. To enable OSPF mismatch detection, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf mtu-ignore[disable]
no ip ospf mtu-ignore
Syntax Description
(Optional) Causes OSPF MTU mismatch detection to occur because OSPF MTU mismatch
detection is being disabled.
This keyword is available only in virtual network interface mode.
Note
disable
Command Default
OSPF MTU mismatch detection is enabled.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(3)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
15.0(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SG.15.1(1)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG
Usage Guidelines
OSPF checks whether neighbors are using the same MTU on a common interface. This check is performed
when neighbors exchange DBD packets. If the receiving MTU in the DBD packet is higher than the IP MTU
configured on the incoming interface, OSPF adjacency will not be established.
If the ip ospf mtu-ignore command is enabled for a virtual network and you want to disable it, use the disable
keyword in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Examples
The following example disables OSPF MTU mismatch detection on receiving DBD packets:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
98
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf mtu-ignore

interface serial 0/0
ip ospf mtu-ignore
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
99
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf mtu-ignore

ip ospf multi-area
To configure multiarea adjacency on a interface that is configured with Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), use
the ip ospf multi-area command in interface configuration mode. To disable multiarea adjacency, use the
no form of this command.
ip ospf multi-area multi-area-id
no ip ospf multi-area multi-area-id
Syntax Description
Identifier of the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be specified
as an IP address or a decimal value. The range is from 0 to 4294967295.
multi-area-id
Command Default
No OSPF multiarea adjacency interface is defined.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS Release XE 3.10S
Examples
The following example shows how to configure OSPF multiarea adjacency on an interface with an
area identifier of 1:
Device# enable
Device (config)# interface Ethernet 0/0
Device (config-if)# ip ospf multi-area 1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Specifies the cost of sending a packet on an OSPF multiarea interface.ip ospf multi-area cost
Displays the interface information related to OSPF.show ip ospf interface
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
100
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf multi-area

ip ospf multi-area cost
To specify the cost of sending a packet on an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) multiarea interface, use the ip
ospf multi-area cost command in interface configuration mode. To reset the multiarea path cost to the default
value, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf multi-area multi-area-id cost interface-cost
no ip ospf multi-area multi-area-id cost interface-cost
Syntax Description
Identifier of the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be specified
as an IP address or a decimal value. The range is from 0 to 4294967295.
multi-area-id
Unsigned integer value expressed as the link-state metric. The range is from 1 to 65535.interface-cost
Command Default
No interface cost is defined for OSPF multiarea adjacency.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS Release XE 3.10S
Examples
The following example shows how to set the OSPF multiarea interface cost value to 65:
Device# enable
Device (config)# interface Ethernet 0/0
Device (config-if)# ip ospf multi-area 1 cost 65
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables multiarea adjacency on the OSPF interface.ip ospf multi-area
Displays the interface information related to OSPF.show ip ospf interface
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
101
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf multi-area cost

ip ospf name-lookup
To configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) to look up Domain Name System (DNS) names for use in all
OSPF show EXEC command displays, use the ip ospf name-lookup command in global configuration mode.
To disable this function, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf name-lookup
noipospfname-lookup
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
This command makes it easier to identify a router because the router is displayed by name rather than by its
router ID or neighbor ID.
Examples
The following example configures OSPF to look up DNS names for use in all OSPF show EXEC
command displays:
ip ospf name-lookup
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
102
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf name-lookup

ip ospf network
To configure the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) network type to a type other than the default for a given
medium, use the ip ospf network command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default value,
use the no form of this command.
ip ospf network{broadcast | non-broadcast | {point-to-multipoint [non-broadcast] | point-to-point}}
no ip ospf network
Syntax Description
Sets the network type to broadcast.broadcast
Sets the network type to nonbroadcast multiaccess (NBMA).non-broadcast
Sets the network type to point-to-multipoint. The optional
non-broadcast keyword sets the point-to-multipoint network to be
nonbroadcast. If you use the non-broadcast keyword, the neighbor
command is required.
point-to-multipoint
non-broadcast
Sets the network type to point-to-point.point-to-point
Command Default
Depends on the network type.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
The point-to-multipoint keyword was added.10.3
The non-broadcast keyword used with the point-to-multipoint keyword was
added.
11.3AA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
Using this feature, you can configure broadcast networks as NBMA networks when, for example, routers in
your network do not support multicast addressing. You can also configure nonbroadcast multiaccess networks
(such as X.25, Frame Relay, and Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS)) as broadcast networks. This
feature saves you from needing to configure neighbors.
Configuring NBMA networks as either broadcast or nonbroadcast assumes that there are virtual circuits from
every router to every router or fully meshed networks. However, there are other configurations where this
assumption is not true. For example, a partially meshed network. In these cases, you can configure the OSPF
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
103
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf network

network type as a point-to-multipoint network. Routing between two routers that are not directly connected
will go through the router that has virtual circuits to both routers. You need not configure neighbors when
using this feature.
If this command is issued on an interface that does not allow it, this command will be ignored.
OSPF has two features related to point-to-multipoint networks. One feature applies to broadcast networks;
the other feature applies to nonbroadcast networks:
• On point-to-multipoint, broadcast networks, you can use the neighbor command, and you must specify
a cost to that neighbor.
• On point-to-multipoint, nonbroadcast networks, you must use the neighbor command to identify neighbors.
Assigning a cost to a neighbor is optional.
Examples
The following example sets your OSPF network as a broadcast network:
interface serial 0
ip address 192.168.77.17 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network broadcast
encapsulation frame-relay
The following example illustrates a point-to-multipoint network with broadcast:
interface serial 0
ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation frame-relay
ip ospf cost 100
ip ospf network point-to-multipoint
frame-relay map ip 10.0.1.3 202 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 10.0.1.4 203 broadcast
frame-relay map ip 10.0.1.5 204 broadcast
frame-relay local-dlci 200
!
router ospf 1
network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
neighbor 10.0.1.5 cost 5
neighbor 10.0.1.4 cost 10
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Defines mapping between a destination protocol address and the DLCI used to connect
to the destination address.
frame-relay map
Configures OSPF routers interconnecting to nonbroadcast networks.neighbor (OSPF)
Sets up the LAN protocols-to-remote host mapping.x25 map
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
104
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf network

ip ospf prefix-suppression
To prevent Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) from advertising all IP prefixes that belong to a specific interface,
except for prefixes that are associated with secondary IP addresses, use the ip ospf prefix-suppression
command in interface configuration mode. To remove the per-interface configuration from the interface and
allow the interface to inherit the IP prefix suppression setting from the router configuration, use the no form
of this command.
ip ospf prefix-suppression [disable]
no ip ospf prefix-suppression
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies that OSPF will advertise the interface IP prefix, regardless of the router mode
configuration for IP prefix suppression.
disable
Command Default
All IP prefixes that are associated with the interface are advertised.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.4(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6
Usage Guidelines
You can suppress IP prefixes on a per-interface basis for all interface types by entering the ip ospf
prefix-suppression command in interface configuration mode.
When the ip ospf prefix-suppressioncommand is configured, it takes precedence over the prefix-suppression
router configuration command. If the prefix-suppression router configuration command has been entered,
the interfaces for the specified OSPF process will inherit the prefix suppression setting from the router
configuration command.
When you enter the ip ospf prefix-suppression command, prefix generation for any interface type, including
loopbacks and passive interfaces, is suppressed. Only prefixes associated with secondary IP addressees remain
unaffected.
Examples
The following example suppresses all IP prefixes, except for those associated with secondary IP
addresses, for GigabitEthernet interface 1/1/1:
interface gigabitethernet 1/1/1
ip ospf prefix-suppression
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Prevents OSPF from advertising all IP prefixes except prefixes that are associated
with loopbacks, secondary IP addresses, and passive interfaces for a specific OSPF
process.
prefix-suppression
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
105
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf prefix-suppression

ip ospf priority
To set the router priority, which helps determine the designated router for this network, use the ip ospf priority
command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default value, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf prioritynumber-value
noip ospf priority
Syntax Description
A number value that specifies the priority of the router. The range is from 0 to 255.number-value
Command Default
Priority of 1
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
When two routers attached to a network both attempt to become the designated router, the one with the higher
router priority takes precedence. If there is a tie, the router with the higher router ID takes precedence. A
router with a router priority set to zero is ineligible to become the designated router or backup designated
router. Router priority is configured only for interfaces to multiaccess networks (in other words, not to
point-to-point networks).
This priority value is used when you configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) for nonbroadcast networks
using the neighbor router configuration command for OSPF.
Examples
The following example sets the router priority value to 4:
interface ethernet 0
ip ospf priority 4
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures the OSPF network type to a type other than the default for a given medium.ip ospf network
Configures OSPF routers interconnecting to nonbroadcast networks.neighbor (OSPF)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
106
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf priority

ip ospf resync-timeout
To configure how long the router will wait before taking a neighbor adjacency down if the out-of-band
resynchronization (oob-resync) has not taken place since the time a restart signal (Open Shortest Path First
[OSPF] hello packet with RS-bit set) was received from the neighbor, use the ip ospf resync-timeoutcommand
in interface configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf resync-timeout seconds
no ip ospf resync-timeout
Syntax Description
Number of seconds the router will wait before taking a neighbor adjacency down if the out-of-band
resynchronization (oob-resync) has not taken place since the time a restart signal (OSPF hello
packet with RS-bit set) was received from the neighbor. The value is in the range from 1 to 65535
seconds. The default value is 40 seconds or the value set for the OSPF dead interval for the
interface, whichever is greater.
seconds
Command Default
The default value is 40 seconds or the value set for the interface’s OSPF dead interval, whichever is greater.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
When an OSPF nonstop forwarding (NSF) router performs a route processor (RP) switchover, it notifies its
neighbors, via a special hello packet, of such action and requests that each neighbor help resynchronize the
Link State Database.
When a neighbor (that is NSF-aware) receives the special hello packet from the NSF-capable router, it starts
a resync timeout timer and waits to synchronize its database with the NSF-capable router. If the NSF-capable
router does not initiate the database resynchronization process before the resync-timeout timer expires, the
NSF-aware neighbor will take down the adjacency with the NSF-capable router.
By default, the resync-timeout timer is set to 40 seconds or the dead interval of the interface, whichever is
greater. (By default, the dead interval is 4 times the hello interval; the hello interval defaults to 10 seconds
for Ethernet or 30 seconds for nonbroadcast.) The ip ospfresync-timeout command allows the resync-timeout
to be changed and independent of the dead interval or default value.
Examples
This example sets the OSPF resync-timeout interval to 50 seconds:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
107
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf resync-timeout

interface GigabitEthernet 6/0/0
ip ospf resync-timeout 50
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Sets the interval at which hello packets must not be seen before neighbors declare
the router down.
ip ospf dead-interval
Sets the interval between hello packets that the software sends on the interface.ip ospf hello-interval
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
108
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf resync-timeout

ip ospf retransmit-interval
To specify the time between link-state advertisement (LSA) retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to the
interface, use the ip ospf retransmit-interval command in interface configuration mode. To return to the
default value, use the no form of this command.
ip ospf retransmit-intervalseconds
no ip ospf retransmit-interval
Syntax Description
Time (in seconds) between retransmissions. The range is from 1 to 65535 seconds. The default
is 5 seconds.
seconds
Command Default
5 seconds
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
When a router sends an LSA to its neighbor, it keeps the LSA until it receives back the acknowledgment
message. If the router receives no acknowledgment, it will resend the LSA.
The setting of the seconds argument should be greater than the expected round-trip delay between any two
routers on the attached network. The setting of this parameter should also be conservative, or needless LSA
retransmissions may occur. The value should be larger for serial lines and virtual links.
It is recommended to use the same value for the seconds argument on neighbor OSPF routers. Using inconsistent
values on neighbor routers can cause needless LSA retransmissions.
Note
Examples
The following example sets the retransmit interval value to 8 seconds:
interface ethernet 2
ip ospf retransmit-interval 8
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
109
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf retransmit-interval

ip ospf shutdown
To initiate an graceful shutdown of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol at the interface level, use the
ip ospf shutdown command in interface configuration mode. To restart the OSPF protocol on an interface,
use the no form of this command.
ip ospf shutdown [disable]
no ip ospf shutdown
Syntax Description
(Optional) Disables the initiation of the OSPF graceful shutdown at the interface level; OSPF stays
active at the interface level.
This keyword is available only in virtual network interface mode.
Note
disable
Command Default
OSPF stays active at the interface level.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
This command was modified. The disable keyword was added. Support was
added for this command in virtual network interface configuration mode.
15.0(1)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SG.15.1(1)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3SG
Usage Guidelines
Use the ip ospf shutdown command to put OSPF in shutdown mode under a specific interface.
If the ip ospf shutdown command is enabled for a virtual network and you want to disable it, use the disable
keyword in virtual network interface configuration mode.
Examples
The following example shows how to initiate a graceful shutdown of the OSPF protocol on Ethernet
interface 0/2:
Router(config)# interface ethernet 0/2
Router(config-if)# ip ospf shutdown
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
110
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf shutdown

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Initiates a graceful shutdown of the OSPF protocol under the current instance.shutdown (router OSPF)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
111
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf shutdown

ip ospf transmit-delay
To set the estimated time required to send a link-state update packet on the interface, use the ip ospf
transmit-delay command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default value, use the no form of
this command.
ip ospf transmit-delayseconds
no ip ospf transmit-delay
Syntax Description
Time (in seconds) required to send a link-state update. The range is from 1 to 65535 seconds. The
default is 1 second.
seconds
Command Default
1 second
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
Link-state advertisements (LSAs) in the update packet must have their ages incremented by the amount
specified in the seconds argument before transmission. The value assigned should take into account the
transmission and propagation delays for the interface.
If the delay is not added before transmission over a link, the time in which the LSA propagates over the link
is not considered. This setting has more significance on very low-speed links.
Examples
The following example sets the retransmit delay value to 3 seconds:
interface ethernet 0
ip ospf transmit-delay 3
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
112
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf transmit-delay

ip ospf ttl-security
To configure the Time-to-Live (TTL) security check feature on a specific interface, use the ip ospf
ttl-securitycommand in interface configuration mode. To disable TTL security on an interface, use the noform
of this command.
ip ospf ttl-security [{hops hop-count | disable}]
no ip ospf ttl-security
Syntax Description
(Optional) Configures the maximum number of IP hops. The hop-countargument range
is from 1 to 254.
hops hop-count
(Optional) Disables TTL security on an interface.disable
Command Default
TTL security is disabled on all Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) interfaces.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if) Virtual network interface (config-if-vnet)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was modified. Support was added for this command in virtual
network interface configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.2S
Usage Guidelines
Use the ip ospf ttl-security command to configure TTL security on a specific interface.
The disable keyword can be used to disable TTL security on a specific interface but is only useful if the
ttl-security all-interfaces command was used in router mode to first configure TTL security on all OSPF
interfaces. In this way, all OSPF interfaces can be configured with TTL security and then individual interfaces
can be disabled. This can save time as opposed to configuring each interface one-by-one from the start.
Examples
The following example shows how to effectively use the disable keyword to disable TTL security
on Ethernet interface 0/0 after the feature has first been configured on all OSPF interfaces:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# ttl-security all-interfaces
Router(config-router)# exit
Router(config
)
# interface ethernet 0/0
Router(config-if
)
# ip ospf ttl-security disable
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
113
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf ttl-security

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures TTL security check on all OSPF interfaces.ttl-security all-interfaces
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
114
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ip ospf ttl-security

limit retransmissions
To modify the number of retransmissions of database exchange and update packets for both demand and
non-demand circuits, use the limit retransmissions command in router configuration mode. To reset the
maximum number of retransmissions back to the default value of 24, use the no form of this command.
limit retransmission {dc | {max-retransmissions | disable} | [non-dc] | non-dc | {max-retransmissions
| disable} | [dc]}
no limit transmissions [{dc | non-dc}]
Syntax Description
Demand circuit retransmissions.dc
Maximum number of retransmissions. Range from 1 to 255.max-retransmissions
Nondemand circuit retransmissions.non-dc
Disables or removes the limit to the number of retransmissions.disable
Command Default
Maximum number of retransmissions is 24.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)#
Address family configuration (config-router-af)#
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(11)T
This command was modified. This command was implemented on the Cisco
ASR 1006 Series Device. This command is now supported in address-family
configuration mode.
Cisco IOS XE 3.7S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)SY.Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)SY
Usage Guidelines
There is a limit to the number of retransmissions of database exchange and update packets for both demand
and nondemand circuits. The retransmission of these packets stops once this retry limit is reached, thus
preventing unnecessary use of the link in continual retransmission of the packets if, for some reason, a neighbor
is not responding during adjacency forming. The limit for both demand circuit and nondemand circuit
retransmissions is 24.
The limit-retransmissions command allows you to either remove (disable) the limit or change the maximum
number of retransmissions to be a number from 1 to 255. The configuration of this command provides for
backward compatibility for previous or other releases of Cisco IOS Software or other routers that do not have
this feature.
The limit to the number of retransmissions does not apply for update packets on nonbroadcast multiaccess
(NBMA) point-to-multipoint direct circuits. In this situation, the dead timer is used to end communication
with nonresponding neighbors and thus stop the retransmissions.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
115
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
limit retransmissions

This command can be used in the router configuration mode and address-family mode. The command is also
applicable for both OSPF and OSPFv3 protocols.
Note
Examples
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of demand circuit retransmissions
to 10 in the router configuration mode:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# router {ospf|ospfv3} 11
Device(config-router)# limit retransmissions dc 10
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of demand circuit retransmissions
to 10 in the address-family configuration mode:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# router {ospf|ospfv3} 11
Device(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast
Device(config-router-af)# limit retransmissions dc 10
The following example shows how to remove the limit for the number of demand circuit
retransmissions:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# router {ospf|ospfv3} 11
Device(config-router)# limit retransmissions dc disable
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of demand circuit retransmissions
to 10 and to set the maximum number of nondemand circuit retransmissions to 20:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# router {ospf|ospfv3} 11
Device(config-router)# limit retransmissions dc 10 non-dc 20
The following example shows how to set the maximum number of demand circuit retransmissions
to 10, and to remove the limit for the number of nondemand circuit retransmissions:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# router {ospf|ospfv3} 11
Device(config-router)# limit retransmissions dc 10 non-dc disable
The following example shows how to reset both the demand circuit and nondemand circuit maximum
number of retransmissions back to the default of 24:
Device> enable
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# router {ospf|ospfv3} 11
Device(config-router)# no limit retransmissions
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures an OSPF routing process.router ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
116
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
limit retransmissions

DescriptionCommand
Enters IPv4 or IPv6 address family configuration mode for OSPFv3.address-family
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
117
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
limit retransmissions

local-rib-criteria
To specify that the OSPF local Routing Information Base (RIB) will be used for route validation, use the
local-rib-criteria command in router configuration mode. To remove local RIB route validation, use the
noform of this command.
local-rib-criteria [forwarding-address] [inter-area-summary] [nssa-translation]
no local-rib-criteria [forwarding-address] [inter-area-summary] [nssa-translation]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies that the local RIB is to be used only for route validation criteria
for external or NSSA forwarding addresses.
forwarding-address
(Optional) Specifies that the local RIB is to be used only for route validation criteria
for inter-area summaries.
inter-area-summary
(Optional) Specifies that the local RIB is to be used only for route validation criteria
for NSSA translation.
nssa-translation
Command Default
The global RIB (not the local RIB) is used for route validation.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.4(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release
12.2(33)SRC.
12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release
12.2(33)SB.
12.2(33)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release
3.12S.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.12S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release
15.4(2)S.
15.4(2)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release
15.2(3)E.
15.2(3)E
Usage Guidelines
If the local-rib-criteria is command is entered without any optional keywords, the local RIB will be used as
criteria for all of the options (forwarding address, inter-area summary, and NSSA translation).
You can enter the local-rib-criteria command with one or more of the optional keywords to configure the
OSPF routing process to use the local RIB only for forwarding address, inter-area-summary, or NSSA
translation route generation.
The local-rib-criteria command is enabled by default for OSPFv3.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
118
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
local-rib-criteria

It is recommended to keep the default behavior (the global RIB is used for route validation). Although entering
the local-rib-criteria command alone or with one or more of the optional keywords may result in slightly
faster network convergence in some cases, you may potentially cause a problem such as a routing loop or null
route.
Note
When the forwarding-address keyword is entered to specify that forwarding-address verification is modified
to use the local RIB, packet forwarding will still be dependent on the global RIB. If the global RIB contains
a more preferred or more specific route from a different protocol, this preferred route still will still be used
for packet forwarding.
Note
Examples
The following example specifies that the local RIB should be used as the criteria for NSSA translation:
router ospf 23
local-rib-criteria nssa-translation
The following example enables all local RIB criteria options:
router ospf 1
local-rib-criteria
The following example specifies that the local RIB will be used only for inter-area summary route
generation:
router ospf 1
local-rib-criteria inter-area-summary
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays information for the OSPF local RIB or locally redistributed routes.show ip ospf rib
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
119
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
local-rib-criteria

log-adjacency-changes
To configure the router to send a syslog message when an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) neighbor goes up
or down, use the log-adjacency-changes command in router configuration mode. To turn off this function,
use the no form of this command.
log-adjacency-changes [detail]
no log-adjacency-changes [detail]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Sends a syslog message for each state change, not just when a neighbor goes up or down.detail
Command Default
Enabled
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced as ospf log-adjacency-changes.11.2
The ospf keyword was omitted and the detail keyword was added.12.1
Support for IPv6 was added.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific 12.2SX
release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)S.15.1(2)S
Usage Guidelines
This command allows you to know about OSPF neighbors going up or down without turning on the debug
ip ospf packetcommand or the debugipv6 ospf adjacency command. The log-adjacency-changes command
provides a higher level view of those changes of the peer relationship with less output than the debug command
provides. The log-adjacency-changes command is on by default but only up/down (full/down) events are
reported, unless the detail keyword is also used.
Examples
The following example configures the router to send a syslog message when an OSPF neighbor state
changes:
log-adjacency-changes detail
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays information about each OSPF packet received for IPv4.debug ip ospf packet
Displays debugging information for OSPF for IPv6.debug ipv6 ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
120
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
log-adjacency-changes

max-lsa
To limit the number of nonself-generated link-state advertisements (LSAs) that an Open Shortest Path First
(OSPF) routing process can keep in the OSPF link-state database (LSDB), use the max-lsacommand in router
configuration mode. To remove the limit of non self-generated LSAs that an OSPF routing process can keep
in the OSPF LSDB, use the no form of this command.
max-lsa maximum-number [threshold-percenta ge] [warning-only] [ignor e-time minutes] [ignore-count
count-number] [reset-time minutes]
no max-lsa maximum-number [threshold-percentage] [warning-only] [ignore-time minutes]
[ignore-count count-number] [reset-time minutes]
Syntax Description
Maximum number of nonself-generated LSAs the OSPF process can keep
in the OSPF LSBD.
maximum-number
(Optional) The percentage of the maximum LSA number, as specified by
the maximum-number argument, at which a warning message is logged. The
default is 75 percent.
threshold-percentage
(Optional) Specifies that only a warning message is sent when the maximum
limit for LSAs is exceeded. Disabled by default.
warning-only
(Optional) Specifies the time, in minutes, to ignore all neighbors after the
maximum limit of LSAs has been exceeded. The default is 5 minutes.
ignore-time minutes
(Optional) Specifies the number of times the OSPF process can consecutively
be placed into the ignore state. The default is 5 times.
ignore-count count-number
(Optional) Specifies the time, in minutes, after which the ignore count is
reset to zero. The default is 10 minutes.
reset-time minutes
Command Default
The number of nonself-generated LSAs that an OSPF routing process can keep in the OSPF LSDB is not
limited.
threshold-percentage : 75 percentwarning-only warning message: disabledignore-time minutes: 5
minutesignore-count count-number:5 timesreset-time minutes: 10 minutes
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(27)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(7)T.12.3(7)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SXE.12.2(18)SXE
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
121
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
max-lsa

ModificationRelease
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
Usage Guidelines
To prevent the OSPF process from endlessly changing from the normal state of operation to the ignore state
as a result of the LSA count exceeding the maximum configured number immediately after it returns from
the ignore state to the normal state of operation, the OSPF process keeps a counter on how many times the
process went into the ignore state. This counter is called the ignore count. If the ignore count exceeds the
maximum number of LSAs that is specified by the ignore-count keyword and counter-number argument, the
OSPF process remains in the ignore state permanently. To return the OSPF process to the state of normal
operation, enter the clear ip ospf command.
If the router is placed into a permanent ignore state, we recommend that you identify and correct the cause of
the problem involving the router that is generating the LSAs, or, if possible, increase the limit that has been
configured by the max-lsa command before you try to bring the router back into normal operation.
If the router that has generated large numbers of LSAs is not reachable, these LSAs cannot be removed from
the OSPF area and domain. As a result, any other router leaving the ignore state and returning to normal
operation may reach the ignore state again. We recommend that you take one of the following actions in order
to bring the router back into the network:
• Temporarily increase the LSA limit to account for the stale LSAs.
• Wait until the stale LSAs are removed as a result of reaching their maximum age.
• Make sure that the router that has generated the large number of LSAs is connected to the network and
is no longer generating large numbers of LSAs.
When the warning-only keyword is used, the OSPF process never enters the ignore state. When the LSA
count exceeds the maximum limit that is specified by the maximum-number argument, only an error message
is logged and the OSPF process continues in its normal operation.
When the max-lsa command is entered for the first time or when any of the parameters of the command are
changed, the OSPF process undergoes a soft-reset procedure.
Examples
The following example sets a limit of 12,000 LSAs that can be received before the OSPF process
enters the ignore state:
Router(config)# router ospf 100
Router(config-router)# router-id 209.165.201.0
Router(config-router)# log-adjacency-changes
Router(config-router)# max-lsa 12000
Router(config-router)# network 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.255
In the following example, an OSPF process has remained in the ignore state permanently. When the
clear ip ospf command is entered the OSPF process returns to the state of normal operation and
clears redistribution based on the OSPF routing process ID.
Router(config-router)# clear ip ospf 100 process
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Clears redistribution based on the OSPF routing process ID.clear ip ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
122
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
max-lsa

max-metric router-lsa
To configure a router that is running the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol to advertise a maximum
metric so that other routers do not prefer the router as an intermediate hop in their shortest path first (SPF)
calculations, use the max-metric router-lsacommand in router address family topology or router configuration
mode. To disable the advertisement of a maximum metric, use the no form of this command.
max-metric router-lsa [external-lsa [max-metric-value]] [include-stub] [on-startup {seconds |
wait-for-bgp}] [summary-lsa [max-metric-value]]
no max-metric router-lsa [external-lsa [max-metric-value]] [include-stub] [on-startup {seconds |
wait-for-bgp}] [summary-lsa [max-metric-value]]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Configures the router to override the external LSA metric with the maximum
metric value.
external-lsa
(Optional) Maximum metric value for LSAs. The configurable range is from 1 to
16777215. The default value is 16711680.
max-metric-value
(Optional) Configures the router to advertise the maximum metric for stub links in router
LSAs.
include-stub
(Optional) Configures the router to advertise a maximum metric at startup.on-startup
(Optional) Maximum metric value for the specified time interval. The configurable
range is from 5 to 86400 seconds. There is no default timer value for this configuration
option.
seconds
(Optional) Configures the router to advertise a maximum metric until Border Gateway
Protocol (BGP) routing tables have converged or the default timer has expired. The
default timer is 600 seconds.
wait-for-bgp
(Optional) Configures the router to override the summary LSA metric with the maximum
metric value.
summary-lsa
Command Default
Router link-state advertisements (LSAs) are originated with normal link metrics.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(15)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(16)ST.12.0(16)ST
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(4)T.12.2(4)T
The include-stub, summary-lsa,and external-lsa keywords and the max-metric-value
argument were made available under router configuration mode.
12.4(10)
The include-stub, summary-lsa,and external-lsa keywords and the max-metric-value
argument were made available under router configuration mode.
12.4(11)T
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
123
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
max-metric router-lsa

ModificationRelease
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S.12.2(14)S
The include-stub, summary-lsa,and external-lsa keywords and the max-metric-value
argument were made available under router configuration mode.
12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.
The include-stub, summary-lsa,and external-lsa keywords and the max-metric-value
argument were made available under router configuration mode.
12.2(33)SRB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.15.2(1)E
Usage Guidelines
Enabling the max-metric router-lsa command will cause a router to originate LSAs with a maximum metric
(LSInfinity: 0xFFFF) through all nonstub links, which allows BGP routing tables to converge without attracting
transit traffic (if there are not alternate lower cost paths around the router). The router will advertise accurate
(normal) metrics after the configured or default timers expire or after BGP sends a notification that routing
tables have converged.
Directly connected links in a stub network are not affected by the configuration of a maximum or infinite
metric because the cost of a stub link is always set to the output interface cost.
Note
The max-metric router-lsa command is useful in the following situations:
• Reloading a router. After a router is reloaded, Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) converge very quickly,
and other routers may try to forward traffic through the newly reloaded router. If the router is still building
BGP routing tables, packets destined for other networks that the router has not learned through BGP may
be dropped. In the case of an Internet backbone router, a large number of packets may be dropped.
• Introducing a router into a network without routing traffic through it. You may want to connect a router
to an OSPF network but not want real traffic flowing through the router if there are better alternate paths.
If there are no alternate paths, this router would still accept transit traffic as before.
• Gracefully removing a router from a network. This feature allows you to gracefully remove a router from
the network by advertising a maximum metric through all links, which allows other routers to select
alternate paths for transit traffic to follow before the router is shut down.
You should not save the running configuration of a router when it is configured for a graceful shutdown
because the router will continue to advertise a maximum metric after it is reloaded.
Note
In older OSPF implementations (RFC 1247 and earlier implementations), the router link costs in received
LSAs with a metric of LSInfinity are not used during SPF calculations, which means that no transit traffic
will be sent to the routers that originate these LSAs.
Note
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
124
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
max-metric router-lsa

Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the max-metric
router-lsacommand in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router
configuration command to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example configures a router that is running OSPF to advertise a maximum metric for
100 seconds:
Router(config)# router ospf 100
Router(config-router)# max-metric router-lsa on-startup 100
The following example configures a router to advertise a maximum metric until BGP routing tables
converge or until the default timer expires (600 seconds):
Router(config)# router ospf 100
Router(config-router)# max-metric router-lsa on-startup wait-for-bgp
The following example configures a router that is running OSPF to advertise a maximum metric,
which causes neighbor routers to select alternate paths for transit traffic before the router shuts down:
Router(config)# router ospf 100
Router(config-router)# max-metric router-lsa
Router(config-router)# end
The following example configures stub links to be advertised with the maximum-metric in routers
LSAs.
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# router-id 10.1.1.1
Router(config-router)# max-metric router-lsa include-stub
Router(config-router)# end
Entering the show ip ospf max-metriccommand with the include-stub keyword displays output
that confirms that stub links are advertised with the maximum metric.
Router# show ip ospf max-metric
Routing Process “ospf 1” with ID 10.1.1.1
Start time: 00:00:03.524, Time elapsed: 01:02:28.292
Originating router-LSAs with maximum metric
Condition: always, State: active
Advertise stub links with maximum metric in router-LSAs
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays general information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Displays lists of information related to the OSPF database for a specific router.show ip ospf database
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
125
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
max-metric router-lsa

neighbor (OSPF)
To configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routers interconnecting to nonbroadcast networks, use the
neighbor command in router address family topology or router configuration mode. To remove a configuration,
use the no form of this command.
neighbor ip-address [priority number] [poll-interval seconds] [cost number] [database-filter all]
no neighbor ip-address [priority number] [poll-interval seconds] [cost number] [database-filter
all]
Syntax Description
Interface IP address of the neighbor.ip-address
(Optional) A number that indicates the router priority value of the nonbroadcast
neighbor associated with the IP address specified.The default is 0. This keyword
does not apply to point-to-multipoint interfaces.
priority number
(Optional) A number value that represents the poll interval time (in seconds). RFC
1247 recommends that this value be much larger than the hello interval. The
default is 120 seconds (2 minutes). This keyword does not apply to
point-to-multipoint interfaces. The range is from 0 to 4294967295 seconds.
poll-interval seconds
(Optional) Assigns a cost to the neighbor, in the form of an integer from 1 to
65535. Neighbors with no specific cost configured will assume the cost of the
interface, based on the ip ospf costcommand. For point-to-multipoint interfaces,
the cost keyword and the number argument are the only options that are applicable.
This keyword does not apply to nonbroadcast multiaccess (NBMA) networks.
cost number
(Optional) Filters outgoing link-state advertisements (LSAs) to an OSPF neighbor.database-filter all
Command Default
This command is disabled by default. No configuration is specified.
Command Modes
Router address family topology configuration (config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
The cost keyword was added.11.3AA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family topology configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation Services Routers.15.1(2)SNG
Usage Guidelines
X.25 and Frame Relay provide an optional broadcast capability that can be configured in the map to allow
OSPF to run as a broadcast network. At the OSPF level you can configure the router as a broadcast network.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
126
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
neighbor (OSPF)

Refer to the x25 map and frame-relay map commands in the “X.25 Commands” and “Frame Relay
Commands” chapters, respectively, in the Cisco IOSWide-Area Networking Command Referencefor more
detail.
One neighbor entry must be included in the Cisco IOS software configuration for each known nonbroadcast
network neighbor. The neighbor address must be on the primary address of the interface.
If a neighboring router has become inactive (hello packets have not been received for the Router Dead Interval
period), it may still be necessary to send hello packets to the dead neighbor. These hello packets will be sent
at a reduced rate called Poll Interval.
When the router first starts up, it sends only hello packets to those routers with nonzero priority, that is, routers
that are eligible to become designated routers (DRs) and backup designated routers (BDRs). After the DR
and BDR are selected, DR and BDR will then start sending hello packets to all neighbors in order to form
adjacencies.
You cannot use the neighbor (OSPF) command to specify an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) neighbor on
non-broadcast networks within an OSPF Virtual Private Network (VPN) routing instance.
Note
Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.0, the neighbor command applied to NBMA networks only. With Release
12.0, the neighbor command applies to NBMA networks and point-to-multipoint networks. On NBMA
networks, the cost keyword is not accepted.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the neighborcommand
in router address family topology configuration mode in order for this OSPF router configuration command
to become topology-aware.
Examples
The following example declares a router at address 192.168.3.4 on a nonbroadcast network, with a
priority of 1 and a poll interval of 180 seconds:
router ospf
neighbor 192.168.3.4 priority 1 poll-interval 180
The following example illustrates a point-to-multipoint network with nonbroadcast:
interface Serial0
ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf network point-to-multipoint non-broadcast
encapsulation frame-relay
no keepalive
frame-relay local-dlci 200
frame-relay map ip 10.0.1.3 202
frame-relay map ip 10.0.1.4 203
frame-relay map ip 10.0.1.5 204
no shut
!
router ospf 1
network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
neighbor 10.0.1.3 cost 5
neighbor 10.0.1.4 cost 10
neighbor 10.0.1.5 cost 15
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
127
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
neighbor (OSPF)

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Sets the router priority, which helps determine the designated router for this network.ip ospf priority
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
128
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
neighbor (OSPF)

neighbor database-filter all out
To filter outgoing link-state advertisements (LSAs) to an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) neighbor, use the
neighbor database-filter all outcommand in router configuration mode. To restore the forwarding of LSAs
to the neighbor, use the no form of this command.
neighbor ip-address database-filter allout [cost metric]
no neighbor ip-address database-filter all out
Syntax Description
IP address of the neighbor to which outgoing LSAs are blocked.ip-address
(Optional) Cost metric configured for the specified neighbor. The range of this value is from
0 to 65535.
cost metric
Command Default
This command is disabled by default. All outgoing LSAs are flooded to the neighbor.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
This command performs the same function that the ip ospf database-filter all outcommand performs on an
interface basis.
Examples
The following example prevents flooding of OSPF LSAs to point-to-multipoint networks to the
neighbor at IP address 10.2.3.4:
router ospf 109
neighbor 10.2.3.4 database-filter all out
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Filters outgoing LSAs to an OSPF interface.ip ospf database-filter all out
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
129
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
neighbor database-filter all out

network area
To define the interfaces on which Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) runs and to define the area ID for those
interfaces, use the network area command in router configuration mode. To disable OSPF routing for interfaces
defined with the ip-address wildcard-maskpair, use the no form of this command.
network ip-address wildcard-mask area area-id
no network ip-address wildcard-mask area area-id
Syntax Description
IP address.ip-address
IP-address-type mask that includes “don’t care” bits.wildcard-mask
Area that is to be associated with the OSPF address range. It can be specified as either a
decimal value or as an IP address. If you intend to associate areas with IP subnets, you can
specify a subnet address as the value of the area-id argument.
area-id
Command Default
This command is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation Services Routers.15.2(2)SNI
Usage Guidelines
The ip-address and wildcard-mask arguments together allow you to define one or multiple interfaces to be
associated with a specific OSPF area using a single command. Using the wildcard-mask argument allows you
to define one or multiple interfaces to be associated with a specific OSPF area using a single command. If
you intend to associate areas with IP subnets, you can specify a subnet address as the value of the
area-idargument.
For OSPF to operate on the interface, the primary address of the interface must be covered by the network
areacommand. If the network areacommand covers only the secondary address, it will not enable OSPF
over that interface.
The Cisco IOS software sequentially evaluates the ip-address wildcard-mask pair for each interface as follows:
1. The wildcard-maskargument is logically ORed with the interface IP address.
2. The wildcard-maskargument is logically ORed with the ip-addressargument in the network command.
3. The software compares the two resulting values. If they match, OSPF is enabled on the associated interface
and this interface is attached to the OSPF area specified.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
130
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
network area

There is no limit to the number of network area commands you can use on the router.
Any individual interface can only be attached to a single area. If the address ranges specified for different
areas overlap, the software will adopt the first area in the network command list and ignore the subsequent
overlapping portions. In general, we recommend that you configure address ranges that do not overlap in
order to avoid inadvertent conflicts.
Note
When a more specific OSPF network range is removed, interfaces belonging to that network range will be
retained and remain active if and only if a less specific network range exists.
For example, consider the following configuration:
router ospf 1
network 192.168.129.16 0.0.0.3 area 20
network 192.168.129.40 0.0.0.3 area 20
network 192.168.129.44 0.0.0.3 area 20
network 192.168.129.96 0.0.0.3 area 20
network 192.168.128.0 0.0.127.255 area 20
!
Enter the following:
no network 192.168.129.40 0.0.0.3 area 20
Interfaces falling into the network range 192.168.129.40/0.0.0.3 will still remain active because the superset,
192.168.128.0/0.0.127.255, exists for area 20. A more specific network statement will cause interfaces
belonging to that range to be removed from a different area only if a less specific network statement (superset)
exists.
Consider a configuration such as the following:
!
router ospf 1
network 192.168.128.0 0.0.127.255 area 20
!
If the following network statement is entered:
network 192.168.129.96 0.0.0.3 area 40
then interfaces belonging to range 192.168.129.96/0.0.0.3, if any, are removed from area 20 and moved to
area 40. Network statements with identical ranges but with different area IDs are considered as area changes.
For example, the following network statements will cause interfaces belonging to network range
192.168.129.40/0.0.0.3 to move from area 20 to area 40:
network 192.168.129.40 0.0.0.3 area 20
network 192.168.129.40 0.0.0.3 area 40
Examples
The following partial example initializes OSPF routing process 109, and defines four OSPF areas:
10.9.50.0, 2, 3, and 0. Areas 10.9.50.0, 2, and 3 mask specific address ranges, and area 0 enables
OSPF for all other networks.
interface ethernet 0
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
131
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
network area

ip address 10.108.20.1 255.255.255.0
router ospf 109
network 10.108.20.0 0.0.0.255 area 10.9.50.0
network 10.108.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 2
network 10.109.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures an OSPF routing process.router ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
132
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
network area

nsf (OSPF)
Effective with Cisco IOS Release 12.0(32)S, the nsf (OSPF) command has been replaced by the nsf cisco
command. See the nsf cisco command for more information.
Note
To configure Cisco nonstop forwarding (NSF) operations for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), use the nsf
command in router configuration mode. To disable Cisco NSF for OSPF, use the no form of this command.
nsf [enforce global]
no nsf [enforce global]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Cancels NSF restart when non-NSF-aware neighboring networking devices
are detected.
enforce global
Command Default
This command is disabled by default; therefore, NSF operations for OSPF is not configured.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(22)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)S.12.2(18)S
This command was implemented on the Cisco 7304 router.12.2(20)S
This command was replaced by the nsf cisco command.12.0(32)S
Usage Guidelines
The user must configure NSF operation for OSPF only if a router is expected to perform NSF during restart.
For users to have full NSF benefits, all OSPF neighbors of the specified router must be NSF-aware.
If neighbors that are not NSF-aware are detected on a network interface, NSF restart is terminated on the
interface; however, NSF restart will continue on other interfaces. This functionality applies to the default NSF
mode of operation when NSF is configured.
If the user configures the optional enforceglobalkeywords, NSF restart will be canceled for the entire process
when neighbors that are not NSF-aware are detected on any network interface during restart. NSF restart will
also be canceled for the entire process if a neighbor adjacency reset is detected on any interface or if an OSPF
interface goes down. To revert to the default NSF mode, enter the no nsf enforce global command.
Examples
The following example enters router configuration mode and cancels the NSF restart for the entire
OSPF process if neighbors that are not NSF-aware are detected on any network interface during
restart:
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# nsf cisco enforce global
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
133
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf (OSPF)

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays debugging messages related to OSPF NSF commands.debug ip ospf nsf
Enables OSPF routing and places the router in router configuration mode.router ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
134
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf (OSPF)

nsf cisco
To enable Cisco nonstop forwarding (NSF) operations on a router that is running Open Shortest Path First
(OSPF), use the nsf cisco command in router configuration mode. To return to the default, use the no form
of this command.
nsf cisco [{enforce global | helper [disable]}]
no nsf cisco [{enforce global | helper disable}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Cancels NSF restart on all interfaces when neighboring networking devices
that are not NSF-aware are detected on any interface during the restart process.
enforce global
(Optional) Configures Cisco NSF helper mode.helper
(Optional) Disables helper mode.disable
Command Default
Cisco NSF restarting mode is disabled. Cisco NSF helper mode is enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced. This command replaces the nsf(OSPF) command.12.0(32)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Usage Guidelines
For Cisco IOS Release 12.0(32)S and later releases, this command replaces the nsf (OSPF) command.
This command enables Cisco NSF on an OSPF router. When NSF is enabled on a router, the router is
NSF-capable and will operate in restarting mode.
If a router is expected to cooperate with a neighbor that is doing an NSF graceful restart only, the neighbor
router must be running a Cisco software release that supports NSF but NSF need not be configured on the
router. When a router is running a Cisco software release that supports NSF, the router is NSF-aware.
By default, neighboring NSF-aware routers will operate in NSF helper mode during a graceful restart. To
disable Cisco NSF helper mode on an NSF-aware router, use this command with the disable keyword. To
reenable helper mode after explicitly disabling helper mode on an NSF-aware router, use the no nsf cisco
helper disable command.
If neighbors that are not NSF-aware are detected on a network interface during an NSF graceful restart, restart
is terminated on that interface only and graceful restart will continue on other interfaces. To cancel restart for
the entire OSPF process when neighbors that are not NSF-aware are detected during restart, configure this
command with the enforce global keywords.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
135
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf cisco

The NSF graceful restart will also be canceled for the entire process when a neighbor adjacency reset is
detected on any interface or when an OSPF interface goes down.
Note
Examples
The following example enables Cisco NSF restarting mode on a router and causes the NSF restart
to be canceled for the entire OSPF process if neighbors that are not NSF-aware are detected on any
network interface during the restart.
router ospf 24
nsf cisco enforce global
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables IETF NSF.nsf ietf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
136
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf cisco

nsf cisco helper disable
To disable Cisco nonstop forwarding (NSF) helper mode on a Cisco router that is running Open Shortest Path
First (OSPF), use the nsf cisco helper disablecommand in router configuration mode. To reenable Cisco NSF
helper mode, use the no form of this command.
nsf cisco helper disable
no nsf cisco helper disable
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
This command is enabled by default; therefore, NSF helper mode is disabled on a Cisco router that is running
OSPF.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(32)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(6)T.12.4(6)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6
Usage Guidelines
When a router in an OSPF process has NSF enabled, the router is said to be NSF-capable and will operate in
graceful restart mode--the OSPF router process performs nonstop forwarding recovery due to a Route Processor
(RP) switchover. By default, the neighboring routers of the NSF-capable router will be NSF-aware and will
operate in NSF helper mode. When the NSF-capable router is performing graceful restart, the helper routers
assist in the nonstop forwarding recovery process. If you do not want the router to help the restarting neighbor
with nonstop forwarding recovery, enter the nsf cisco helper disable command.
Examples
The following example disables NSF helper mode for the Cisco router on OSPF process 3:
router ospf 3
nsf cisco helper disable
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables Cisco NSF on a Cisco router.nsf cisco
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
137
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf cisco helper disable

DescriptionCommand
Enables IETF nonstop forwarding operations on a router that is running
OSPF.
nsf ietf
Disables IETF NSF helper mode on a router.nsf ietf helper disable
Enables strict LSA checking on a router.nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
138
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf cisco helper disable

nsf ietf
To configure Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) nonstop forwarding (NSF) operations on a router that
is running Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), use the nsf ietf command in router configuration mode. To return
to the default, use the no form of this command.
nsf ietf [{restart-interval seconds | helper [{disable | strict-lsa-checking}]}]
no nsf ietf [{restart-interval | helper [{disable | strict-lsa-checking}]}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies length of the graceful restart interval, in seconds. The range
is from 1 to 1800. The default is 120.
restart-interval seconds
(Optional) Configures NSF helper mode.helper
(Optional) Disables helper mode on an NSF-aware router.disable
(Optional) Enables strict link-state advertisement (LSA) checking for helper
mode.
strict-lsa-checking
Command Default
IETF NSF graceful restart mode is disabled. IETF NSF helper mode is enabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(32)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Usage Guidelines
This command enables IETF NSF on an OSPF router. When NSF is enabled on a Cisco router, the router is
NSF-capable and will operate in restarting mode.
If a router is expected to cooperate with a neighbor that is doing an NSF graceful restart only, the neighbor
router must be running a Cisco software release that supports NSF but NSF need not be configured on the
router. When a router is running a Cisco software release that supports NSF, the router is NSF-aware.
By default, neighboring NSF-aware routers will operate in NSF helper mode during a graceful restart. To
disable IETF NSF helper mode on an NSF-aware router, use this command with the disable keyword. To
reenable helper mode after explicitly disabling helper mode on an NSF-aware router, use the no nsf ietf
helper disable command.
Strict LSA checking allows a router in IETF NSF helper mode to terminate the graceful restart process if it
detects a changed LSA that would cause flooding during the graceful restart process. You can configure strict
LSA checking on NSF-aware and NSF-capable routers but it is effective only when the router is in helper
mode.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
139
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf ietf

Examples
The following example enables IETF NSF restarting mode on a router and changes the graceful
restart interval from default (120 seconds) to 200 seconds:
router ospf 24
nsf ietf restart-interval 200
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables Cisco NSF.nsf cisco
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
140
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf ietf

nsf ietf helper disable
To disable Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) nonstop forwarding (NSF) helper mode on a router that
is running Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), use the nsf ietf helper disablecommand in router configuration
mode. To reenable IETF NSF helper mode, use the no form of this command.
nsf ietf helper disable
no nsf ietf helper disable
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
This command is disabled by default; therefore, IETF NSF helper mode is enabled on a router that is running
OSPF.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(32)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(6)T.12.4(6)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6
Usage Guidelines
When a router in an OSPF process has NSF enabled, the router is said to be NSF-capable and will operate in
graceful restart mode--the OSPF router process performs nonstop forwarding recovery due to a Route Processor
(RP) switchover. By default, the neighboring routers of the NSF-capable router will be NSF-aware and will
operate in NSF helper mode. When the NSF-capable router is performing graceful restart, the helper routers
assist in the nonstop forwarding recovery process. If you do not want the router to help the restarting neighbor
with nonstop forwarding recovery, enter the nsf ietf helper disable command.
Examples
The following example disables IETF NSF helper mode on a router on OSPF process 4:
router ospf 4
nsf ietf helper disable
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables Cisco NSF on a router.nsf cisco
Disables Cisco NSF helper mode on a router.nsf cisco helper disable
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
141
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf ietf helper disable

DescriptionCommand
Enables IETF nonstop forwarding operations on a router that is running
OSPF.
nsf ietf
Enables strict LSA checking on a router.nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
142
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf ietf helper disable

nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking
To enable strict link-state advertisement (LSA) checking on routers in an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
process, use the nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checkingcommand in router configuration mode. To disable strict
LSA checking, use the no form of this command.
nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking
no nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
This command is disabled by default; therefore, strict LSA checking is not done on routers in an OSPF process.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(32)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(6)T.12.4(6)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6
Usage Guidelines
To enable strict LSA checking on both NSF-aware and NSF-capable routers, enter the nsf ietf helper
strict-lsa-checking command. However, strict LSA checking will not become effective until the router
becomes a helper router during an IETF graceful restart process. With strict LSA checking enabled, the helper
router will terminate the helping process of the restarting router if it detects that there is a change to an LSA
that would be flooded to the restarting router or if there is a changed LSA on the retransmission list of the
restarting router when the graceful restart process is initiated.
Examples
The following example enables strict LSA checking on a router on OSPF process 12:
router ospf 12
nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables Cisco NSF on a router.nsf cisco
Disables Cisco NSF helper mode on a router.nsf cisco helper disable
Enables IETF nonstop forwarding operations on a router that is running OSPF.nsf ietf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
143
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking

DescriptionCommand
Disables IETF NSF helper mode on a router.nsf ietf helper disable
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
144
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsf ietf helper strict-lsa-checking

nsr
To enable nonstop routing (NSR) operations on a router that is running Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), use
the nsrcommand in router configuration mode. To disable NSR and return to the default, use the no form of
this command.
nsr
no nsr
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
NSR is disabled.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(2)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(2)SY.15.1(2)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(1)E.15.2(1)E
Usage Guidelines
This command enables NSR on an OSPF router. With NSR enabled, a router with redundant Route Processors
(RPs) is allowed to maintain its OSPF state and adjacencies across planned and RP switchovers. It does this
by checkpointing state information from OSPF on the active RP to the standby RP. Later, following a switchover
to the standby RP, OSPF can use this checkpointed information to continue operation without interruption.
This command is present only in images for platforms that have a hardware or software redundancy capability.
Examples
The following example enables NSR on an OSPF router:
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# nsr
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays OSPF NSR status information.show ip ospf nsr
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
145
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
nsr

ospfv3 authentication (key-chain)
To specify the cryptographic authentication keys for an Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) instance,
use the ospfv3 authentication command in interface configuration mode. To remove the authentication key
chain, use theno form of this command.
ospfv3 [pid] [ipv4|ipv6] authentication {key-chain chain-name | null}
no ospfv3 [pid] [ipv4|ipv6] authentication {key-chain | null}
Syntax Description
(Optional) Internal identification. The number used here is the number assigned
administratively when enabling the OSPFv3 routing process and can be a value from 1
through 65535.
pid
(Optional) IPv4 address family.ipv4
(Optional) IPv6 address family.ipv6
Enables area authentication.authentication
Configures a key chain for cryptographic authentication keys.key-chain
Name of the authentication key that is valid..chain-name
(Optional) Enables Message Digest 5 (MD5) authentication on the area specified by the
area-id argument.
null
Command Default
No authentication key is specified.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S
Usage Guidelines
Use the ospfv3 authentication command to specify the OSPFv3 authentication key chain on an interface.
The null keyword is used to override less specific authentication.
Examples
The following example specifies the cryptographic authentication key chain for an OSPFv3 instance:
Device(config-if)# ospfv3 1 ipv4 authentication key-chain ospf-1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables authentication trailer for an OSPFv3 area.area authentication (key-chain)
Specifies the authentication mode used in OSPFv3.authentication mode (OSPF)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
146
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ospfv3 authentication (key-chain)

ospfv3 multi-area
To configure multiarea adjacency on an interface that is configured with Open Shortest Path First version 3
(OSPFv3), use the ospfv3 multi-area command in interface configuration mode. To disable multiarea
adjacency, use the no form of this command.
ospfv3 multi-area multi-area-id
no ospfv3 multi-area multi-area-id
Syntax Description
Identifies the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be specified
as an IP address or a decimal value. The decimal value range is from 0 to 4294967295.
multi-area-id
Command Default
No OSPFv3 multiarea adjacency interface is defined.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release
3.11S
Example
The following example shows how to configure OSPFv3 multiarea adjacency on an interface with
an area identifier of 100:
Device# enable
Device(config)# interface serial 2/0
Device(config-if)# ospfv3 multi-area 100
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Specifies the cost of sending a packet on an OSPFv3
multiarea interface.
ospfv3 multi-area cost
Displays the interface information related to OSPFv3.show ospfv3 multi-area
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
147
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ospfv3 multi-area

ospfv3 multi-area cost
To specify the cost of sending a packet on an Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) multiarea interface,
use the ospfv3 multi-area cost command in interface configuration mode. To reset the multiarea path cost
to the default value, use the no form of this command.
ospfv3 multi-area multi-area-id cost interface-cost
no ospfv3 multi-area multi-area-id cost interface-cost
Syntax Description
Identifies the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be specified
as an IP address or a decimal value. The decimal value range is from 0 to 4294967295.
multi-area-id
Specifies the unsigned integer value expressed as the link-state metric. The range is from 1
to 65535.
interface-cost
Command Default
Interface cost of the primary interface is inherited for OSPFv3 multiarea adjacency.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S
Example
The following example shows how to set the OSPFv3 multiarea interface cost value to 512:
Device# enable
Device(config)# interface serial 2/0
Device(config-if)# ospfv3 multi-area 100 cost 512
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables multiarea adjacency on the OSPFv3 interface.ospfv3 multi-area
Displays the interface information related to OSPFv3.show ospfv3 multi-area
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
148
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
ospfv3 multi-area cost

prefix-suppression
To prevent Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) from advertising all IP prefixes except prefixes that are associated
with loopbacks, secondary IP addresses, and passive interfaces for a specific OSPF process, use the
prefix-suppression command in router configuration mode. To advertise all IP prefixes, use the no form of
this command.
prefix-suppression
no prefix-suppression
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
All IP prefixes are advertised.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.4(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6Cisco IOS XE Release 2.6
Usage Guidelines
You can globally suppress all IP prefixes (except prefixes that are associated with loopbacks, secondary IP
addresses, and passive interfaces) for an entire OSPF process by using the prefix-suppression command in
router configuration mode. You can also suppress IP prefixes on a per-interface basis by using the ip ospf
prefix-suppr essioncommand in interface configuration mode. When the ip ospfprefix-suppression command
is configured, it takes precedence over the prefix-suppression router configuration command.
Examples
The following example globally suppresses all IP prefixes except prefixes that are associated with
loopbacks, secondary IP addresses, and passive interfaces for OSPF process 4:
router ospf 4
prefix-suppression
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Prevents OSPF from advertising all IP prefixes that belong to a specific
interface, except for IP prefixes that are associated with secondary IP addresses.
ip ospf prefix-suppression
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
149
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
prefix-suppression

process-min-time percent
Effective with Cisco IOS 15.1(1)T release, the process-min-time percent command is not available in Cisco
IOS 15.1(1)T and later releases. Improvements in Cisco IOS scheduler have made this command unnecessary.
Note
To specify the minimum percentage of CPU process time OSPF takes before the CPU should yield to a process
with a higher priority, use the process-min-time percent command in router configuration mode. To disable
this function, use the no form of this command.
process-min-time percent percentage
no process-min-time percent
Syntax Description
Percentage of CPU process time to be used before trying to release the CPU for other processes.
The valid value range is from 1 to 100. The default is 25.
percentage
Command Default
The default is 25 percent.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced on the Supervisor Engine 720 and the Supervisor Engine 320.12.2(18)SXF
Support for IPv6 was added.12.4(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was removed.15.1(1)T
Usage Guidelines
Use this command under the direction of Cisco TAC only.
Note
This command is supported by OSPFv2 and OSPFv3.
Use the process-min-time percentcommand to configure the minimum percentage of the process maximum
time. Lowering the minimum percentage of CPU usage that a process can utilize is useful in some circumstances
to ensure equitable division of CPU resources among different tasks. Once the percentage has been exceeded,
CPU control may be given to a higher priority process.
The process maximum time is set using the process-max-time command. Use the process-min-time
percentcommand in conjunction with the process-max-time command.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the percentage of CPU process time to be used before
releasing the CPU:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
150
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
process-min-time percent

Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf
Router(config-router)# process-min-time percent 35
The following example shows how to return to the default setting in IPv4:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf
Router(config-router)# no process-min-time percent
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures the amount of time after which a process should voluntarily yield to another
process.
process-max-time
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
151
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
process-min-time percent

redistribute maximum-prefix
To limit the number of prefixes redistributed into Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) or to generate a warning
when the number of prefixes redistributed into OSPF reaches a maximum, use the redistribute
maximum-prefixcommand in router configuration mode. To remove the values, use the no form of this
command.
redistribute maximum-prefix maximum [percentage] [{warning-only | withdraw}]
no redistribute maximum-prefix
Syntax Description
Integer from 1 to 4294967295 that specifies the maximum number of IP prefixes that can
be redistributed into OSPF.
When the warning-onlykeyword is configured, the maximum value specifies the number
of prefixes that can be redistributed into OSPF before the system logs a warning message.
Redistribution is not limited.
The maximum number of IP prefixes that are allowed to be redistributed into OSPF, or the
number of prefixes allowed to be redistributed into OSPF before the system logs a warning
message, depends on whether the warning-onlykeyword is present.
• There is no default value for the maximum argument.
• If the warning-onlykeyword is also configured, this value does not limit redistribution;
it is simply the number of redistributed prefixes that, when reached, causes a warning
message to be logged.
maximum
(Optional) Integer from 1 to 100 that specifies the threshold value, as a percentage, at which
a warning message should be generated.
• The percentage default is 75.
percentage
(Optional) Causes a warning message to be logged when the number of prefixes defined
by the maximumargumenthas been exceeded. Additional redistribution is not prevented.
warning-only
(Optional) Prevents additional redistribution when the number of prefixes defined by the
maximumargumenthas been exceeded.
Also, IS-IS rebuilds link-state PDUs (LSPs) without the external (redistributed) IP prefixes.
withdraw
Command Default
The percentage default is 75.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)S.12.2(18)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
152
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
redistribute maximum-prefix

ModificationRelease
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in
a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and
platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was introduced on Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services
Routers.
Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1
Usage Guidelines
If someone mistakenly injects a large number of IP prefixes into IS-IS, perhaps by redistributing Border
Gateway Protocol (BGP) into IS-IS, the network can be severely flooded. Limiting the number of redistributed
prefixes prevents this potential problem.
When the redistribute maximum-prefix command is configured and the number of redistributed prefixes
reaches the maximum value configured, no more prefixes will be redistributed (unless the warning-only
keyword was configured).
The redistribution limit applies only to external IP prefixes. Default prefixes and summarized prefixes are not
limited.
The limit is tracked separately for each not-so-stubby-area (NSSA) because redistribution to NSSAs is done
independently for each NSSA and independently of all other regular areas.
Select a maximum value based on your knowledge of how many prefixes are redistributed on the router to the
OSPF process.
Examples
Examples for IS-IS Protocol
The following example shows how to set a maximum of 600 prefixes that can be redistributed into
IS-IS. If the number of prefixes redistributed reaches 75 percent of 600 (450 prefixes), a warning
message is logged.
router isis
redistribute maximum-prefix 600
The following example shows how to set a maximum of 1200 prefixes that can be redistributed into
IS-IS. If the number of prefixes redistributed reaches 80 percent of 1200 (960 prefixes), a warning
message is logged.
router isis
redistribute maximum-prefix 1200 80
The following example shows how to allow two warning messages to be logged. The first message
is logged when the number of prefixes redistributed reaches 85 percent of 600 (510 prefixes), and
the second message is logged when the number of redistributed prefixes reaches 600. However, the
number of redistributed prefixes is not limited.
router isis
redistribute maximum-prefix 600 85 warning-only
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
153
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
redistribute maximum-prefix

Examples for OSPF Routing Protocol
The following example shows how to set a maximum of 2000 prefixes that can be redistributed into
OSPF process when the number of prefixes redistributed reaches 75 percent of 2000 (1500 prefixes),
a warning message is logged. Another warning is logged when the limit is reached, and no more
prefixes are redistributed.
router ospf 1
network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
redistribute eigrp 10 subnets
redistribute maximum-prefix 2000
The following example shows how to set a maximum of 1200 prefixes that can be redistributed into
OSPF process when the number of prefixes redistributed reaches 80 percent of 1200 (960 prefixes),
a warning message is logged. Another warning is logged when the limit is reached, and no more
prefixes are redistributed.
router ospf 1
network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
redistribute eigrp 10 subnets
redistribute maximum-prefix 1200 80
The following example shows how to allow two warning messages to be logged. The first message
is logged when the number of prefixes redistributed reaches 85 percent of 600 (510 prefixes), and
the second message is logged when the number of redistributed prefixes reaches 600. However, the
number of redistributed prefixes is not limited.
router ospf 1
network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
redistribute eigrp 10 subnets
redistribute maximum-prefix 600 85 warning-only
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
154
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
redistribute maximum-prefix

router ospf
To configure an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing process, use the router ospf command in global
configuration mode. To terminate an OSPF routing process, use the noform of this command.
router ospf process-id [vrf vrf-name]
no router ospf process-id [vrf vrf-name]
Syntax Description
Internally used identification parameter for an OSPF routing process. It is locally assigned
and can be any positive integer. A unique value is assigned for each OSPF routing process.
process-id
(Optional) Specifies the name of the VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance to associate
with OSPF VRF processes.
vrf vrf-name
Command Default
No OSPF routing process is defined.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
The vrf keyword and vpn-name arguments were added to identify a VPN.12.0(7)T
The vrf keyword and vpn-name arguments were added.12.0(9)ST
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation Services Routers.15.1(2)SNG
Usage Guidelines
You can specify multiple OSPF routing processes in each router.
After you enter the router ospf command, you can enter the maximum number of paths. There can be from
1 to 32 paths.
Examples
The following example configures an OSPF routing process and assign a process number of 109:
Router(config)# router ospf 109
This example shows a basic OSPF configuration using the router ospf command to configure OSPF
VRF instance processes for the VRFs first, second, and third:
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf 12 vrf first
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
155
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
router ospf

Router(config)# router ospf 13 vrf second
Router(config)# router ospf 14 vrf third
Router(config)# exit
The following example shows usage of the maximum-paths option:
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# router ospf
Router(config-router)# maximum-paths?
Router(config-router)# 20
Router(config-router)# exit
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Defines the interfaces on which OSPF runs and defines the area ID for those interfaces.network area
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
156
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
router ospf

router-id
To use a fixed router ID, use the router-id command in router configuration mode. To force Open Shortest
Path First (OSPF) to use the previous OSPF router ID behavior, use the no form of this command.
router-id ip-address
no router-id ip-address
Syntax Description
Router ID in IP address format.ip-address
Command Default
No OSPF routing process is defined.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(1)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
You can configure an arbitrary value in the IP address format for each router. However, each router ID must
be unique.
If this command is used on an OSPF router process which is already active (has neighbors), the new router-ID
is used at the next reload or at a manual OSPF process restart. To manually restart the OSPF process, use the
clear ip ospf command.
Examples
The following example specifies a fixed router-id:
router-id 10.1.1.1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Clears redistribution based on the OSPF routing process ID.clear ip ospf
Configures the OSPF routing process.router ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
157
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
router-id

Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
158
OSPF Commands: ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix through R
router-id

OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
• show ip ospf, on page 161
• show ip ospf border-routers, on page 169
• show ip ospf database, on page 170
• show ip ospf events, on page 180
• show ip ospf fast-reroute, on page 182
• show ip ospf flood-list, on page 185
• show ip ospf interface, on page 187
• show ip ospf max-metric, on page 191
• show ip ospf multi–area, on page 192
• show ip ospf neighbor, on page 194
• show ip ospf nsf, on page 200
• show ip ospf nsr, on page 201
• show ip ospf request-list, on page 202
• show ip ospf retransmission-list, on page 204
• show ip ospf rib, on page 206
• show ip ospf sham-links, on page 208
• show ip ospf statistics, on page 209
• show ip ospf summary-address, on page 212
• show ip ospf timers rate-limit, on page 213
• show ip ospf traffic, on page 214
• show ip ospf virtual-links, on page 219
• show ipv6 ospf, on page 221
• show ipv6 ospf traffic, on page 225
• show ospfv3 multi-area, on page 229
• show ospfv3 sham-links, on page 230
• show tech-support ospf, on page 232
• shutdown (router OSPF), on page 236
• snmp-server enable traps ospf, on page 237
• snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors, on page 239
• snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error, on page 241
• snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink, on page 243
• snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa, on page 245
• snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit, on page 247
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
159

• snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change, on page 249
• snmp-server enable traps ospf errors, on page 251
• snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa, on page 253
• snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit, on page 255
• snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit, on page 257
• snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change, on page 259
• snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 errors, on page 261
• snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 rate-limit, on page 263
• snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 state-change, on page 264
• summary-address (OSPF), on page 266
• timers lsa arrival, on page 268
• timers pacing flood, on page 270
• timers pacing lsa-group, on page 272
• timers pacing retransmission, on page 274
• timers throttle lsa all, on page 276
• timers throttle spf, on page 278
• ttl-security all-interfaces, on page 280
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
160
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T

show ip ospf
To display general information about Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing processes, use the showipospf
command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf [process-id]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Process ID. If this argument is included, only information for the specified routing
process is included.
process-id
Command Modes
User EXEC Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationMainline Release
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
Modification0S Release
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(25)S and the output was
expanded to display link-state advertisement (LSA) throttling timers.
12.0(25)S
Support for the Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) feature was added.12.0(31)S
ModificationS Release
Support for displaying packet pacing timers was added.12.2(14)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SXE and support for the
BFD feature was added.
12.2(18)SXE
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
ModificationT Release
This command was modified to show packet pacing timers in the displayed output.12.2(4)T
This command was modified to show additional information if the OSPF Forwarding
Address Suppression in Type-5 LSAs feature is configured.
12.2(15)T
The output of this command was expanded to display LSA throttling timers and the limit
on redistributed routes.
12.3(2)T
Support for the BFD feature was added.12.4(4)T
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospf command when entered without a specific
OSPF process ID:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
161
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf

Router# show ip ospf
Routing Process "ospf 201" with ID 10.0.0.1 and Domain ID 10.20.0.1
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
SPF schedule delay 5 secs, Hold time between two SPFs 10 secs
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs. Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs
LSA group pacing timer 100 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 55 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 100 msecs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 2. 2 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
External flood list length 0
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
Area has message digest authentication
SPF algorithm executed 4 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 4. Checksum Sum 0x29BEB
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless LSA 3
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
Area 172.16.26.0
Number of interfaces in this area is 0
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm executed 1 times
Area ranges are
192.168.0.0/16 Passive Advertise
Number of LSA 1. Checksum Sum 0x44FD
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless LSA 1
Number of indication LSA 1
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SXE, 12.0(31)S, and 12.4(4)T
The following is sample output from the showipospfcommand to verify that the BFD feature has
been enabled for OSPF process 123. The relevant command output is shown in bold in the output.
Router# show ip ospf
Routing Process "ospf 123" with ID 172.16.10.1
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Incremental-SPF disabled
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
162
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf

Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
External flood list length 0
BFD is enabled
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:00:03.708 ago
SPF algorithm executed 27 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 3. Checksum Sum 0x00AEF1
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 3: show ip ospf Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Process ID and OSPF router ID.Routing process “ospf 201” with ID 10.0.0.1
Number of types of service supported (Type 0 only).Supports...
Delay time (in seconds) of SPF calculations.SPF schedule delay
Minimum interval (in seconds) between link-state
advertisements.
Minimum LSA interval
Configured LSA group pacing timer (in seconds).LSA group pacing timer
Configured LSA flood pacing timer (in milliseconds).Interface flood pacing timer
Configured LSA retransmission pacing timer (in
milliseconds).
Retransmission pacing timer
Number of external link-state advertisements.Number of external LSA
Number of opaque link-state advertisements.Number of opaque AS LSA
Number of demand circuit external and opaque link-state
advertisements.
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS
LSA
Number of do not age external and opaque link-state
advertisements.
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS
LSA
Number of areas configured for the router.Number of areas in this router is
External flood list length.External flood list length
BFD has been enabled on the OSPF process.BFD is enabled
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
163
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf

The following is an excerpt of output from the showipospf command when the OSPF Forwarding
Address Suppression in Type-5 LSAs feature is configured:
Router# show ip ospf
.
.
.
Area 2
Number of interfaces in this area is 4
It is a NSSA area
Perform type-7/type-5 LSA translation, suppress forwarding address
.
.
.
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 192.168.0.1
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Incremental-SPF disabled
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 0. 0 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
External flood list length 0
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 4: show ip ospf Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
OSPF area and tag.Area
Number of interfaces configured in the area.Number of interfaces...
Possible types are internal, area border, or autonomous system
boundary.
It is...
Process ID and OSPF router ID.Routing process “ospf 1” with ID
192.168.0.1
Number of types of service supported (Type 0 only).Supports...
Delay time of SPF calculations at startup.Initial SPF schedule delay
Minimum hold time (in milliseconds) between consecutive SPF
calculations.
Minimum hold time
Maximum wait time (in milliseconds) between consecutive SPF
calculations.
Maximum wait time
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
164
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf

DescriptionField
Status of incremental SPF calculations.Incremental-SPF
Minimum time interval (in seconds) between link-state
advertisements, and minimum arrival time (in milliseconds) of
link-state advertisements,
Minimum LSA...
Configured LSA group pacing timer (in seconds).LSA group pacing timer
Configured LSA flood pacing timer (in milliseconds).Interface flood pacing timer
Configured LSA retransmission pacing timer (in milliseconds).Retransmission pacing timer
Number and type of link-state advertisements that have been
received.
Number of...
Number of external link-state advertisements.Number of external LSA
Number of opaque link-state advertisements.Number of opaque AS LSA
Number of demand circuit external and opaque link-state
advertisements.
Number of DCbitless external and opaque
AS LSA
Number of do not age external and opaque link-state
advertisements.
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque
AS LSA
Number of areas configured for the router listed by type.Number of areas in this router is
External flood list length.External flood list length
The following is sample output from the showipospf command. In this example, the user had
configured the redistributionmaximum-prefix command to set a limit of 2000 redistributed routes.
SPF throttling was configured with the timersthrottlespf command.
Router# show ip ospf 1
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 10.0.0.1
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
It is an autonomous system boundary router
Redistributing External Routes from,
static, includes subnets in redistribution
Maximum limit of redistributed prefixes 2000
Threshold for warning message 75%
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 5: show ip ospf Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Process ID and OSPF router ID.Routing process “ospf 1” with ID
10.0.0.1
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
165
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf
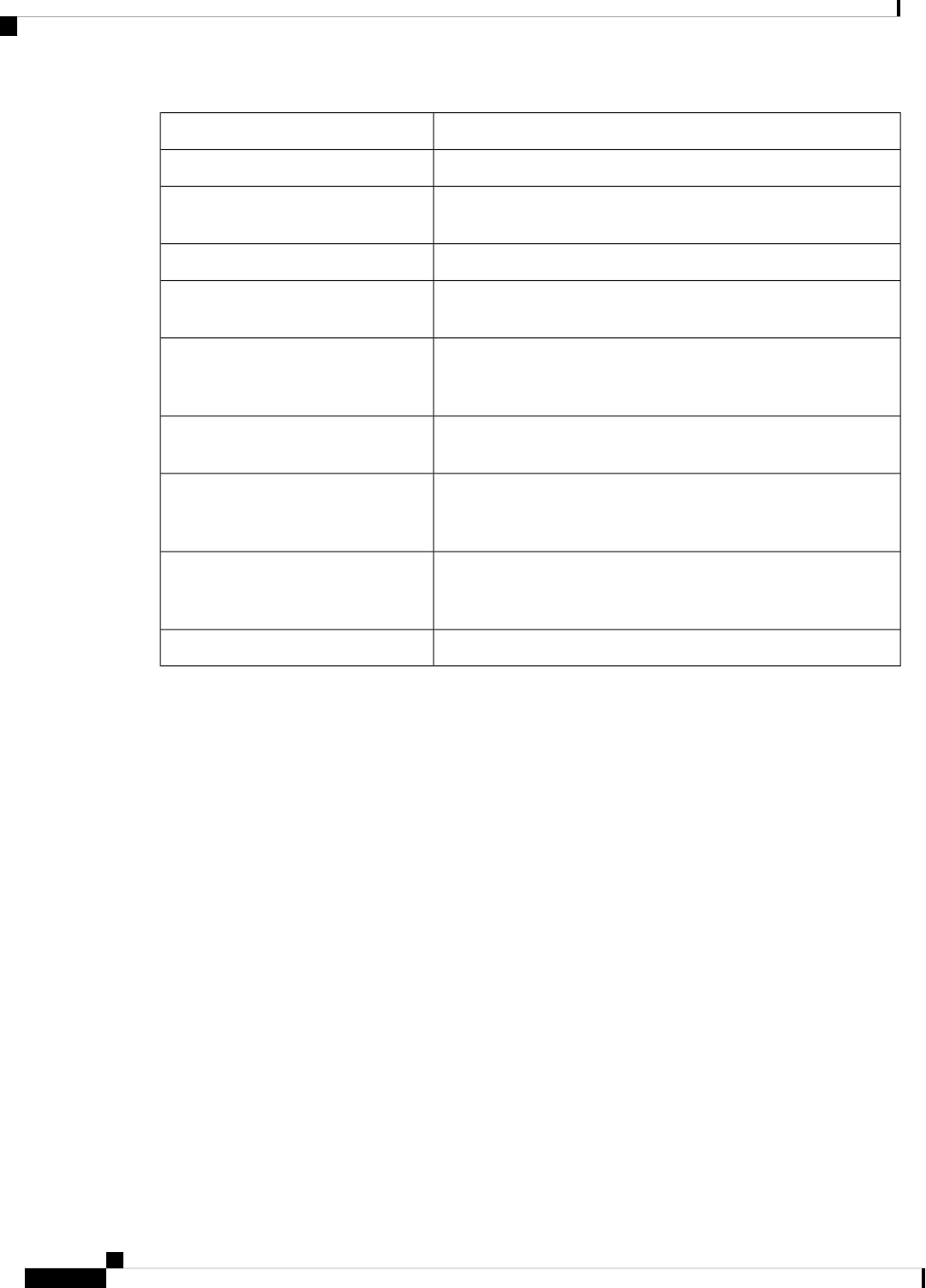
DescriptionField
Number of Types of Service supported.Supports ...
Possible types are internal, area border, or autonomous system
boundary router.
It is ...
Lists of redistributed routes, by protocol.Redistributing External Routes from
Value set in the redistributionmaximum-prefix command to set
a limit on the number of redistributed routes.
Maximum limit of redistributed
prefixes
Percentage set in the redistributionmaximum-prefix command
for the threshold number of redistributed routes needed to cause a
warning message. The default is 75 percent of the maximum limit.
Threshold for warning message
Delay (in milliseconds) before initial SPF schedule for SPF throttling.
Configured with the timersthrottlespf command.
Initial SPF schedule delay
Minimum hold time (in milliseconds) between two consecutive SPF
calculations for SPF throttling. Configured with the
timersthrottlespf command.
Minimum hold time between two
consecutive SPFs
Maximum wait time (in milliseconds) between two consecutive SPF
calculations for SPF throttling. Configured with the
timersthrottlespf command.
Maximum wait time between two
consecutive SPFs
Number of areas in router, area addresses, and so on.Number of areas
The following is sample output from the showipospf command. In this example, the user had
configured LSA throttling, and those lines of output are displayed in bold.
Router# show ip ospf 1
Routing Process "ospf 4" with ID 10.10.24.4
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Incremental-SPF disabled
Initial LSA throttle delay 100 msecs
Minimum hold time for LSA throttle 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time for LSA throttle 45000 msecs
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
External flood list length 0
Area 24
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
Area has no authentication
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
166
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf

SPF algorithm last executed 04:28:18.396 ago
SPF algorithm executed 8 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 4. Checksum Sum 0x23EB9
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
The following is sample showipospfcommand. In this example, the user had configured the
redistributionmaximum-prefix command to set a limit of 2000 redistributed routes. SPF throttling
was configured with the timersthrottlespf command.
Router# show ip ospf 1
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 192.168.0.0
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
It is an autonomous system boundary router
Redistributing External Routes from,
static, includes subnets in redistribution
Maximum limit of redistributed prefixes 2000
Threshold for warning message 75%
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 6: show ip ospf Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Process ID and OSPF router ID.Routing process “ospf 1” with ID
192.168.0.0.
Number of TOS supported.Supports ...
Possible types are internal, area border, or autonomous system
boundary routers.
It is ...
Lists of redistributed routes, by protocol.Redistributing External Routes from
Value set in the redistributionmaximum-prefix command to set
a limit on the number of redistributed routes.
Maximum limit of redistributed prefixes
Percentage set in the redistributionmaximum-prefix command
for the threshold number of redistributed routes needed to cause a
warning message. The default is 75 percent of the maximum limit.
Threshold for warning message
Delay (in milliseconds) before the initial SPF schedule for SPF
throttling. Configured with the timersthrottlespf command.
Initial SPF schedule delay
Minimum hold time (in milliseconds) between two consecutive SPF
calculations for SPF throttling. Configured with the
timersthrottlespf command.
Minimum hold time between two
consecutive SPFs
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
167
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf

DescriptionField
Maximum wait time (in milliseconds) between two consecutive SPF
calculations for SPF throttling. Configured with the
timersthrottlespf command.
Maximum wait time between two
consecutive SPFs
Number of areas in router, area addresses, and so on.Number of areas
The following is sample output from the showipospf command. In this example, the user had
configured LSA throttling, and those lines of output are displayed in bold.
Router# show ip ospf 1
Routing Process "ospf 4" with ID 10.10.24.4
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Incremental-SPF disabled
Initial LSA throttle delay 100 msecs
Minimum hold time for LSA throttle 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time for LSA throttle 45000 msecs
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
External flood list length 0
Area 24
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 04:28:18.396 ago
SPF algorithm executed 8 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 4. Checksum Sum 0x23EB9
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
168
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf

show ip ospf border-routers
To display the internal Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing table entries to an Area Border Router (ABR)
and Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR), use the sho wipospfborder-routers command in privileged
EXEC mode.
show ip ospf border-routers
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospfborder-routers command:
Router# show ip ospf border-routers
OSPF Process 109 internal Routing Table
Codes: i - Intra-area route, I - Inter-area route
i 192.168.97.53 [10] via 172.16.1.53, Serial0, ABR, Area 0.0.0.3, SPF 3
i 192.168.103.51 [10] via 192.168.96.51, Serial0, ABR, Area 0.0.0.3, SPF 3
I 192.168.103.52 [22] via 192.168.96.51, Serial0, ASBR, Area 0.0.0.3, SPF 3
I 192.168.103.52 [22] via 172.16.1.53, Serial0, ASBR, Area 0.0.0.3, SPF 3
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 7: show ip ospf border-routers Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Router ID of the destination.192.168.97.53
Cost of using this route.[10]
Next hop toward the destination.via 172.16.1.53
Interface type for the outgoing interface.Serial0
The router type of the destination; it is either an ABR or ASBR or both.ABR
The area ID of the area from which this route is learned.Area
The internal number of the shortest path first (SPF) calculation that installs this route.SPF 3
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
169
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf border-routers

show ip ospf database
To display lists of information related to the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) database for a specific router,
use the showipospfdatabase command in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [adv-router [ip-address]]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [asbr-summary] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [asbr-summary] [link-state-id] [adv-router [ip-address]]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [asbr-summary] [link-state-id] [self-originate]
[link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [database-summary]
show ip ospf [process-id] database [external] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id] database [external] [link-state-id] [adv-router [ip-address]]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [external] [link-state-id] [self-originate] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [network] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [network] [link-state-id] [adv-router [ip-address]]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [network] [link-state-id] [self-originate] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [nssa-external] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [nssa-external] [link-state-id] [adv-router [ip-address]]
show ip ospf [pr ocess-id area-id] database [nssa-external] [link-state-id] [self-originate] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [router] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [router] [adv-router [ip-address]]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [router] [self-originate] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [self-originate] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [summary] [link-state-id]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [summary] [link-state-id] [adv-router [ip-address]]
show ip ospf [process-id area-id] database [summary] [link-state-id] [self-originate] [link-state-id]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Internal identification. It is locally assigned and can be any positive
integer. The number used here is the number assigned administratively when
enabling the OSPF routing process.
process-id
(Optional) Area number associated with the OSPF address range defined in the
network router configuration command used to define the particular area.
area-id
(Optional) Displays all the LSAs of the specified router. If no IP address is included,
the information is about the local router itself (in this case, the same as
self-originate).
adv-router [ip-address
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
170
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

(Optional) Portion of the Internet environment that is being described by the
advertisement. The value entered depends on the advertisement’s LS type. It must
be entered in the form of an IP address.
When the link state advertisement is describing a network, the link-state-id can
take one of two forms:
The network’s IP address (as in type 3 summary link advertisements and in
autonomous system external link advertisements).
A derived address obtained from the link state ID. (Note that masking a network
links advertisement’s link state ID with the network’s subnet mask yields the
network’s IP address.)
When the link state advertisement is describing a router, the link state ID is always
the described router’s OSPF router ID.
When an autonomous system external advertisement (LS Type = 5) is describing
a default route, its link state ID is set to Default Destination (0.0.0.0).
link-state-id
(Optional) Displays information only about the autonomous system boundary
router summary LSAs.
asbr-summary
(Optional) Displays how many of each type of LSA for each area there are in the
database, and the total.
database-summary
(Optional) Displays information only about the external LSAs.external
(Optional) Displays information only about the network LSAs.network
(Optional) Displays information only about the NSSA external LSAs.nssa-external
(Optional) Displays information only about the router LSAs.router
(Optional) Displays only self-originated LSAs (from the local router).self-originate
(Optional) Displays information only about the summary LSAs.summary
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
The database-summary keyword was added.11.0
The following keywords were added:
• self-originate
• adv-router
12.0
The output of the showipospfdatabasedatabase-summarycommand was increased to include
Self-originated Type-7 and Self-originated Type-5 output.
12.0(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
171
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

ModificationRelease
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
The various forms of this command deliver information about different OSPF link state advertisements.
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospfdatabase command when no arguments or
keywords are used:
Router# show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with id(192.168.239.66) (Process ID 300)
Displaying Router Link States(Area 0.0.0.0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
172.16.21.6 172.16.21.6 1731 0x80002CFB 0x69BC 8
172.16.21.5 172.16.21.5 1112 0x800009D2 0xA2B8 5
172.16.1.2 172.16.1.2 1662 0x80000A98 0x4CB6 9
172.16.1.1 172.16.1.1 1115 0x800009B6 0x5F2C 1
172.16.1.5 172.16.1.5 1691 0x80002BC 0x2A1A 5
172.16.65.6 172.16.65.6 1395 0x80001947 0xEEE1 4
172.16.241.5 172.16.241.5 1161 0x8000007C 0x7C70 1
172.16.27.6 172.16.27.6 1723 0x80000548 0x8641 4
172.16.70.6 172.16.70.6 1485 0x80000B97 0xEB84 6
Displaying Net Link States(Area 0.0.0.0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
172.16.1.3 192.168.239.66 1245 0x800000EC 0x82E
Displaying Summary Net Link States(Area 0.0.0.0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
172.16.240.0 172.16.241.5 1152 0x80000077 0x7A05
172.16.241.0 172.16.241.5 1152 0x80000070 0xAEB7
172.16.244.0 172.16.241.5 1152 0x80000071 0x95CB
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 8: show ip ospf Database Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Router ID number.Link ID
Advertising router’s ID.ADV Router
Link state age.Age
Link state sequence number (detects old or duplicate link state advertisements).Seq#
Fletcher checksum of the complete contents of the link state advertisement.Checksum
Number of interfaces detected for router.Link count
The following is sample output from the showipospfdatabasecommand with the
asbr-summarykeyword:
Router# show ip ospf database asbr-summary
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
172
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

OSPF Router with id(192.168.239.66) (Process ID 300)
Displaying Summary ASB Link States(Area 0.0.0.0)
LS age: 1463
Options: (No TOS-capability)
LS Type: Summary Links(AS Boundary Router)
Link State ID: 172.16.245.1 (AS Boundary Router address)
Advertising Router: 172.16.241.5
LS Seq Number: 80000072
Checksum: 0x3548
Length: 28
Network Mask: 0.0.0.0 TOS: 0 Metric: 1
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 9: show ip ospf database asbr-summary Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Router ID number.OSPF Router with id
OSPF process ID.Process ID
Link state age.LS age
Type of service options (Type 0 only).Options
Link state type.LS Type
Link state ID (autonomous system boundary router).Link State ID
Advertising router’s ID.Advertising Router
Link state sequence (detects old or duplicate link state advertisements).LS Seq Number
LS checksum (Fletcher checksum of the complete contents of the link state
advertisement).
Checksum
Length in bytes of the link state advertisement.Length
Network mask implemented.Network Mask
Type of service.TOS
Link state metric.Metric
The following is sample output from the showipospfdatabasecommand with the externalkeyword:
Router# show ip ospf database external
OSPF Router with id(192.168.239.66) (Autonomous system 300)
Displaying AS External Link States
LS age: 280
Options: (No TOS-capability)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 10.105.0.0 (External Network Number)
Advertising Router: 172.16.70.6
LS Seq Number: 80000AFD
Checksum: 0xC3A
Length: 36
Network Mask: 255.255.0.0
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
173
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
TOS: 0
Metric: 1
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 0
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 10: show ip ospf database external Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Router ID number.OSPF Router with id
OSPF autonomous system number (OSPF process ID).Autonomous system
Link state age.LS age
Type of service options (Type 0 only).Options
Link state type.LS Type
Link state ID (external network number).Link State ID
Advertising router’s ID.Advertising Router
Link state sequence number (detects old or duplicate link state advertisements).LS Seq Number
LS checksum (Fletcher checksum of the complete contents of the LSA).Checksum
Length in bytes of the link state advertisement.Length
Network mask implemented.Network Mask
External Type.Metric Type
Type of service.TOS
Link state metric.Metric
Forwarding address. Data traffic for the advertised destination will be forwarded to
this address. If the forwarding address is set to 0.0.0.0, data traffic will be forwarded
instead to the advertisement’s originator.
Forward Address
External route tag, a 32-bit field attached to each external route. This is not used by
the OSPF protocol itself.
External Route Tag
The following is sample output from the showipospfdatabasecommand with the networkkeyword:
Router# show ip ospf database network
OSPF Router with id(192.168.239.66) (Process ID 300)
Displaying Net Link States(Area 0.0.0.0)
LS age: 1367
Options: (No TOS-capability)
LS Type: Network Links
Link State ID: 172.16.1.3 (address of Designated Router)
Advertising Router: 192.168.239.66
LS Seq Number: 800000E7
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
174
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

Checksum: 0x1229
Length: 52
Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Attached Router: 192.168.239.66
Attached Router: 172.16.241.5
Attached Router: 172.16.1.1
Attached Router: 172.16.54.5
Attached Router: 172.16.1.5
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 11: show ip ospf database network Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Router ID number.OSPF Router with id
OSPF process ID.Process ID 300
Link state age.LS age
Type of service options (Type 0 only).Options
Link state type.LS Type:
Link state ID of designated router.Link State ID
Advertising router’s ID.Advertising Router
Link state sequence (detects old or duplicate link state advertisements).LS Seq Number
LS checksum (Fletcher checksum of the complete contents of the link state
advertisement).
Checksum
Length in bytes of the link state advertisement.Length
Network mask implemented.Network Mask
Definition of router type.AS Boundary Router
List of routers attached to the network, by IP address.Attached Router
The following is sample output from the showipospfdatabasecommand with the routerkeyword:
Router# show ip ospf database router
OSPF Router with id(192.168.239.66) (Process ID 300)
Displaying Router Link States(Area 0.0.0.0)
LS age: 1176
Options: (No TOS-capability)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 172.16.21.6
Advertising Router: 172.16.21.6
LS Seq Number: 80002CF6
Checksum: 0x73B7
Length: 120
AS Boundary Router
155 Number of Links: 8
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 172.16.21.5
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
175
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

(Link Data) Router Interface address: 172.16.21.6
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 2
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 12: show ip ospf database router Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Router ID number.OSPF Router with id
OSPF process ID.Process ID
Link state age.LS age
Type of service options (Type 0 only).Options
Link state type.LS Type
Link state ID.Link State ID
Advertising router’s ID.Advertising Router
Link state sequence (detects old or duplicate link state advertisements).LS Seq Number
LS checksum (Fletcher checksum of the complete contents of the link state
advertisement).
Checksum
Length in bytes of the link state advertisement.Length
Definition of router type.AS Boundary Router
Number of active links.Number of Links
Link type.link ID
Router interface address.Link Data
Type of service metric (Type 0 only).TOS
The following is sample output from showipospfdatabasecommand with the summarykeyword:
Router# show ip ospf database summary
OSPF Router with id(192.168.239.66) (Process ID 300)
Displaying Summary Net Link States(Area 0.0.0.0)
LS age: 1401
Options: (No TOS-capability)
LS Type: Summary Links(Network)
Link State ID: 172.16.240.0 (summary Network Number)
Advertising Router: 172.16.241.5
LS Seq Number: 80000072
Checksum: 0x84FF
Length: 28
Network Mask: 255.255.255.0 TOS: 0 Metric: 1
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
176
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

Table 13: show ip ospf database summary Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Router ID number.OSPF Router with id
OSPF process ID.Process ID
Link state age.LS age
Type of service options (Type 0 only).Options
Link state type.LS Type
Link state ID (summary network number).Link State ID
Advertising router’s ID.Advertising Router
Link state sequence (detects old or duplicate link state advertisements).LS Seq Number
LS checksum (Fletcher checksum of the complete contents of the link state
advertisement).
Checksum
Length in bytes of the link state advertisement.Length
Network mask implemented.Network Mask
Type of service.TOS
Link state metric.Metric
The following is sample output from showipospfdatabasecommand with the
database-summarykeyword:
Router# show ip ospf database database-summary
OSPF Router with ID (10.0.0.1) (Process ID 1)
Area 0 database summary
LSA Type Count Delete Maxage
Router 3 0 0
Network 0 0 0
Summary Net 0 0 0
Summary ASBR 0 0 0
Type-7 Ext 0 0 0
Self-originated Type-7 0
Opaque Link 0 0 0
Opaque Area 0 0 0
Subtotal 3 0 0
Process 1 database summary
LSA Type Count Delete Maxage
Router 3 0 0
Network 0 0 0
Summary Net 0 0 0
Summary ASBR 0 0 0
Type-7 Ext 0 0 0
Opaque Link 0 0 0
Opaque Area 0 0 0
Type-5 Ext 0 0 0
Self-originated Type-5 200
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
177
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

Opaque AS 0 0 0
Total 203 0 0
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 14: show ip ospf database database-summary Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Area number.Area 0 database summary
Count of LSAs of the type identified in the first column.Count
Number of router link state advertisements in that area.Router
Number of network link state advertisements in that area.Network
Number of summary link state advertisements in that area.Summary Net
Number of summary autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) link state
advertisements in that area.
Summary ASBR
Type-7 LSA count.Type-7 Ext
Self-originated Type-7 LSA.Self-originated Type-7
Type-9 LSA count.Opaque Link
Type-10 LSA countOpaque Area
Sum of LSAs for that area.Subtotal
Number of link state advertisements that are marked “Deleted” in that area.Delete
Number of link state advertisements that are marked “Maxaged” in that area.Maxage
Database summary for the process.Process 1 database summary
Count of LSAs of the type identified in the first column.Count
Number of router link state advertisements in that process.Router
Number of network link state advertisements in that process.Network
Number of summary link state advertisements in that process.Summary Net
Number of summary autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) link state
advertisements in that process.
Summary ASBR
Type-7 LSA count.Type-7 Ext
Type-9 LSA count.Opaque Link
Type-10 LSA count.Opaque Area
Type-5 LSA count.Type-5 Ext
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
178
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

DescriptionField
Self-originated Type-5 LSA count.Self-Originated Type-5
Type-11 LSA count.Opaque AS
Sum of LSAs for that process.Total
Number of link state advertisements that are marked “Deleted” in that process.Delete
Number of link state advertisements that are marked “Maxaged” in that process.Maxage
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
179
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf database

show ip ospf events
To display the IP Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) events information, use the show ip ospf events command
in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf events [generic] [interface] [lsa] [neighbor] [reverse] [rib] [spf]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Displays the generic event information.generic
(Optional) Displays the interface state change event information.interface
(Optional) Displays the OSPF Link State Advertisements (LSA) arrival and LSA generation event
information.
lsa
(Optional) Displays the neighbor state change event information.neighbor
(Optional) Displays the events in reverse order.reverse
(Optional) Displays the Routing Information Base (RIB) update, delete, and redistribution event
information.
rib
(Optional) Displays the Shortest Path First (SPF) scheduling and SPF run information.spf
Command Modes
User EXEC (>) Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced in a release earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.3(33)SRC.12.3(33)SRC
This command was integrated into a release earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.3(33)SRD.12.3(33)SRD
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1.Cisco IOS XE 2.1
Examples
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf ev entscommand. The fields are self-explanatory.
Router# show ip ospf events
OSPF Router with ID (4.4.4.4) (Process ID 1)
1 Jan 22 01:51:03.090: DB free: 1.1.1.10x6CF250 103
2 Jan 22 01:51:03.090: delete MAXAGE lsa: 0x666CF2500x666CF250
3 Jan 22 01:50:56.086: DB free: 1.1.1.10x6025D4 103
4 Jan 22 01:50:56.086: DB free: 1.1.1.10x6D59A0 103
5 Jan 22 01:50:56.082: Insert MAXAGE lsa: 0x666D59A01.1.1.1
6 Jan 22 01:50:55.590: Timer Exp: if_ack_delayed0x64782774
7 Jan 22 01:50:55.590: Timer Exp: if_ack_delayed0x64786CB4
8 Jan 22 01:50:55.586: Timer Exp: if_ack_delayed0x647CD1A8
9 Jan 22 01:50:55.586: Timer Exp: if_ack_delayed0x647C8134
10 Jan 22 01:50:53.586: Insert MAXAGE lsa: 0x666025D41.1.1.1
11 Jan 22 01:50:53.586: Rcv Changed Type-3 LSA, LSID 1.1.1.1, Adv-Rtr 3.3.3.3, Seq#
80000002, Age 3600, Area 1
12 Jan 22 01:50:53.586: Insert MAXAGE lsa: 0x666D59A01.1.1.1
13 Jan 22 01:50:53.586: Generate Changed Type-3 LSA, LSID 1.1.1.1, Seq# 80000002, Age
3600, Area 0
14 Jan 22 01:50:53.290: End of SPF, Topo Base, SPF time 4ms, next wait-interval 200ms
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
180
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf events

15 Jan 22 01:50:53.290: Generic: ospf_external_route_sync0x1
16 Jan 22 01:50:53.290: Generic: ospf_external_route_sync0x0
17 Jan 22 01:50:53.290: Generic: ospf_external_route_sync0x0
18 Jan 22 01:50:53.290: Starting External processing, Topo Base in area 1
19 Jan 22 01:50:53.290: Starting External processing, Topo Base in area 0
20 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Starting External processing, Topo Base
21 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Generic: ospf_inter_route_sync0x0
22 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Starting summary processing, Topo Base, Area 0
23 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Generic: ospf_inter_route_sync0x1
24 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Generic: post_spf_intra0x0
25 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Generic: ospf_intra_route_sync0x1
26 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Generic: update_rtr_route0x1
27 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Generic: update_rtr_route0x1
28 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Generic: update_rtr_route0x1
29 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Starting Intra-Area SPF, Topo Base, Area 1, spf_type Full
30 Jan 22 01:50:53.286: Starting SPF, Topo Base, wait-interval 200ms
31 Jan 22 01:50:53.118: Rcv New Type-3 LSA, LSID 1.1.1.1, Adv-Rtr 3.3.3.3, Seq# 80000001,
Age 1, Area 1
32 Jan 22 01:50:53.118: DB add: 1.1.1.10x6025D4 103
33 Jan 22 01:50:53.090: Insert MAXAGE lsa: 0x666CF2501.1.1.1
34 Jan 22 01:50:53.090: Rcv Changed Type-3 LSA, LSID 1.1.1.1, Adv-Rtr 3.3.3.3, Seq#
80000002, Age 3600, Area 0
35 Jan 22 01:50:53.086: Rcv Changed Type-1 LSA, LSID 1.1.1.1, Adv-Rtr 1.1.1.1, Seq#
80000008, Age 2, Area 1
36 Jan 22 01:50:53.086: Schedule SPF, Topo Base, Area 1, spf-type Full, Change in LSA
Type R, LSID 1.1.1.1, Adv-Rtr 1.1.1.1
37 Jan 22 01:50:46.310: Timer Exp: exfaddr0x0
38 Jan 22 01:50:16.310: Timer Exp: exfaddr0x0
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
181
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf events

show ip ospf fast-reroute
To display information for an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) per-prefix loop-free alternate (LFA) fast reroute
(FRR) configuration, use the show ip ospf fast-reroute command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf [{process-id}] fast-reroute [{prefix-summary | remote-lfa tunnels}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Internal identification. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer.
The number used here is the number assigned administratively when enabling the OSPF
routing process.
process-id
(Optional) Displays information about prefixes protected by LFA FRR repair paths.prefix-summary
(Optional) Displays information about tunnel interfaces created by remote LFA FRR.remote-lfa tunnels
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(3)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S
This command was modified. The remote-lfa tunnels keyword was added.15.2(2)S
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation
Services Routers.
15.2(2)SNI
Usage Guidelines
Use the show ip ospf fast-reroute command to display information on the current tiebreaker policy. Use the
prefix-summary keyword to display the number of prefixes per area, per priority, and how many that, in
absolute numbers and in percentages, have repair paths.
Use the remote-lfa tunnels keyword to display information about tunnel interfaces created by remote LFA
FRR using the fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa tunnel command.
Examples
The following example displays summary information about LFA FRR status, including the current
tiebreaker policy:
Router# show ip ospf fast-reroute
OSPF Router with ID (192.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Loop-free Fast Reroute protected prefixes:
Area Topology name Priority
1 Base Low
172.69.69.66 Base High
AS external Base Low
Repair path selection policy tiebreaks:
23 srlg
34 lowest-metric
67 primary-path (required)
256 load-sharing
Last SPF calculation started 00:00:11 ago and was running for 20 ms.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
182
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf fast-reroute

The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 15: show ip ospf fast-reroute Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Priority assigned to the protected prefix.Priority
Tiebreaking policy attributes and their priority-index assignments.Repair path selection policy tiebreaks
The following example displays information about prefixes that are protected by the OSPFv2 loop-free
alternate FRR feature. It displays information on the number of prefixes by area and by priority (high
or low) and how many are protected, that is, have repair paths configured.
Router# show ip ospf fast-reroute prefix-summary
OSPF Router with ID (192.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
Area 0:
Interface Protected Primary paths Protected paths Percent protected
All High Low All High Low All High Low
Loopback0 Yes 0 0 0 0 0 0 0% 0% 0%
Ethernet0/3 Yes 1 1 0 0 0 0 0% 0% 0%
Ethernet0/2 Yes 3 2 1 2 1 1 66% 50% 100%
Ethernet0/1 Yes 2 1 1 2 1 1 100% 100% 100%
Ethernet0/0 Yes 4 2 2 4 2 2 100% 100% 100%
Area total: 10 6 4 8 4 4 80% 66% 100%
Process total: 10 6 4 8 4 4 80% 66% 100%
The following example displays information about tunnel interfaces created by remote LFA FRR:
Router# show ip ospf fast-reroute remote-lfa tunnels
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Area with ID (0)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
Interface MPLS-Remote-Lfa3
Tunnel type: MPLS-LDP
Tailend router ID: 192.168.3.3
Termination IP address: 192.168.3.3
Outgoing interface: Ethernet0/0
First hop gateway: 192.168.14.4
Tunnel metric: 20
Protects:
192.168.12.2 Ethernet0/1, total metric 30
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays debugging information for per-prefix LFA FRR paths.debug ip ospf fast-reroute
Keeps a list of all the candidate repair paths that were considered
when a per-prefix LFA FRR path was computed.
fast-reroute keep-all-paths
Configures a per-prefix LFA FRR path that redirects traffic to an
alternative next hop other than the primary neighbor.
fast-reroute per-prefix (OSPF)
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
183
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf fast-reroute

DescriptionCommand
Configures the maximum distance to the tunnel endpoint.fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa
maximum-cost
Configures a per-prefix LFA FRR path that redirects traffic to a
remote LFA.
fast-reroute per-prefix remote-lfa
tunnel
Configures the LFA FRR tiebreaking priority.fast-reroute tie-break (OSPF)
Configures an interface as either protecting or protected.ip ospf fast-reroute per-prefix
Configures a set of prefixes to have high priority for protection
in an OSPF local RIB.
prefix-priority
Displays OSPF neighbor information on a per-interface basis.show ip ospf neighbor
Displays information for the OSPF local RIB or locally
redistributed routes.
show ip ospf rib
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
184
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf fast-reroute

show ip ospf flood-list
To display a list of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) link-state advertisements (LSAs) waiting to be flooded
over an interface, use the showipospfflood-listcommand in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf flood-list commandshow ip ospf flood-list interface-type interface-number
Syntax Description
Interface type over which the LSAs will be flooded.interface-type
Interface number over which the LSAs will be flooded.interface-number
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(1)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to observe OSPF packet pacing.
Examples
The following is sample output of the showipospfflood-list command:
Router# show ip ospf flood-list ethernet 1
Interface Ethernet1, Queue length 20
Link state flooding due in 12 msec
Type LS ID ADV RTR Seq NO Age Checksum
5 10.2.195.0 192.168.0.163 0x80000009 0 0xFB61
5 10.1.192.0 192.168.0.163 0x80000009 0 0x2938
5 10.2.194.0 192.168.0.163 0x80000009 0 0x757
5 10.1.193.0 192.168.0.163 0x80000009 0 0x1E42
5 10.2.193.0 192.168.0.163 0x80000009 0 0x124D
5 10.1.194.0 192.168.0.163 0x80000009 0 0x134C
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 16: show ip ospf flood-list Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Interface for which information is displayed.Interface Ethernet1
Number of LSAs waiting to be flooded.Queue length
Length of time before next link-state transmission.Link state flooding due in
Type of LSA.Type
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
185
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf flood-list

DescriptionField
Link-state ID of the LSA.LS ID
IP address of advertising router.ADV RTR
Sequence number of LSA.Seq NO
Age of LSA (in seconds).Age
Checksum of LSA.Checksum
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
186
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf flood-list

show ip ospf interface
To display interface information related to Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), use the show ip ospf interface
command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip [ospf] [process-id] interface [type number] [brief] [multicast] [topology {topology-name
| base}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Process ID number. If this argument is included, only information for
the specified routing process is included. The range is 1 to 65535.
process-id
(Optional) Interface type. If the type argument is included, only information for
the specified interface type is included.
type
(Optional) Interface number. If the number argument is included, only information
for the specified interface number is included.
number
(Optional) Displays brief overview information for OSPF interfaces, states,
addresses and masks, and areas on the device.
brief
(Optional) Displays multicast information.multicast
(Optional) Displays OSPF-related information about the named topology instance.topology topology-name
(Optional) Displays OSPF-related information about the base topology.topology base
Command Modes
User EXEC (>)
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was modified. The brief keyword was added.12.0(25)S
This command was modified. The brief keyword was added.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
The multicast, topology, base, and topology-name keywords and argument were added.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Support for the OSPF TTL Security Check feature was added.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was modified to display output when loop-free alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute
(FRR) is enabled on an interface and whether it can be a protected or a protecting interface.
15.1(3)S
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
187
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf interface

Examples
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf interface command when Ethernet interface
0/0 is specified. It shows that LFA and FRR is enabled on the interface and that it can be both a
protected and a protecting interface.
Device# show ip ospf interface ethernet 0/0
Ethernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.254.202/24, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 192.168.99.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 10
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 10 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 192.168.99.1, Interface address 192.168.254.202
Backup Designated router (ID) 192.168.254.10, Interface address 192.168.254.10
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:05
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Can be protected by per-prefix Loop-free FastReroute
Can be used for per-prefix Loop-free FastReroute repair paths
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 192.168.254.10 (Backup Designated Router)
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB, the following sample output from the show ip ospf interface
brief topology VOICE command shows a summary of information, including a confirmation that
the Multitopology Routing (MTR) VOICE topology is configured in the interface configuration:
Device# show ip ospf interface brief topology VOICE
VOICE Topology (MTID 10)
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Lo0 1 0 10.0.0.2/32 1 LOOP 0/0
Se2/0 1 0 10.1.0.2/30 10 P2P 1/1
The following sample output from the show ip ospf interface brief topology VOICE command
displays details of the MTR VOICE topology for the interface. When the command is entered without
the brief keyword, more information is displayed.
Device# show ip ospf interface topology VOICE
VOICE Topology (MTID 10)
Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.0.0.2/32, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.0.0.2, Network Type LOOPBACK
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
10 1 no no VOICE
Loopback interface is treated as a stub Host Serial2/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 10.1.0.2/30, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 10.0.0.2, Network Type POINT_TO_POINT
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
10 10 no no VOICE
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
188
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf interface

oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:03
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 10.0.0.1
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
In Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC, the following sample output from the show ip ospf interface
command displays details about the configured Time-to-Live (TTL) limits:
Device# show ip ospf interface ethernet 0
.
.
.
Strict TTL checking enabled
! or a message similar to the following is displayed
Strict TTL checking enabled, up to 4 hops allowed
.
.
.
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the displays.
Table 17: show ip ospf interface Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Status of the physical link and operational status of the protocol.Ethernet
OSPF process ID.Process ID
OSPF area.Area
Administrative cost assigned to the interface.Cost
Operational state of the interface.State
OSPF neighbor count.Nbrs F/C
Interface IP address, subnet mask, and area address.Internet Address
MTR topology Multitopology Identifier (MTID). A number assigned
so that the protocol can identify the topology associated with
information that it sends to its peers.
Topology-MTID
Transmit delay in seconds, interface state, and device priority.Transmit Delay
Designated router ID and respective interface IP address.Designated Router
Backup designated router ID and respective interface IP address.Backup Designated router
Configuration of timer intervals.Timer intervals configured
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
189
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf interface

DescriptionField
Number of seconds until the next hello packet is sent out this
interface.
Hello
Only one hop is allowed.Strict TTL checking enabled
A set number of hops has been explicitly configured.Strict TTL checking enabled, up to 4
hops allowed
Count of network neighbors and list of adjacent neighbors.Neighbor Count
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
190
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf interface

show ip ospf max-metric
To display IP Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) max-metric origination information, use the show ip ospf
max-metric command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf max-metric [{multicast topology | topology}] [{topology-name | base}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Specifies the multicast topology.multicast
(Optional) Specifies the unicast or the multicast topology.topology
(Optional) The multicast topology name.topology-name
(Optional) Specifies the multicast or unicast base topology.base
Command Modes
User EXEC (>) Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationMainline Release
This command was introduced in a release earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.4(24)T.12.4(24)T
This command was integrated into a release earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI.12.2(33)SXI
This command was integrated into a release earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.4(24)T.12.2(33)SRE
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1.Cisco IOS XE
2.1
Examples
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf max-metriccommand. The fields are
self-explanatory.
Router# show ip ospf
max-metric
OSPF Router with ID (190.0.30.1) (Process ID 2)
Base Topology (MTID 0)Start time: 3d12h, Time elapsed: 00:01:07.964
Originating router-LSAs with maximum metric
Condition: always, State: active
Advertise external-LSAs with metric 16711680
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
191
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf max-metric

show ip ospf multi–area
To display interface information about Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) multiarea adjacency, use the show
ip ospf multi-area command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf process-id multi-area
Syntax Description
Identifies the OSPF process. The range is from 1 to 65535.process-id
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
User EXEC (>)
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS Release XE 3.10S
Examples
The following example shows sample output from the show ip ospf multi-area command:
Device# show ip ospf 1 multi-area
OSPF_MA1 is up, line protocol is up
Primary Interface Ethernet0/0, Area 2
Interface ID 2
MTU is 1500 bytes
Neighbor Count is 1
The table below describes the significant fields in the output.
Table 18: show ip ospf multi-area Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Status of the OSPF multiarea interface.OSPF_MA1
Status of the physical link and operational status of
the protocol.
Ethernet
OSPF area.Area
The largest size of packets that the OSPF interface
can transmit without the need to fragment.
MTU
Count of network neighbors and if applicable, a list
of adjacent neighbors.
Neighbor Count
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables multiarea adjacency on the OSPF interface.ip ospf multi-area
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
192
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf multi–area

DescriptionCommand
Specifies the cost of sending a packet on an OSPF multiarea interface.ip ospf multi-area cost
Displays the interface information related to OSPF.show ip ospf interface
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
193
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf multi–area

show ip ospf neighbor
To display Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) neighbor information on a per-interface basis, use the
showipospfneighbor command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf neighbor [interface-type interface-number] [neighbor-id] [detail] [fast-reroute]
[summary [per-instance]]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Type and number associated with a specific OSPF interface.interface-type interface-number
(Optional) Neighbor hostname or IP address in A.B.C.D format.neighbor-id
(Optional) Displays all neighbors given in detail (lists all neighbors).detail
(Optional) Displays per-neighbor border router tables and SPF statistics.fast-reroute
(Optional) Displays total number summary of all neighbors.summary
(Optional) Displays total number of neighbors in each neighbor state. The
output is printed for each configured OSPF instance separately.
per-instance
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support
in a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform,
and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Support for the OSPF TTL Security Check feature was added.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was modified. The fast-reroute was keyword were added.15.1(3)S
This command was modified. The summary and per-instance keywords were
added.
15.1(1)SY
This command was modified.The summary and per-instance keywords were
added.
15.3(1)S
This command was modified. The summary and per-instance keywords were
added. .
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8S
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
194
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf neighbor

Examples
The following sample output from the show ip ospf neighbor command shows a single line of
summary information for each neighbor:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
10.199.199.137 1 FULL/DR 0:00:31 192.168.80.37 Ethernet0
172.16.48.1 1 FULL/DROTHER 0:00:33 172.16.48.1 Fddi0
172.16.48.200 1 FULL/DROTHER 0:00:33 172.16.48.200 Fddi0
10.199.199.137 5 FULL/DR 0:00:33 172.16.48.189 Fddi0
The following is sample output showing summary information about the neighbor that matches the
neighbor ID:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor 10.199.199.137
Neighbor 10.199.199.137, interface address 192.168.80.37
In the area 0.0.0.0 via interface Ethernet0
Neighbor priority is 1, State is FULL
Options 2
Dead timer due in 0:00:32
Link State retransmission due in 0:00:04
Neighbor 10.199.199.137, interface address 172.16.48.189
In the area 0.0.0.0 via interface Fddi0
Neighbor priority is 5, State is FULL
Options 2
Dead timer due in 0:00:32
Link State retransmission due in 0:00:03
If you specify the interface along with the neighbor ID, the system displays the neighbors that match
the neighbor ID on the interface, as in the following sample display:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor ethernet 0 10.199.199.137
Neighbor 10.199.199.137, interface address 192.168.80.37
In the area 0.0.0.0 via interface Ethernet0
Neighbor priority is 1, State is FULL
Options 2
Dead timer due in 0:00:37
Link State retransmission due in 0:00:04
You can also specify the interface without the neighbor ID to show all neighbors on the specified
interface, as in the following sample display:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor fddi 0
ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
172.16.48.1 1 FULL/DROTHER 0:00:33 172.16.48.1 Fddi0
172.16.48.200 1 FULL/DROTHER 0:00:32 172.16.48.200 Fddi0
10.199.199.137 5 FULL/DR 0:00:32 172.16.48.189 Fddi0
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf neighbor detail command:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor detail
Neighbor 192.168.5.2, interface address 10.225.200.28
In the area 0 via interface GigabitEthernet1/0/0
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
195
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf neighbor

Neighbor priority is 1, State is FULL, 6 state changes
DR is 10.225.200.28 BDR is 10.225.200.30
Options is 0x42
LLS Options is 0x1 (LR), last OOB-Resync 00:03:08 ago
Dead timer due in 00:00:36
Neighbor is up for 00:09:46
Index 1/1, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 1
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the displays.
Table 19: show ip ospf neighbor detail Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Neighbor router ID.Neighbor
IP address of the interface.interface address
Area and interface through which the OSPF neighbor is known.In the area
Router priority of the neighbor and neighbor state.Neighbor priority
OSPF state. If one OSPF neighbor has enabled TTL security, the other
side of the connection will show the neighbor in the INIT state.
State
Number of state changes since the neighbor was created. This value can
be reset using the clearipospfcountersneighbor command.
state changes
Router ID of the designated router for the interface.DR is
Router ID of the backup designated router for the interface.BDR is
Hello packet options field contents. (E-bit only. Possible values are 0 and
2; 2 indicates area is not a stub; 0 indicates area is a stub.)
Options
Link-Local Signaling and out-of-band (OOB) link-state database
resynchronization performed hours:minutes:seconds ago. This is nonstop
forwarding (NSF) information. The field indicates the last successful
out-of-band resynchronization with the NSF-capable router.
LLS Options..., last OOB-Resync
Expected time in hours:minutes:seconds before Cisco IOS software will
declare the neighbor dead.
Dead timer due in
Number of hours:minutes:seconds since the neighbor went into the
two-way state.
Neighbor is up for
Neighbor location in the area-wide and autonomous system-wide
retransmission queue.
Index
Number of elements in the retransmission queue.retransmission queue length
Number of times update packets have been re-sent during flooding.number of retransmission
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
196
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf neighbor

DescriptionField
Memory location of the flooding details.First
Memory location of the flooding details.Next
Number of link state advertisements (LSAs) in the last retransmission
packet.
Last retransmission scan length
Maximum number of LSAs sent in any retransmission packet.maximum
Time taken to build the last retransmission packet.Last retransmission scan time
Maximum time, in milliseconds, taken to build any retransmission packet.maximum
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf neighbor command showing a single line
of summary information for each neighbor. If one OSPF neighbor has enabled TTL security, the
other side of the connection will show the neighbor in the INIT state.
Device# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
10.199.199.137 1 FULL/DR 0:00:31 192.168.80.37 Ethernet0
172.16.48.1 1 FULL/DROTHER 0:00:33 172.16.48.1 Fddi0
172.16.48.200 1 FULL/DROTHER 0:00:33 172.16.48.200 Fddi0
10.199.199.137 5 FULL/DR 0:00:33 172.16.48.189 Fddi0
172.16.1.201 1 INIT/DROTHER 00.00.35 10.1.1.201 Ethernet0/0
Cisco IOS Release 15.1(3)S
The following sample output from the show ip ospf neighbor command shows the network from
the neighbor’s point of view:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor 192.0.2.1 fast-reroute
OSPF Router with ID (192.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Area with ID (0)
Neighbor with Router ID 192.0.2.1:
Reachable over:
Ethernet0/0, IP address 192.0.2.1, cost 10
SPF was executed 1 times, distance to computing router 10
Router distance table:
192.1.1.1 i [10]
192.0.2.1 i [0]
192.3.3.3 i [10]
192.4.4.4 i [20]
192.5.5.5 i [20]
Network LSA distance table:
192.2.12.2 i [10]
192.2.13.3 i [20]
192.2.14.4 i [20]
192.2.15.5 i [20]
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
197
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf neighbor

The following is sample output from the show ip ospf neighbor summary command:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor summary
Neighbor summary for all OSPF processes
DOWN 0
ATTEMPT 0
INIT 0
2WAY 0
EXSTART 0
EXCHANGE 0
LOADING 0
FULL 1
Total count 1 (Undergoing NSF 0)
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf neighbor summary per-instance
command:
Device# show ip ospf neighbor summary
OSPF Router with ID (1.0.0.10) (Process ID 1)
DOWN 0
ATTEMPT 0
INIT 0
2WAY 0
EXSTART 0
EXCHANGE 0
LOADING 0
FULL 1
Total count 1 (Undergoing NSF 0)
Neighbor summary for all OSPF processes
DOWN 0
ATTEMPT 0
INIT 0
2WAY 0
EXSTART 0
EXCHANGE 0
LOADING 0
FULL 1
Total count 1 (Undergoing NSF 0)
Table 20: show ip ospf neighbor summary and show ip ospf neighbor summary per-instance Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
No information (hellos) has been received from this neighbor, but hello packets can still be
sent to the neighbor in this state.
DOWN
This state is only valid for manually configured neighbors in a Non-Broadcast Multi-Access
(NBMA) environment. In Attempt state, the router sends unicast hello packets every poll
interval to the neighbor, from which hellos have not been received within the dead interval.
ATTEMPT
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
198
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf neighbor

DescriptionField
This state specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor, but the
receiving router's ID was not included in the hello packet. When a router receives a hello
packet from a neighbor, it should list the sender's router ID in its hello packet as an
acknowledgment that it received a valid hello packet.
INIT
This state designates that bi-directional communication has been established between two
routers.
2WAY
This state is the first step in creating an adjacency between the two neighboring routers. The
goal of this step is to decide which router is the primary, and to decide upon the initial DD
sequence number. Neighbor conversations in this state or greater are called adjacencies.
EXSTART
In this state, OSPF routers exchange database descriptor (DBD) packets. Database descriptors
contain link-state advertisement (LSA) headers only and describe the contents of the entire
link-state database. Each DBD packet has a sequence number which can be incremented only
by primary which is explicitly acknowledged by subordinate. Routers also send link-state
request packets and link-state update packets (which contain the entire LSA) in this state. The
contents of the DBD received are compared to the information contained in the routers link-state
database to check if new or more current link-state information is available with the neighbor.
EXCHANGE
In this state, the actual exchange of link state information occurs. Based on the information
provided by the DBDs, routers send link-state request packets. The neighbor then provides
the requested link-state information in link-state update packets. During the adjacency, if a
device receives an outdated or missing LSA, it requests that LSA by sending a link-state
request packet. All link-state update packets are acknowledged.
LOADING
In this state, devices are fully adjacent with each other. All the device and network LSAs are
exchanged and the devices' databases are fully synchronized.
Full is the normal state for an OSPF device. If a device is stuck in another state, it's an indication
that there are problems in forming adjacencies. The only exception to this is the 2-way state,
which is normal in a broadcast network. Devices achieve the full state with their DR and BDR
only. Neighbors always see each other as 2-way.
FULL
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
199
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf neighbor

show ip ospf nsf
To display IP Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) nonstop forwarding (NSF) state information, use the show ip
ospf nsf command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf nsf
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
User EXEC (>) Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationMainline
Release
This command was introduced in a release earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXI.12.2(33)SXI
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRE.12.2(33)SRE
Examples
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf nsfcommand. The fields are self-explanatory.
Router# show ip ospf
nsf
Routing Process "ospf 2"
Non-Stop Forwarding enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
OSPF restart state is NO_RESTART
Handle 1786466308, Router ID 192.0.2.1, checkpoint Router ID 0.0.0.0
Config wait timer interval 10, timer not running
Dbase wait timer interval 120, timer not running
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
200
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf nsf

show ip ospf nsr
To display IP Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) nonstop routing (NSR) status information, use the show ip
ospf nsr command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf [process-id] nsr [{[objects] | [statistics]}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Process ID. If this argument is used, only information for the specified OSPF routing
process is included.
process-id
(Optional) Displays information on the OSPF NSR objects in the different OSPF routing
processes.
objects
(Optional) Displays OSPF NSR statistical information for the different OSPF routing processes.statistics
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.1(2)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.3S
This command was integrated into 15.2(1) E.15.2(1) E
Examples
The following sample output from the show ip ospf nsrcommand shows that OSPF on the standby
RP is fully synchronized and ready to continue operation if the active RP fails or if a manual
switchover is performed. NSR is configured and enabled for the “ospf 1” OSPF routing process. The
fields are self-explanatory.
Router# show ip ospf
1 nsr
Active RP
Operating in duplex mode
Redundancy state: ACTIVE
Peer redundancy state: STANDBY HOT
Checkpoint peer ready
Checkpoint messages enabled
ISSU negotiation complete
ISSU versions compatible
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 10.1.1.100
NSR configured
Checkpoint message sequence number: 6360
Standby synchronization state: synchronized
Bulk sync operations: 1
Next sync check time: 18:48:27.097 PST Fri Dec 10 2010
LSA Count: 3301, Checksum Sum 0x06750217
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables NSR on a router that is running OSPF.nsr
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
201
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf nsr

show ip ospf request-list
To display a list of all link-state advertisements (LSAs) requested by a router, use the
showipospfrequest-listcommand in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf request-list [neighbor] [interface] [interface-neighbor]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Displays the list of all LSAs requested by the router from this neighbor.neighbor
(Optional) Displays the list of all LSAs requested by the router from this interface.interface
(Optional) Displays the list of all LSAs requested by the router on this interface from
this neighbor.
interface-neighbor
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
The information displayed by the showipospfrequest-listcommand is useful in debugging Open Shortest
Path First (OSPF) routing operations.
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospfrequest-list command:
Router# show ip ospf request-list serial 0
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.1.11) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor 192.168.1.12, interface Serial0 address 172.16.1.12
Type LS ID ADV RTR Seq NO Age Checksum
1 192.168.1.12 192.168.1.12 0x8000020D 8 0x6572
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the displays.
Table 21: show ip ospf request-list Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
LSA-type.Type
IP address of the neighbor router.LS ID
IP address of the advertising router.ADV RTR
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
202
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf request-list

DescriptionField
Packet sequence number of the LSA.Seq NO
Age, in seconds, of the LSA.Age
Checksum number of the LSA.Checksum
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
203
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf request-list

show ip ospf retransmission-list
To display a list of all link-state advertisements (LSAs) waiting to be re-sent, use the
showipospfretransmission-listcommand in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf retransmission-list [neighbor] [interface] [interface-neighbor]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Displays the list of all LSAs waiting to be re-sent for this neighbor.neighbor
(Optional) Displays the list of all LSAs waiting to be re-sent on this interface.interface
(Optional) Displays the list of all LSAs waiting to be re-sent on this interface, from
this neighbor.
interface neighbor
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
The information displayed by the showipospfretransmission-listcommand is useful in debugging Open
Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing operations.
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospfretransmission-list command:
Router# show ip ospf retransmission-list serial 0
OSPF Router with ID (192.168.1.12) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor 192.168.1.11, interface Serial0 address 172.16.1.11
Link state retransmission due in 3764 msec, Queue length 2
Type LS ID ADV RTR Seq NO Age Checksum
1 192.168.1.12 192.168.1.12 0x80000210 0 0xB196
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the displays.
Table 22: show ip ospf retransmission-list Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
LSA-type.Type
IP address of the neighbor router.LS ID
IP address of the advertising router.ADV RTR
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
204
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf retransmission-list

DescriptionField
Packet sequence number of the LSA.Seq NO
Age, in seconds, of the LSA.Age
Checksum number of the LSA.Checksum
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
205
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf retransmission-list

show ip ospf rib
To display information for the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) local Routing Information Base (RIB) or
locally redistributed routes, use the showipospfribcommand in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf process-id rib [redistribution] [network-prefix] [network-mask] [detail]
Syntax Description
Internally used identification parameter for an OSPF routing process. It is locally assigned
and can be any positive integer. A unique value is assigned for each OSPF routing process.
process-id
(Optional) Displays IP OSPF redistribution RIB information.redistribution
(Optional) Network prefix. Displays paths for a specific route.network-prefix
(Optional) IP address mask. Displays paths for all routes under a major network.network-mask
(Optional) Displays more detailed information about the OSPF local RIB.detail
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.4(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SB.12.2(33)SB
This command was modified. Output was enhanced to display both primary paths and any
loop-free alternate (LFA) and Fast Reroute (FRR) repair paths protecting them.
15.1(3)S
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation Services Routers.15.2(2)SNI
Usage Guidelines
If the network-prefix and network-mask arguments are both entered, only the route that matches the network
prefix and IP address mask is displayed. If only the network-prefix argument is entered, a longest prefix lookup
is performed and the matching route is displayed.
Examples
The following example displays information about locally redistributed routes:
Router# show ip ospf 1 rib redistribution 192.168.240.0
OSPF Redistribution for Process 1
192.168.240/20, metric 0, tag 0, from OSPF Router 130
Attributes 0x1000220, event 1
via Ethernet0/0
OSPF Redistribution Process 130
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
206
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf rib

Table 23: show ip ospf rib redistribution F ield Descriptions
DescriptionField
Routing redistribution information for OSPF process 1.OSPF Redistribution for Process 1
Network number and mask.192.168.240/20
OSPF metric type.metric 0
OSPF process tag identifier.tag 0
OSPF router from which routing information was redistributed.from OSPF Router
OSPF attribute.Attributes 0x1000220
OSPF redistribution event 1.event
The interface through which routing information has been redistributed.Via Ethernet0/0
Routing redistribution information for OSPF process 13.OSPF Redistribution Process
The following example displays information about primary paths and the LFA and FRR repair paths
protecting them:
Router# show ip ospf 1 rib
OSPF Router with ID (192.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
OSPF local RIB
Codes: * - Best, > - Installed in global RIB
* 192.168.15.0/24, Intra, cost 10, area 0, Connected
via 192.168.15.1, Ethernet0/3
*> 192.168.23.0/24, Intra, cost 20, area 0
via 192.168.12.2, Ethernet0/0
repair path via 192.168.13.3, Ethernet0/1, cost 20
via 192.168.13.3, Ethernet0/1
repair path via 192.168.12.2, Ethernet0/0, cost 20
*> 192.168.26.0/24, Intra, cost 20, area 0
via 192.168.12.2, Ethernet0/0
repair path via 192.168.13.3, Ethernet0/1, cost 30
*> 192.168.46.0/24, Intra, cost 30, area 0
via 192.168.12.2, Ethernet0/0
repair path via 192.168.13.3, Ethernet0/1, cost 40
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays debugging information for OSPF Version 2 routes in the global or
local RIB.
debug ip ospf rib
Displays information about prefixes protected by LFA FRR repair paths.show ip ospf fast-reroute
Displays OSPF interface information.show ip ospf interface
Displays OSPF neighbor information on a per-interface basis.show ip ospf neighbor
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
207
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf rib

show ip ospf sham-links
To display information about all sham-links configured for a provider edge (PE) router in the Virtual Private
Network (VPN) backbone, use the show ip ospf sham-links command in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf sham-links
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(8)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(21)ST, and support for Cisco
12000 series Internet Router was added.
12.0(21)ST
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S, and support for Cisco 10000
series Internet Routers was added.
12.0(22)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to display Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) information about the sham-links configured
on a PE router.
Examples
The following example shows sample output from the show ip ospf sham-links command for a PE
router in the VPN backbone:
Router1# show ip ospf sham-links
Sham Link OSPF_SL0 to address 10.44.0.1 is up
Area 120 source address 10.0.0.1
Run as demand circuit
DoNotAge LSA allowed., Cost of using 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT,
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:09
Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed)
Index 2/2, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 27
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 2
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
208
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf sham-links

show ip ospf statistics
To display Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) shortest path first (SPF) calculation statistics, use the
showipospfstatisticscommand in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf statistics [detail]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Displays statistics separately for each OSPF area and includes additional, more detailed
statistics.
detail
Command Modes
User EXEC Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(24)S
The command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)S.12.2(18)S
The command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)T.12.3(2)T
Usage Guidelines
The showipospfstatistics command provides important information about SPF calculations and the events
that trigger them. This information can be meaningful for both OSPF network maintenance and troubleshooting.
For example, entering the showipospfstatistics command is recommended as the first troubleshooting step
for link-state advertisement (LSA) flapping.
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospfstatisticscommand that shows a single line of
information for each SPF calculation:
Router# show ip ospf statistics
OSPF process ID 200
------------------------------------------
Area 0: SPF algorithm executed 10 times
Area 200: SPF algorithm executed 8 times
Summary OSPF SPF statistic
SPF calculation time
Delta T Intra D-Intra Summ D-Summ Ext D-Ext Total Reason
08:17:16 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 R,
08:16:47 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 R, N,
08:16:37 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 R, X
00:04:40 208 40 208 44 220 0 720 R, N, SN, X
00:03:15 0 112 4 108 8 96 328 R, N, SN, X
00:02:55 164 40 176 44 188 0 612 R, N, SN, X
00:01:49 0 4 4 0 4 4 16 R, N, SN, X
00:01:48 0 0 4 0 4 0 12 R, N, SN, SA, X
00:01:43 0 0 4 0 4 0 8 R,
00:00:53 164 40 176 44 188 0 612 R, N, SN, X
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
209
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf statistics

Table 24: show ip ospf statistics F ield Descriptions
DescriptionField
A unique value assigned to the OSPF process in the configuration.OSPF process ID
OSPF area ID.Area
Number of times SPF algorithm has been executed for the particular area.SPF algorithm executed
Amount of time in milliseconds that has passed from when SPF started its
calculation to the current time.
Delta T
Time in milliseconds for the SPF algorithm to process intra-area LSAs and install
intra-area routes in the routing table.
Intra
Time in milliseconds for the SPF algorithm to delete invalid intra-area routes from
the routing table.
D-Intra
Time in milliseconds for the SPF algorithm to process interarea LSAs and install
interarea routes in the routing table.
Summ
Time in milliseconds for the SPF algorithm to delete invalid interarea routes from
the routing table.
D-Summ
Time in milliseconds for the SPF algorithm to process external and not so stubby
area (NSSA) LSAs and install external and NSSA routes in the routing table.
Ext
Time in milliseconds for the SPF algorithm to delete invalid external and NSSA
routes from the routing table.
D-Ext
Total duration time, in milliseconds, for the SPF algorithm process.Total
Record of reasons causing SPF to be executed:
• N--A change in a network LSA (type 2) has occurred.
• R--A change in a router LSA (type 1) has occurred.
• SA--A change in a Summary autonomous system boundary router (ASBR)
(SA) LSA has occurred.
• SN--A change in a Summary Network (SN) LSA has occurred.
• X--A change in an External Type-7 (X7) LSA has occurred.
Reason
The following is sample output from the showipospfstatisticscommand with the detail keyword
entered to show the statistics separately for a specific area:
Router# show ip ospf statistics detail
SPF 7 executed 2d17h ago, SPF type Full
SPF calculation time (in msec):
SPT Intra D-Intr Summ D-Summ Ext7 D-Ext7 Total
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
LSIDs processed R:4 N:1 Stub:5 SN:17 SA:1 X7:0
Change record R,
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
210
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf statistics

LSIDs changed 1
Last 10 LSIDs:
2.0.0.202(R)
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 25: show ip ospf statistics detail F ield Descriptions
DescriptionField
Number of SPF algorithms executed in the OSPF area. The number increases by one for
each SPF algorithm that is executed in the area.
SPF
Time in milliseconds that has passed between the start of the SPF algorithm execution
and the current time.
Executed ago
SPF type can be Full or Incremental.SPF type
Time in milliseconds requires to compute the first stage of the SPF algorithm (to build a
short path tree). The SPT time plus the time required to process links to stub networks
equals the Intra time.
SPT
Time in milliseconds for the SPF algorithm to process external and not so stubby area
(NSSA) link-state advertisements (LSAs) and install external and NSSA routes in the
routing table.
Ext
Total duration time, in milliseconds, for the SPF algorithm process.
Total time is the sum of previous times excluding the SPT time, which is
already included in the Intra time.
Note
Total
Number of LSAs processed during the SPF calculation:
• N--Network LSA.
• R--Router LSA.
• SA--Summary autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) (SA) LSA.
• SN--Summary Network (SN) LSA.
• Stub--Stub links.
• X7--External Type-7 (X7) LSA.
LSIDs processed
Number of LSAs changed between this SPF calculation and the previous one. LSA changes
force SPF to be scheduled.
LSIDs changed
List of last ten Intra area LSAs that have changed between this SPF calculation and the
previous one. LSID types:
• R--Router LSA (type 1)
• N--Network LSA (type 2)
Last 10 LSIDs
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
211
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf statistics

show ip ospf summary-address
To display a list of all summary address redistribution information configured under an Open Shortest Path
First (OSPF) process, use the showipospfsummary-addresscommand in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf [process-id] summary-address
Syntax Description
(Optional) OSPF area ID.process-id
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
The process-id argument can be entered as a decimal number or as an IP address format.
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospfsummary-address command:
Router# show ip ospf summary-address
OSPF Process 2, Summary-address
10.2.0.0/255.255.0.0 Metric -1, Type 0, Tag 0
10.2.0.0/255.255.0.0 Metric -1, Type 0, Tag 10
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the displays.
Table 26: show ip ospf request-list Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
IP address and mask of the router for the OSPF process.10.2.0.0/255.255.0.0
OSPF metric type.Metric -1
Type indicates the external type (type 1 or type 2) that is a component of the summary.
0 indicates that neither type 1 or type 2 external routes include the component.
Type 0
OSPF process tag identifier.Tag 0
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
212
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf summary-address

show ip ospf timers rate-limit
To display all of the link-state advertisements (LSAs) in the rate limit queue, use the
showipospftimersrate-limitcommand in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf timers rate-limit
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
Use this command if you need to see when LSAs in the queue will be sent.
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospftimersrate-limit command:
Router# show ip ospf timers rate-limit
LSAID: 10.1.1.1 Type: 1 Adv Rtr: 172.16.2.2 Due in: 00:00:00.028
LSAID: 172.16.4.1 Type: 3 Adv Rtr: 172.16.2.2 Due in: 00:00:00.028
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 27: show ip ospf timers rate-limit Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
ID of the LSA.LSAID
Type of LSA.Type
ID of advertising router.Adv Rtr
When the LSA is scheduled to be sent (in hours:minutes:seconds).Due in
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
213
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf timers rate-limit

show ip ospf traffic
To display Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) traffic statistics, use the showipospftraffic command in user
EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ip ospf [process-id] traffic [interface-type interface-number]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Process ID. If the process-id argument is included, only
information for the specified routing process is displayed.
process-id
(Optional) Type and number associated with a specific OSPF interface.interface-type interface-number
Command Default
When the showipospftraffic command is entered without any arguments, global OSPF traffic statistics are
displayed, including queue statistics for each OSPF process, statistics for each interface, and per-OSPF process
statistics.
Command Modes
User EXEC (>) Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(11)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(28)S.12.0(28)S
Support for the OSPF Enhanced Traffic Statistics for OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 feature was added.12.4(6)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.12.2(33)SRB
Support for the OSPF TTL Security Check feature was added.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
Usage Guidelines
You can limit the displayed traffic statistics to those for a specific OSPF process by entering a value for the
process-id argument, or you can limit output to traffic statistics for a specific interface associated with an
OSPF process by entering values for the interface-type and interface-number arguments. To reset counters
and clear statistics, use the clearipospftraffic command.
Examples
Cisco IOS Release 12.0(28)S
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf traffic command.
Router# show ip ospf traffic
OSPF statistics:
Rcvd: 5300 total, 730 checksum errors
333 hello, 10 database desc, 3 link state req
24 link state updates, 13 link state acks
Sent: 264 total
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
214
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf traffic

222 hello, 12 database desc, 3 link state req
17 link state updates, 12 link state acks
OSPF Router with ID (10.0.1.2) (Process ID 100)
OSPF queues statistic for process ID 100:
OSPF Hello queue size 0, no limit, max size 3
OSPF Router queue size 0, limit 200, drops 0, max size 3
Interface statistics:
Interface Loopback0
OSPF packets received/sent
Invalid Hellos DB-des LS-req LS-upd LS-ack Total
Rx: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Tx: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
OSPF header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, Bad Source 0,
No Virtual Link 0, Area Mismatch 0, No Sham Link 0,
Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0, LLS 0,
Authentication 0,
OSPF LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
Interface Serial3/0
OSPF packets received/sent
Invalid Hellos DB-des LS-req LS-upd LS-ack Total
Rx: 0 111 3 1 7 6 128
Tx: 0 111 4 1 12 5 133
OSPF header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, Bad Source 0,
No Virtual Link 0, Area Mismatch 0, No Sham Link 0,
Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0, LLS 0,
Authentication 0,
OSPF LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
Interface Serial2/0
OSPF packets received/sent
Invalid Hellos DB-des LS-req LS-upd LS-ack Total
Rx: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Tx: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
OSPF header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, Bad Source 0,
No Virtual Link 0, Area Mismatch 0, No Sham Link 0,
Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0, LLS 0,
Authentication 0,
OSPF LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
Interface Ethernet0/0
OSPF packets received/sent
Invalid Hellos DB-des LS-req LS-upd LS-ack Total
Rx: 0 222 7 2 17 7 255
Tx: 0 111 8 2 5 7 133
OSPF header errors
Length 0, Checksum 730, Version 800, Bad Source 0,
No Virtual Link 0, Area Mismatch 0, No Sham Link 0,
Self Originated 3387, Duplicate ID 0, LLS 0,
Authentication 0,
OSPF LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
Summary traffic statistics for process ID 100:
Rcvd: 5300 total, 4917 errors
333 hello, 10 database desc, 3 link state req
24 link state upds, 13 link state acks, 0 invalid
Sent: 266 total
222 hello, 12 database desc, 3 link state req
17 link state upds, 12 link state acks, 0 invalid
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
215
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf traffic

Table 28: show ip ospf traffic Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Traffic statistics accumulated for all OSPF processes running on the router.
To ensure compatibility with the showiptraffic command, only checksum
errors are displayed. Identifies the route map name.
OSPF statistics
Statistics specific to Cisco IOS software.OSPF queues statistic for
process ID
Statistics for the internal Cisco IOS queue between the packet switching
code (process IP Input) and the OSPF hello process for all received OSPF
packets.
OSPF Hello queue
Statistics for the internal Cisco IOS queue between the OSPF hello process
and the OSPF router for all received OSPF packets except OSPF hellos.
OSPF Router queue
Actual size of the queue.queue size
Maximum allowed size of the queue.queue limit
Maximum recorded size of the queue.queue max size
Per-interface traffic statistics for all interfaces that belong to the specific
OSPF process ID.
Interface statistics
Number of OSPF packets received and sent on the interface, sorted by packet
types.
OSPF packets received/sent
Packet appears in this section if it was discarded because of an error in the
header of an OSPF packet. The discarded packet is counted under the
appropriate discard reason. Number of packets dropped due to TTL security
check is displayed if that feature has been configured.
OSPF header errors
Packet appears in this section if it was discarded because of an error in the
header of an OSPF link-state advertisement (LSA). The discarded packet is
counted under the appropriate discard reason.
OSPF LSA errors
Summary traffic statistics accumulated for an OSPF process.
The OSPF process ID is a unique value assigned to the OSPF
process in the configuration.
Note
The value for the received errors is the sum of the OSPF header errors that
are detected by the OSPF process, unlike the sum of the checksum errors
that are listed in the global OSPF statistics.
Summary traffic statistics for
process ID
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC
The following is sample output from the show ip ospf traffic command. The output has been modified
to include the number of packets dropped due a TTL security check.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
216
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf traffic

Router# show ip ospf traffic
.
.
.
OSPF header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, Bad Source 0,
No Virtual Link 0, Area Mismatch 0, No Sham Link 0,
Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0, LLS 0,
Authentication 0, TTL Check Fail 2,
.
Cisco IOS Release 12.4(6)T
The following is sample output from the showipospftraffic command that displays the detailed
traffic information for OSPF packets received and sent on each OSPF interface and OSPF process.
Router# show ip ospf traffic
OSPF statistics:
.
.
.
Interface Ethernet0/0.1
OSPF packets received/sent
Type Packets Bytes
RX Invalid 0 0
RX Hello 0 0
RX DB des 0 0
RX LS req 0 0
RX LS upd 0 0
RX LS ack 0 0
RX Total 0 0
TX Failed 0 0
TX Hello 16 1216
TX DB des 0 0
TX LS req 0 0
TX LS upd 0 0
TX LS ack 0 0
TX Total 16 1216
.
.
.
Interface Serial2/0
OSPF packets received/sent
Type Packets Bytes
RX Invalid 0 0
RX Hello 11 528
RX DB des 4 148
RX LS req 1 60
RX LS upd 3 216
RX LS ack 2 128
RX Total 21 1080
TX Failed 0 0
TX Hello 14 1104
TX DB des 3 252
TX LS req 1 56
TX LS upd 3 392
TX LS ack 2 128
TX Total 23 1932
.
.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
217
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf traffic

.
Interface Ethernet0/0
OSPF packets received/sent
Type Packets Bytes
RX Invalid 0 0
RX Hello 13 620
RX DB des 3 116
RX LS req 1 36
RX LS upd 3 228
RX LS ack 4 216
RX Total 24 1216
TX Failed 0 0
TX Hello 17 1344
TX DB des 4 276
TX LS req 1 56
TX LS upd 7 656
TX LS ack 2 128
TX Total 31 2460
.
.
.
Summary traffic statistics for process ID 1:
OSPF packets received/sent
Type Packets Bytes
RX Invalid 0 0
RX Hello 24 1148
RX DB des 7 264
RX LS req 2 96
RX LS upd 6 444
RX LS ack 6 344
RX Total 45 2296
TX Failed 0 0
TX Hello 31 2448
TX DB des 7 528
TX LS req 2 112
TX LS upd 10 1048
TX LS ack 4 256
TX Total 54 4392
OSPF header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, Bad Source 13,
No Virtual Link 0, Area Mismatch 0, No Sham Link 0,
Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0, Hello 0,
MTU Mismatch 0, Nbr Ignored 0, LLS 0,
Authentication 0,
OSPF LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
To start collecting new statistics, reset the counters and clear the traffic statistics by entering the
clearipospftraffic command as follows:
Router# clear ip ospf traffic
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Clears OSPFv2 traffic statistics.clear ip ospf traffic
Clears OSPFv3 traffics statistics.clear ipv6 ospf traffic
Displays OSPFv3 traffic statistics.show ipv6 ospf traffic
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
218
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf traffic

show ip ospf virtual-links
To display parameters and the current state of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) virtual links, use the
showipospfvirtual-links command in EXEC mode.
show ip ospf virtual-links
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
The information displayed by the showipospfvirtual-links command is useful in debugging OSPF routing
operations.
Examples
The following is sample output from the showipospfvirtual-links command:
Router# show ip ospf virtual-links
Virtual Link to router 192.168.101.2 is up
Transit area 0.0.0.1, via interface Ethernet0, Cost of using 10
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 0:00:08
Adjacency State FULL
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 29: show ip ospf virtual-links Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Specifies the OSPF neighbor, and if the link to that neighbor is
up or down.
Virtual Link to router 192.168.101.2 is up
The transit area through which the virtual link is formed.Transit area 0.0.0.1
The interface through which the virtual link is formed.via interface Ethernet0
The cost of reaching the OSPF neighbor through the virtual link.Cost of using 10
The transmit delay (in seconds) on the virtual link.Transmit Delay is 1 sec
The state of the OSPF neighbor.State POINT_TO_POINT
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
219
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf virtual-links

DescriptionField
The various timer intervals configured for the link.Timer intervals...
When the next hello is expected from the neighbor.Hello due in 0:00:08
The adjacency state between the neighbors.Adjacency State FULL
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
220
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ip ospf virtual-links

show ipv6 ospf
To display general information about Open Shortest Path First ( OSPF) routing processes, use the show ipv6
ospf command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ipv6 ospf [process-id] [area-id] [rate-limit]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Internal identification. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer. The
number used here is the number assigned administratively when the OSPF routing process is
enabled.
process-id
(Optional) Area ID. This argument displays information about a specified area only.area-id
(Optional) Rate-limited link-state advertisements (LSAs). This keyword displays LSAs that
are currently being rate limited, together with the remaining time to the next generation.
rate-limit
Command Modes
User EXEC
Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(24)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)S.12.2(18)S
Command output is changed when authentication is enabled.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(28)SB.12.2(28)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)SG.12.2(25)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
Command output was updated to display OSPF for IPv6 encryption information.12.4(9)T
Command output was modified to include VMI PPPoE process-level values.12.4(15)XF
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.4(15)T12.4(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
The rate-limit keyword was added. Command output was modified to include
the configuration values for SPF and LSA throttling timers.
12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SB.12.2(33)SB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1.Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.5(1)M.15.0(1)M
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
221
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf

ModificationRelease
This command was modified. Support for IPv6 was added to Cisco IOS Release
15.1(2)T.
15.1(2)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(50)SY.12.2(50)SY
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SG.15.1(1)SG
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)SY.15.0(1)SY
This command was implemented on the Cisco ASR 901 Series Aggregation
Services devices.
15.2(2)SNG
Examples
show ipv6 ospf Output Example
The following is sample output from the show ipv6 ospf command:
Device# show ipv6 ospf
Routing Process "ospfv3 1" with ID 10.10.10.1
SPF schedule delay 5 secs, Hold time between two SPFs 10 secs
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs. Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of areas in this device is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 1
MD5 Authentication, SPI 1000
SPF algorithm executed 2 times
Number of LSA 5. Checksum Sum 0x02A005
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 30: show ipv6 ospf Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Process ID and OSPF device ID.Routing process "ospfv3 1" with ID 10.10.10.1
Configured LSA group pacing timer (in seconds).LSA group pacing timer
Configured LSA flood pacing timer (in milliseconds).Interface flood pacing timer
Configured LSA retransmission pacing timer (in
milliseconds).
Retransmission pacing timer
Number of areas in device, area addresses, and so on.Number of areas
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
222
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf

show ipv6 ospf With Area Encryption Example
The following sample output shows the show ipv6 ospf command with area encryption information:
Device# show ipv6 ospf
Routing Process "ospfv3 1" with ID 10.0.0.1
It is an area border device
SPF schedule delay 5 secs, Hold time between two SPFs 10 secs
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs. Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of areas in this device is 2. 2 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
SPF algorithm executed 3 times
Number of LSA 31. Checksum Sum 0x107493
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 20
Flood list length 0
Area 1
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
NULL Encryption SHA-1 Auth, SPI 1001
SPF algorithm executed 7 times
Number of LSA 20. Checksum Sum 0x095E6A
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 31: show ipv6 ospf with Area Encryption Information Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Subsequent fields describe area 1.Area 1
Displays the encryption algorithm (in this case, null, meaning no
encryption algorithm is used), the authentication algorithm (SHA-1),
and the security policy index (SPI) value (1001).
NULL Encryption SHA-1 Auth, SPI
1001
The following example displays the configuration values for SPF and LSA throttling timers:
Device# show ipv6 ospf
Routing Process "ospfv3 1" with ID 10.9.4.1
Event-log enabled, Maximum number of events: 1000, Mode: cyclic
It is an autonomous system boundary device
Redistributing External Routes from,
ospf 2
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
223
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf

The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 32: show ipv6 ospf with SPF and LSA Throttling Timer Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Delay time of SPF calculations.Initial SPF schedule delay
Minimum hold time between consecutive SPF calculations.Minimum hold time between two consecutive
SPFs
Maximum hold time between consecutive SPF
calculations.
Maximum wait time between two consecutive
SPFs 10000 msecs
Minimum time interval (in seconds) between link-state
advertisements.
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs
Maximum arrival time (in milliseconds) of link-state
advertisements.
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
The following example shows information about LSAs that are currently being rate limited:
Device# show ipv6 ospf rate-limit
List of LSAs that are in rate limit Queue
LSAID: 0.0.0.0 Type: 0x2001 Adv Rtr: 10.55.55.55 Due in: 00:00:00.500
LSAID: 0.0.0.0 Type: 0x2009 Adv Rtr: 10.55.55.55 Due in: 00:00:00.500
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 33: show ipv6 ospf rate-limit Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Link-state ID of the LSA.LSAID
Description of the LSA.Type
ID of the advertising device.Adv Rtr
Remaining time until the generation of the next event.Due in:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
224
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf

show ipv6 ospf traffic
To display IPv6 Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) traffic statistics, use the
showipv6ospftrafficcommand in privileged EXEC mode.
show ipv6 ospf [process-id] traffic [interface-type interface-number]
Syntax Description
(Optional) OSPF process ID for which you want traffic statistics (for
example, queue statistics, statistics for each interface under the OSPF
process, and per OSPF process statistics).
process-id
(Optional) Type and number associated with a specific OSPF interface.interface-type interface-number
Command Default
When the showipv6ospftraffic command is entered without any arguments, global OSPF traffic statistics are
displayed, including queue statistics for each OSPF process, statistics for each interface, and per OSPF process
statistics.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.4(6)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.12.2(33)SRB
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Usage Guidelines
You can limit the displayed traffic statistics to those for a specific OSPF process by entering a value for the
process-id argument, or you can limit output to traffic statistics for a specific interface associated with an
OSPF process by entering values for the interface-type and interface-number arguments. To reset counters
and clear statistics, use the clearipv6ospftraffic command.
Examples
The following example shows the display output for the showipv6ospftraffic command for OSPFv3:
Router# show ipv6 ospf traffic
OSPFv3 statistics:
Rcvd: 32 total, 0 checksum errors
10 hello, 7 database desc, 2 link state req
9 link state updates, 4 link state acks
0 LSA ignored
Sent: 45 total, 0 failed
17 hello, 12 database desc, 2 link state req
8 link state updates, 6 link state acks
OSPFv3 Router with ID (10.1.1.4) (Process ID 6)
OSPFv3 queues statistic for process ID 6
Hello queue size 0, no limit, max size 2
Router queue size 0, limit 200, drops 0, max size 2
Interface statistics:
Interface Serial2/0
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
225
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf traffic

OSPFv3 packets received/sent
Type Packets Bytes
RX Invalid 0 0
RX Hello 5 196
RX DB des 4 172
RX LS req 1 52
RX LS upd 4 320
RX LS ack 2 112
RX Total 16 852
TX Failed 0 0
TX Hello 8 304
TX DB des 3 144
TX LS req 1 52
TX LS upd 3 252
TX LS ack 3 148
TX Total 18 900
OSPFv3 header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, No Virtual Link 0,
Area Mismatch 0, Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0,
Instance ID 0, Hello 0, MTU Mismatch 0,
Nbr Ignored 0, Authentication 0,
OSPFv3 LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
Interface Ethernet0/0
OSPFv3 packets received/sent
Type Packets Bytes
RX Invalid 0 0
RX Hello 6 240
RX DB des 3 144
RX LS req 1 52
RX LS upd 5 372
RX LS ack 2 152
RX Total 17 960
TX Failed 0 0
TX Hello 11 420
TX DB des 9 312
TX LS req 1 52
TX LS upd 5 376
TX LS ack 3 148
TX Total 29 1308
OSPFv3 header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, No Virtual Link 0,
Area Mismatch 0, Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0,
Instance ID 0, Hello 0, MTU Mismatch 0,
Nbr Ignored 0, Authentication 0,
OSPFv3 LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
Summary traffic statistics for process ID 6:
OSPFv3 packets received/sent
Type Packets Bytes
RX Invalid 0 0
RX Hello 11 436
RX DB des 7 316
RX LS req 2 104
RX LS upd 9 692
RX LS ack 4 264
RX Total 33 1812
TX Failed 0 0
TX Hello 19 724
TX DB des 12 456
TX LS req 2 104
TX LS upd 8 628
TX LS ack 6 296
TX Total 47 2208
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
226
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf traffic

OSPFv3 header errors
Length 0, Checksum 0, Version 0, No Virtual Link 0,
Area Mismatch 0, Self Originated 0, Duplicate ID 0,
Instance ID 0, Hello 0, MTU Mismatch 0,
Nbr Ignored 0, Authentication 0,
OSPFv3 LSA errors
Type 0, Length 0, Data 0, Checksum 0,
The network administrator wants to start collecting new statistics, resetting the counters and clearing
the traffic statistics by entering the clearipv6ospftraffic command as follows:
Router# clear ipv6 ospf traffic
The table below describes the significant fields shown in the display.
Table 34: show ipv6 ospf traffic Field Descriptions
DescriptionField
Traffic statistics accumulated for all OSPF processes running on the router.
To ensure compatibility with the showiptraffic command, only checksum
errors are displayed. Identifies the route map name.
OSPFv3 statistics
Queue statistics specific to Cisco IOS software.OSPFv3 queues statistic for
process ID
Statistics for the internal Cisco IOS queue between the packet switching
code (process IP Input) and the OSPF hello process for all received OSPF
packets.
Hello queue
Statistics for the internal Cisco IOS queue between the OSPF hello process
and the OSPF router for all received OSPF packets except OSPF hellos.
Router queue
Actual size of the queue.queue size
Maximum allowed size of the queue.queue limit
Maximum recorded size of the queue.queue max size
Per-interface traffic statistics for all interfaces that belong to the specific
OSPFv3 process ID.
Interface statistics
Number of OSPFv3 packets received and sent on the interface, sorted by
packet types.
OSPFv3 packets received/sent
Packet appears in this section if it was discarded because of an error in the
header of an OSPFv3 packet. The discarded packet is counted under the
appropriate discard reason.
OSPFv3 header errors
Packet appears in this section if it was discarded because of an error in the
header of an OSPF link-state advertisement (LSA). The discarded packet
is counted under the appropriate discard reason.
OSPFv3 LSA errors
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
227
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf traffic

DescriptionField
Summary traffic statistics accumulated for an OSPFv3 process.
The OSPF process ID is a unique value assigned to the OSPFv3
process in the configuration.
Note
The value for the received errors is the sum of the OSPFv3 header errors
that are detected by the OSPFv3 process, unlike the sum of the checksum
errors that are listed in the global OSPF statistics.
Summary traffic statistics for
process ID
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Clears OSPFv2 traffic statistics.clear ip ospf traffic
Clears OSPFv3 traffic statistics.clear ipv6 ospf traffic
Displays OSPFv2 traffic statistics.show ip ospf traffic
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
228
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ipv6 ospf traffic

show ospfv3 multi-area
To display information about the Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) multiarea interfaces, use the
show ospfv3 multi-area command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ospfv3 multi-area
Command Default
No OSPFv3 multiarea interface information is displayed.
Command Modes
User EXEC (>)
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was
introduced.
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.11S
Example
The following example shows sample output from the show ospfv3 multi-area command:
Device# show ip ospf 1 multi-area
OSPF_MA1 is up, line protocol is up
Primary Interface Ethernet0/0, Area 100
Interface ID 7
MTU is 1500 bytes
Neighbor Count is 1
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Specifies the cost of sending a packet on an OSPFv3
multiarea interface.
ospfv3 multi-area cost
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
229
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ospfv3 multi-area

show ospfv3 sham-links
To display parameters and the current state of Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) sham links, use
the show ospfv3 sham-links command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode.
show ospfv3 [process-id] [address-family] [vrf {vrf-name | *}] sham-links
Syntax Description
(Optional) Internal identification. The number used here is the number assigned
administratively when enabling the OSPFv3 routing process and can be a value from 1
through 65535.
process-id
(Optional) Enter ipv6 for the IPv6 address family or ipv4 for the IPv4 address family.address-family
(Optional) VPN Routing/Forwarding instance.vrf
The virtual routing and forwarding table for which the information should be displayed.
If this parameter is not specified, only information for the global routing table is shown.
A VRF name of "*" displays information for all VRFs, including the global table.
{vrf-name | *}
Command Modes
User EXEC or Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)S.15.2(4)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M.15.2(4)M
Examples
The following example displays OSPFv3 sham-link information for all VRFs:
Router# show ospfv3 vrf * sham-links
OSPFv3 1 address-family ipv6 vrf v1 (router-id 8.0.0.22)
Sham Link OSPFv3_SL1 to address 2001:111::824 is up
Interface ID 39
Area 0 source address 2001:111::822
Run as demand circuit
DoNotAge LSA allowed.
Cost of using 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT,
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed)
Index 1/2/2, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 0
First 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Table 1
show ospfv3 virtual-links Field Descriptions Field Description
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
230
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ospfv3 sham-links

Sham Link OSPFv3_SL1 to address 2001:111::824 is up Specifies the
OSPFv3 neighbor, and if the link to that neighbor is up or down.
Interface ID Interface ID and IPv6 address of the router.
Area 0 source address 2001:111::822 The area the sham link is in and the IPv6 source address
of the local
endpoint.
Cost of using 1 The cost of reaching the OSPFv3 neighbor through the sham link.
Transmit Delay is 1 sec The transmit delay (in seconds) on the sham link.
State POINT_TO_POINT The state of the OSPFv3 neighbor.
Timer intervals... The various timer intervals configured for the link.
Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed) The neighbor adjacency state.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
231
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show ospfv3 sham-links

show tech-support ospf
To run show commands that display OSPF information that is useful to Cisco Technical Support personnel
in resolving issues, use the show tech-support ospf command in the privileged EXEC mode.
show tech-support ospf [vrf vrf-instance-name][process-id][detail]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Displays tech-support information for a VPN Routing/Forwarding instance.
If you enter vrf vrf-instance-name with the show tech-support ospf command, the
following commands are executed for the specified VRF:
• show ip route summary vrf vrf-instance-name
• show ip route ospf vrf vrf-instance-name
If you do not enter vrf vrf-instance-name with the show tech-support ospf command,
show ip route summary and show ip route ospf are executed for the default VRF.
vrf
vrf-instance-name
(Optional) ID of the OSPF process.process-id
(Optional) Displays detailed OSPF information.
If you enter the detail keyword with the show tech-support ospf command, the
OSPF-related show commands are run to provide more detailed output. However, the
detail keyword has no effect on the output of show ip route summary and show ip
route ospf .
detail
Command Default
If you do not specify any options, all OSPF information is collected.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
ModificationRelease
Functionality to display OSPF information for a VRF instance introduced.Cisco IOS XE
Gibraltar 16.12.1a
Usage Guidelines
This command generates tech-support information that is useful for Cisco Technical Support representatives
when troubleshooting OSPF issues on a router.
This command can generate a very large amount of output. You may want to redirect the output to a file using
the file send-to keyword and argument. Redirecting the output to a file also makes sending the output to your
Cisco Technical Support representative easier.
Tip
This command is not required during normal use of the router.
Note
The following show commands run automatically when you run the show tech-support ospf command:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
232
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show tech-support ospf

• show ip ospf
• show ip ospf neighbor
• show ip ospf interface
• show ip ospf database database-summary
• show ip ospf max-metric
• show ip ospf multi-area
• show ip ospf border-routers
• show ip ospf fast-reroute
• show ip ospf fast-reroute prefix-summary
• show ip ospf neighbor fast-reroute
• show ip ospf fast-reroute remote-lfa tunnels internal
• show ip ospf fast-reroute ti-lfa
• show ip ospf fast-reroute ti-lfa tunnels
• show ip ospf fast-reroute ti-lfa tunnels internal all
• show ip ospf summary-address
• show ip ospf virtual-links
• show ip ospf statistic
• show ip ospf topology-info
• show ip ospf traffic
• show ip ospf rib
• show ip ospf rib redistribution
• show ip route summary
• show ip route ospf
• show interfaces
• show ip ospf flood-list
• show ip ospf request-list
• show ip ospf retransmission-list
• show ip ospf database
• show ip ospf segment-routing
• show ip ospf segment-routing conflicts internal
• show ip ospf segment-routing global-block
• show ip ospf segment-routing local-prefix
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
233
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show tech-support ospf

• show ip ospf segment-routing mapping-server
• show ip ospf segment-routing protected-adjacencies
• show ip ospf segment-routing sid-database internal
• show segment-routing mpls connected-prefix-sid-map ipv4
• show segment-routing mpls connected-prefix-sid-map protocol backup ipv4
• show segment-routing mpls mapping-server ipv4
• show segment-routing mpls mapping-server remote backup ipv4
• show mpls traffic-eng segment-routing ospf
• show mpls traffic-eng segment-routing prefix
• show ip ospf database dist-ls-pending
• show ip ospf ls-distribution
• show ip ospf database
• show ip ospf database database-summary
• show ip ospf database router
• show ip ospf database network
• show ip ospf database summary
• show ip ospf database external
• show ip ospf database asbr-summary
• show ip ospf database nssa-external
• show ip ospf database opaque-area
• show ip ospf database opaque-as
• show ip ospf database opaque-link
• show ip ospf maxage-list
• show ip ospf route-list
• show ip ospf bad-checksum
• show ip ospf mpls ldp interface
• show ip ospf mpls traffic-eng fragment
• show ip ospf mpls traffic-eng link
• show ip ospf nsf
• show ip ospf sham-links
• show ip ospf timers rate-limit
• show ip ospf timers lsa-group
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
234
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show tech-support ospf

• show ip ospf events
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
235
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
show tech-support ospf

shutdown (router OSPF)
To initiate a graceful shutdown of the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol under the current instance,
use the shutdown command in router configuration mode. To restart the OSPF protocol, use the noform of
this command.
shutdown
no shutdown
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
OSPF stays active under the current instance.
Command Modes
Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
Usage Guidelines
Use the shutdown command in router configuration mode to temporarily shut down a protocol in the least
disruptive manner and to notify its neighbors that it is going away. All traffic that has another path through
the network will be directed to that alternate path.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable a graceful shutdown of the OSPF protocol:
Router(config
)
# router ospf 1
Router(config-router
)
# shutdown
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Initiates a graceful shutdown on a specific OSPF interface.ip ospf shutdown
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
236
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
shutdown (router OSPF)

snmp-server enable traps ospf
T o enable all Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First
(OSPF), use the snmp-server enable traps ospfcommand in global configuration mode. To disable all SNMP
notifications for OSPF, use the noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf
no snmp-server enable traps ospf
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPF are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(30)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T.12.3(14)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
Usage Guidelines
If you wish to enable or disable specific OSPF SNMP notifications, enter one or more of the following
commands of the following commands:
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
[no] snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Examples
The following exampleglobally enables SNMP notifications for OSPF:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
237
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
errors config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs.snmp-server enable trapsospf cisco-specific lsa
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF errors.snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
Limits the number of OSPF traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF packet
retransmissions.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
238
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf

snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
configuration mismatch errors, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errorscommand in
global configuration mode. To disable SNMP notifications for OSPF configuration mismatch errors, use the
noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors [config-error] [virt-config-error]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors [config-error] [virt-config-error]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for configuration mismatch errors on
nonvirtual interfaces.
config-error
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for configuration mismatch errors on virtual
interfaces.
virt-config-error
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPF configuration mismatch errors are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(30)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T.12.3(14)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
Usage Guidelines
To enable the SNMP notifications for OSPF configuration errors for both virtual and nonvirtual interfaces,
enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errorscommand in global configuration mode without
the optional keywords.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send OSPF configuration mismatch errors only for
nonvirtual interfaces:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables all SNMP notifications for OSPF.snmp-server enable traps ospf
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
239
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors

DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF errors.snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
Limits the number of OSPF traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF packet
retransmissions.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
240
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors

snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error
To e nable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
nonvirtual interface mismatch errors, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
config-errorcommand in global configuration mode. To disable OSPF nonvirtual interface mismatch error
SNMP notifications, use the no form of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error
no snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords or arguments.
Command Default
This command is disabled by default; therefore, SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual interface mismatch
errors are not created.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(5)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(26)S.12.0(26)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Usage Guidelines
To enable the cospfShamLinkConfigError trap, you must first enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf
cisco-specific errors config-error command in global configuration mode. The snmp-server enable traps
ospf cisco-specific errors config-error command enables the cospfConfigError trap, so that both traps can
be generated at the same place and maintain consistency with a similar case for configuration errors across
virtual links.
If you try to enable the cospfShamLinkConfigError trap before configuring the cospfospfConfigError trap
you will receive an error message stating you must first configure the cospfConfigError trap.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send nonvirtual interface mismatch error notifications
to the host at the address myhost.cisco.com using the community string defined as public:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error
Router(config)# snmp-server host myhost.cisco.com informs version 2c public
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
241
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF sham-link
errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
shamlink
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF retransmission
errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
242
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error

snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
sham-link errors, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlinkcommand in global
configuration mode. To disable OSPF sham-link error SNMP notifications, use the noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink [authentication [bad-packet]
[{[config] | config [bad-packet]}]]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink [authentication [bad-packet]
[{[config] | config [bad-packet]}]]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for authentication failures on OSPF sham-link
interfaces.
authentication
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for packet parsing failures on OSPF sham-link
interfaces.
bad-packet
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for configuration mismatch errors on OSPF
sham-link interfaces.
config
Command Default
This command is disabled by default; therefore, SNMP notifications for OSPF sham-link errors are not created.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(30)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T.12.3(14)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Usage Guidelines
To enable the cospfShamLinkConfigError trap, you must first enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf
cisco-specific errors config-error command in global configuration mode. The snmp-server enable traps
ospf cisco-specific errors config-error command enables the cospfConfigError trap, so that both traps can
be generated at the same place and maintain consistency with a similar case for configuration errors across
virtual links.
If you try to enable the cospfShamLinkConfigError trap before configuring the cospfospfConfigError trap
you will receive an error message stating you must first configure the cospfConfigError trap.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send OSPF sham-link error notifications to the host at
the address myhost.cisco.com using the community string defined as public:
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
243
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink

Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors config-error
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink
Router(config)# snmp-server host myhost.cisco.com informs version 2c public
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-serverenable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF retransmission
errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
244
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors shamlink

snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
opaque link-state advertisements (LSAs), use the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsacommand
in global configuration mode. To disable SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs, use the noform of this
command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa [lsa-maxage] [lsa-originate]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa [lsa-maxage] [lsa-originate]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for opaque OSPF LSAs that have reached the
maximum age.
lsa-maxage
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for opaque OSPF LSAs that are newly originated.lsa-originate
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(30)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(14)T.12.3(14)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
Usage Guidelines
The snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa command enables the traps that are defined by the
CISCO-OSPF-TRAP-MIB for opaque LSAs. An opaque link-state advertisement (LSA) is used in MPLS
traffic engineering to distribute attributes such as capacity and topology of links in a network. The scope of
this LSA can be confined to the local network (Type 9, Link-Local), OSPF area (Type 20, Area-Local), or
Autonomous System (Type 11, AS scope). The information in an opaque LSA can be used by an external
application across the OSPF network. To enable the cospfMaxAgeLsa trap, enter the snmp-server enable
traps ospf cisco-specific lsacommand with the lsa-maxage keyword. To enable the cospfOriginateLsa trap,
enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsacommand with the lsa-originate keyword. When
you enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa command without either keyword, both traps
will be enabled.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send OSPF opaque LSA notifications to the host at the
address myhost.cisco.com using the community string defined as public whenever new opaque LSAs
are created:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa lsa-originate
Router(config)# snmp-server host myhost.cisco.com informs version 2c public
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
245
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables all SNMP notifications for OSPF.snmp-server enable traps ospf
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF errors.snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
Limits the number of OSPF traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF packet
retransmissions.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Specifies a recipient (target host) for SNMP notification
operations.
snmp-server host
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
246
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa

snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
retransmission errors, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmitcommand in global
configuration mode. To disable OSPF sham-link error SNMP notifications, use the noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit [{packets [{shamlink | virt-packets}] |
shamlink [{packets | virt-packets}] | virt-packets [shamlink]}]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit [{packets [{shamlink | virt-packets}]
| shamlink [{packets | virt-packets}] | virt-packets [shamlink]}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for packet retransmissions on nonvirtual
interfaces.
packets
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for sham-link retransmission notifications.shamlink
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications only for packet retransmissions on virtual interfaces.virt-packets
Command Default
This command is disabled by default; therefore, SNMP notifications for OSPF retransmission errors are not
created.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(5)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(26)S.12.0(26)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
The shamlink keyword and related options were added.12.0(30)S
Support was added for the shamlink keyword and related options.12.3(14)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Examples
The following example enables the router to send OSPF sham-link retransmission notifications:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit shamlink
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
247
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF sham-link
errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
shamlink
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
248
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific retransmit

snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
transition state changes, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-changecommand in
global configuration mode. To disable OSPF transition state change SNMP notifications, use the noform of
this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specif ic state-change [{nssa-trans-change | shamlink [{interface
| interface-old | neighbor}]}]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change [{nssa-trans-change | shamlink
[{interface | interface-old | neighbor}]}]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables only not-so-stubby area (NSSA) translator state changes trap for
the OSPF area.
nssa-trans-change
(Optional) Enables only the sham-link transition state changes trap for the OSPF area.shamlink
(Optional) Enables only the sham-link interface state changes trap for the OSPF area.interface
(Optional) Enables only the replaced interface transition state changes trap for the
OSPF area.
interface -old
(Optional) Enables only the sham-link neighbor transition state changes trap for the
OSPF area.
neighbor
Command Default
This command is disabled by default; therefore, SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state changes are
not created.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(5)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(26)S.12.0(26)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
The shamlink, interface-old, and neighbor keywords were added.12.0(30)S
Support was added for the shamlink, interface-old, and neighbor keywords.12.3(14)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH.12.2(33)SXH
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
249
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change

Usage Guidelines
You cannot enter both the interface and interface-old keywords because you cannot enable both the new
and replaced sham-link interface transition state change traps. You can configure only one of the two traps,
but not both.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send OSPF sham-link transition state change notifications
to the host at the address myhost.cisco.com using the community string defined as public:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change shamlink
Router(config)# snmp-server host myhost.cisco.com informs version 2c public
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF sham-link
errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific errors
shamlink
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF retransmission
errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
250
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific state-change

snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
errors, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf errorscommand in global configuration mode. To disable
SNMP notifications for OSPF errors, use the noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf errors [authentication-failure] [bad-packet] [config-error]
[virt-authentication-failure] [virt-bad-packet] [virt-config-error]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf errors [authentication-failure] [bad-packet] [config-error]
[virt-authentication-failure] [virt-bad-packet] [virt-config-error]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables only the ospfIfFailure trap. Allows SNMP notifications to
be sent when a packet has been received on a nonvirtual interface from a neighbor
router whose authentication key or authentication type conflicts with the
authentication key or authentication type of this router.
authentication-failure
(Optional) Enables only the ospfIfRxBadPacket trap. Allows SNMP notifications
to be sent when an OSPF packet that has not been parsed has been received on
a nonvirtual interface.
bad-packet
(Optional) Enables only the ospfIfConfigError trap. Sends SNMP notifications
when a packet has been received in a nonvirtual interface from a neighbor router
whose configuration parameters conflict with the configuration parameters of
this router.
config-error
(Optional) Enables only the ospfVirtIfFailure trap. Allows SNMP notifications
to be sent when a packet has been received on a virtual interface from a neighbor
router whose authentication key or authentication type conflicts with the
authentication key or authentication type of this router.
virt-authentication-failure
(Optional) Enables only the ospfVirtIfRxBadPacket trap. Allows SNMP
notifications to be sent when an OSPF packet that has not been parsed has been
received on a virtual interface.
virt-bad-packet
(Optional) Enables only the ospfVirtIfConfigError trap. Sends SNMP
notifications when a packet has been received in a virtual interface from a
neighbor router whose configuration parameters conflict with the configuration
parameters of this router.
virt-config-error
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPF errors are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(5)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(26)S. Support was added for the
OSPF MIB.
12.0(26)S
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
251
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf errors

ModificationRelease
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
Usage Guidelines
When you enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf errors command without any optional keywords, all
OSPF error traps will be enabled. To enable only one or more OSPF error traps, enter one or more of the
optional keywords.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send all OSPF error notifications:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables all SNMP notifications for OSPF.snmp-server enable traps ospf
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
errors config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
Limits the number of OSPF traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF packet
retransmissions.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
252
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf errors

snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
link-state advertisements (LSAs), use the snmp-server enable traps ospf lsacommand in global configuration
mode. To disable SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs, use the noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa [lsa-maxage] [lsa-originate]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa [lsa-maxage] [lsa-originate]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables only the ospfMaxAgeLsa trap. Allows SNMP notifications to be sent
when an LSA in the OSPF link-state database of the router has reached the maximum age.
lsa-maxage
(Optional) Enables only the ospfOriginateLsa trap. Enables SNMP notifications when a new
LSA has been originated by the router as a result of a topology change.
lsa-originate
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.3(5)
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(26)S. Support was added for the
OSPF MIB.
12.0(26)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
Usage Guidelines
The snmp-server enable traps ospf lsacommand enables the traps for standard LSAs that are defined by the
OSPF-MIB. To enable the ospfMaxAgeLsa trap, enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf lsacommand with
the lsa-maxage keyword. To enable the ospfOriginateLsa trap, enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf
lsacommand with the lsa-originate keyword. When the ospfOriginateLsa trap is enabled, it will not be invoked
for simple LSA refreshes that take place every 30 minutes or when an LSA has reached its maximum age and
is being flushed. When you enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa command without either keyword,
both traps will be enabled.
To enable the traps that are defined by the CISCO-OSPF-TRAP-MIB for opaque LSAs, enter the snmp-serv er
enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsacommand in global configuration mode.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send SNMP notifications when new LSAs are originated
by the router as a result of a topology change:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa lsa-originate
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
253
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables all SNMP notifications for OSPF.snmp-server enable traps ospf
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
errors config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs.snmp-serverenable trapsospf cisco-specific lsa
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF errors.snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Limits the number of OSPF traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF packet
retransmissions.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
254
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa

snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
T o limit the number of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) traps that are sent during a specified number of
seconds, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limitcommand in global configuration mode. To disable
the limit placed on the number of OSPF traps sent during a specified number of seconds, use the noform of
this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit seconds trap-number
no snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit seconds trap-number
Syntax Description
Sets the rate limit window size, in seconds. A number from 2 to 60. The default value is 10.seconds
Sets the maximum number of traps sent during the window time. A number from 0 to 300.
The default number is 7.
trap-number
Command Default
No limit is placed on the number of OSPF traps sent.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(26)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
Usage Guidelines
There is a possibility that a router sends trap bursts, which can drain network resources in a small interval of
time. It is recommended that you enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit command to configure
a sliding window mechanism that will limit the number of traps that are sent within a specified number of
seconds.
Examples
The following example sets the trap rate limit window so that during a 40-second window of time,
no more that 50 traps are sent.
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit 40 50
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables all SNMP notifications for OSPF.snmp-server enable traps ospf
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
errors config-error
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
255
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit

DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF errors.snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF packet
retransmissions.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
256
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit

snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications when packets are re-sent in an Open
Shortest Path First (OSPF) network, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmitcommand in global
configuration mode. To disable SNMP notifications, use the noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit [packets] [virt-packets]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit [packets] [virt-packets]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables only the ospfTxRetransmit trap. Allows SNMP notifications to be sent
when an OSPF packet has been re-sent on a nonvirtual interface.
packets
(Optional) Enables only the ospfVirtTxRetransmit trap. Allows SNMP notifications to be
sent when an OSPF packet has been re-sent on a virtual interface.
virt-packets
Command Default
SNMP notifications are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(26)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(31)SB2.12.2(31)SB2
Usage Guidelines
To enable the ospfTXRetransmit trap so that SNMP notifications are sent only when packets from nonvirtual
interfaces are re-sent, enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmitcommand with the packets
keyword. To enable the ospfTxRetransmit trap so that SNMP notifications are sent only when packets from
virtual interfaces are re-sent, enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmitcommand with the
virt-packets keyword. When you enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit command without
either keyword, both traps will be enabled.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send SNMP notifications when packets are re-sent by
virtual interfaces:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit virt-packets
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables all SNMP notifications for OSPF.snmp-server enable traps ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
257
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit

DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
errors config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF errors.snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
Limits the number of OSPF traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
258
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit

snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
T o enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
transition state changes, use the snmp-server enable traps ospf state-changecommand in global configuration
mode. To disable SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state changes, use the noform of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change [if-state-change] [neighbor-state-change]
[virtif-state-change] [virtneighbor-state-change]
no snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change [if-state-change] [neighbor-state-change]
[virtif-state-change] [virtneighbor-state-change]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables only the ospfIfStateChange trap. Sends SNMP notifications
when there has been a change in the state of a nonvirtual OSPF interface.
if-state-change
(Optional) Enables only the ospfNbrStateChange trap. Sends SNMP
notifications when there has been a change in the state of a nonvirtual OSPF
neighbor.
neighbor-state-change
(Optional) Enables only the ospfVirtIfStateChange trap. Sends SNMP
notifications when there has been a change in the state of a virtual OSPF
interface.
virtif-state-change
(Optional) Enables only the ospfVirtNbrStateChange trap. Sends SNMP
notifications when there has been a change in the state of a virtual OSPF
neighbor.
virtneighbor-state-change
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPF transition state changes are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(26)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(4)T.12.3(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)S.12.2(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
Usage Guidelines
To enable all traps for transition state changes, enter the snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change
command without of the optional keywords.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send SNMP notifications for transition state changes
for virtual interfaces and virtual neighbors:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change virtif-state-change
virtneighbor-state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
259
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables all SNMP notifications for OSPF.snmp-server enable traps ospf
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF nonvirtual
interface mismatch errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
errors config-error
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF opaque LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific lsa
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
retransmission errors.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
retransmit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF Cisco-specific
transition state changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospf cisco-specific
state-change
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF errors.snmp-server enable traps ospf errors
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF LSAs.snmp-server enable traps ospf lsa
Limits the number of OSPF traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospf rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPF packet
retransmissions.
snmp-server enable traps ospf retransmit
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
260
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server enable traps ospf state-change

snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 errors
To enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First version
3 (OSPFv3) errors, use the snmp-serverenable traps ospfv3 errors command in global configuration mode.
To disable SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 errors, use the no form of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors [bad-packet] [config-error] [virt-bad-packet]
[virt-config-error]
no snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors [bad-packet] [config-error] [virt-bad-packet]
[virt-config-error]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications to be sent when an OSPFv3 packet that could
not be parsed has been received on a nonvirtual interface.
bad-packet
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when a packet has been received in a nonvirtual
interface from a neighbor router whose configuration parameters conflict with the
configuration parameters of this router.
config-error
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications to be sent when an OSPFv3 packet that could
not be parsed has been received on a virtual interface.
virt-bad-packet
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when a packet has been received in a virtual
interface from a neighbor router whose configuration parameters conflict with the
configuration parameters of this router.
virt-config-error
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 errors are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration (config)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.2(4)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)S.15.2(4)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S
Usage Guidelines
When you enter the snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors command without any optional keywords, all
OSPFv3 error traps will be enabled. To enable only one or more OSPFv3 error traps, enter one or more of
the optional keywords.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send all OSPFv3 error notifications:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
261
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 errors

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Limits the number of OSPFv3 traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 rate-limit
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 transition state
changes.
snmp-serverenable trapsospfv3 state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
262
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 errors

snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 rate-limit
To limit the number of Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) traps that are sent during a specified
number of seconds, use the snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 rate-limit command in global configuration
mode. To disable the limit placed on the number of OSPF traps sent during a specified number of seconds,
use the no form of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 rate-limit seconds trap-number
no snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 rate-limit
Syntax Description
Sets the rate limit window size, in seconds. The range is from 2 to 60. The default value is
10.
seconds
Sets the maximum number of traps sent during the window time. The range is from 0 to 300.
The default number is 7.
trap-number
Command Default
No limit is placed on the number of OSPFv3 traps sent.
Command Modes
Global configuration (config)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.2(4)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)S.15.2(4)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S
Usage Guidelines
There is a possibility that a router sends trap bursts, which can drain network resources in a small interval of
time. We recommend that you enter the snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 rate-limit command to configure
a sliding window mechanism that will limit the number of traps that are sent within a specified number of
seconds.
Examples
The following example sets the trap rate limit window so that during a 40-second window of time,
no more than 50 traps are sent.
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 rate-limit 40 50
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 errors.snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 transition state
changes.
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
263
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 rate-limit

snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 state-change
To enable Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) notifications for Open Shortest Path First Version
3 (OSPFv3) transition state changes, use the snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change command in
global configuration mode. To disable SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 transition state changes, use the no
form of this command.
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change [if-state-change]
[neighbor-restart-helper-status-change] [neighbor-state-change] [nssa-translator-status-change]
[restart-status-change] [virtif-state-change] [virtneighbor-restart-helper-status-change]
[virtneighbor-state-change]
no snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change [if-state-change]
[neighbor-restart-helper-status-change] [neighbor-state-change] [nssa-translator-status-change]
[restart-status-change] [virtif-state-change] [virtneighbor-restart-helper-status-change]
[virtneighbor-state-change]
Syntax Description
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when there has been a
change in the state of a nonvirtual OSPFv3 interface.
if-state-change
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when there has been a
change in the status of a neighbor graceful restart helper.
neighbor-restart-helper-status-change
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when there has been a
change in the state of a nonvirtual OSPFv3 neighbor.
neighbor-state-change
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when there has been a
change in the status of a NSSA translator.
nssa-translator-status-change
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when there has been a
change in the graceful restart status.
restart-status-change
(Optional) SNMP notifications when there has been a change
in the state of a virtual OSPFv3 interface.
virtif-state-change
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when there has been a
change in the status of a virtual OSPFv3 neighbor restart helper.
virtneighbor-restart-helper-status-change
(Optional) Enables SNMP notifications when there has been a
change in the state of a virtual OSPFv3 neighbor.
virtneighbor-state-change
Command Default
SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 transition state changes are disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration (config)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.15.2(4)M
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)S.15.2(4)S
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
264
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 state-change

ModificationRelease
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S.Cisco IOS XE Release 3.7S
Usage Guidelines
To enable all traps for transition state changes, enter the snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change
command without any of the optional keywords.
Examples
The following example enables the router to send SNMP notifications for all transition state changes:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 state-change
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Enables SNMP notifications for OSPFv3 errors.snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 errors
Limits the number of OSPFv3 traps that are sent during a
specified number of seconds.
snmp-server enable traps ospfv3 rate-limit
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
265
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
snmp-server snmp traps ospfv3 state-change

summary-address (OSPF)
To create aggregate addresses for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), use the summary-address command in
router configuration mode. To restore the default, use the no form of this command.
summary-address commandsummary-address {ip-address mask | prefix mask} [not-advertise] [tag
tag] [nssa-only]
no summary-address {ip-address mask | prefix mask} [not-advertise] [tag tag] [nssa-only]
Syntax Description
Summary address designated for a range of addresses.ip-address
IP subnet mask used for the summary route.mask
IP route prefix for the destination.prefix
(Optional) Suppresses routes that match the specified prefix/mask pair. This keyword applies
to OSPF only.
not-advertise
(Optional) Specifies the tag value that can be used as a “match” value for controlling
redistribution via route maps. This keyword applies to OSPF only.
tag tag
(Optional) Sets the nssa-only attribute for the summary route (if any) generated for the
specified prefix, which limits the summary to not-so-stubby-area (NSSA) areas.
nssa-only
Command Default
This command behavior is disabled by default.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.10.0
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
This command was modified. The nssa-only keyword was added.15.0(1)M
Usage Guidelines
R outes learned from other routing protocols can be summarized. The metric used to advertise the summary
is the lowest metric of all the more specific routes. This command helps reduce the size of the routing table.
Using this command for OSPF causes an OSPF Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) to advertise
one external route as an aggregate for all redistributed routes that are covered by the address. For OSPF, this
command summarizes only routes from other routing protocols that are being redistributed into OSPF. Use
the area range command for route summarization between OSPF areas.
OSPF does not support the summary-address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0command.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
266
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
summary-address (OSPF)

Examples
In the following example, the summary address 10.1.0.0 includes address 10.1.1.0, 10.1.2.0, 10.1.3.0,
and so on. Only the address 10.1.0.0 is advertised in an external link-state advertisement.
summary-address 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Consolidates and summarizes routes at an area boundary.area range
Assigns a password to be used by neighboring routers that are using the simple
password authentication of OSPF.
ip ospf authentication-key
Enables OSPF MD5 authentication.ip ospf message-digest-key
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
267
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
summary-address (OSPF)

timers lsa arrival
To set the minimum interval at which the software accepts the same link-state advertisement (LSA) from
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) neighbors, use the timerslsa arrivalcommand in router configuration mode.
To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
timers lsa arrival milliseconds
no timers lsa arrival
Syntax Description
Minimum delay in milliseconds that must pass between acceptance of the same LSA arriving
from neighbors. The range is from 0 to 600,000 milliseconds. The default is 1000 milliseconds.
milliseconds
Command Default
1000 milliseconds
Command Modes
OSPF for IPv6 router configuration (config-rtr) Router configuration (config-router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(27)SBC.12.2(27)SBC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in
a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and
platform hardware.
12.2SX
Support for IPv6 was added.12.2(33)SRC
Support for IPv6 was added.12.2(33)SB
This command was introduced on Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.5(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was modified. It was integrated into Cisco IOS Release
12.2(33)XNE.
12.2(33)XNE
Usage Guidelines
The timers lsa arrival command controls the minimum interval for accepting the same LSA. The “same
LSA” is defined as an LSA instance that contains the same LSA ID number, LSA type, and advertising router
ID. If an instance of the same LSA arrives sooner than the interval that is set, the LSA is dropped.
We suggest you keep the millisecondsvalue of the timers lsa arrival command less than or equal to the
neighbors’ hold-interval value of the timers throttle lsa all command.
Examples
The following example sets the minimum interval for accepting the same LSA at 2000 milliseconds:
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
268
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers lsa arrival

timers throttle lsa all 200 10000 45000
timers lsa arrival 2000
network 10.10.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 24
network 10.10.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 24
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays all of the LSAs in the rate limit queue.show ip ospf timers rate-limit
Displays all of the LSAs in the IPv6 rate limit queueshow ipv6 ospf timers rate-limit
Sets rate-limiting values for OSPF for IPv6 LSA generation.timers throttle lsa
Sets rate-limiting values for LSAs being generated.timers throttle lsa all
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
269
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers lsa arrival

timers pacing flood
To configure link-state advertis ement (LSA) flood packet pacing, use the timers pacing flood command in
router configuration mode. To restore the default flood packet pacing value, use the no form of this command.
timers pacing flood milliseconds
no timers pacing flood
Syntax Description
Time (in milliseconds) at which LSAs in the flooding queue are paced in between updates.
The configurable range is from 5 milliseconds to 100 milliseconds. The default value is 33
milliseconds.
milliseconds
Command Default
33 milliseconds
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S.12.2(14)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
Configuring Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) flood pacing timers allows you to control interpacket spacing
between consecutive link-state update packets in the OSPF transmission queue. This command allows you
to control the rate at which LSA updates occur so that high CPU or buffer utilization that can occur when an
area is flooded with a very large number of LSAs can be reduced.
The default settings for OSPF packet pacing timers are suitable for the majority of OSPF deployments. Do
not change the packet pacing timers unless all other options to meet OSPF packet flooding requirements have
been exhausted. Specifically, network operators should prefer summarization, stub area usage, queue tuning,
and buffer tuning before changing the default flood timers. Furthermore, there are no guidelines for changing
timer values; each OSPF deployment is unique and should be considered on a case-by-case basis. The network
operator assumes risks associated with changing the default flood timer values.
Examples
The following example configures LSA flood packet-pacing updates to occur in 55-millisecond
intervals for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing process 1:
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# timers pacing flood 55
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays general information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
270
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers pacing flood

DescriptionCommand
Changes the interval at which OSPF LSAs are collected into a group and
refreshed, checksummed, or aged.
timers pacing lsa-group
Configures LSA retransmission packet pacing.timers pacing retransmission
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
271
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers pacing flood

timers pacing lsa-group
To change th e interval at which Open Shortest Path First ( OSPF) link-state advertisements (LSAs) are
collected into a group and refreshed, checksummed, or aged, use the timers pacing lsa-groupcommandin
router configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
timers pacing lsa-group seconds
no timers pacing lsa-group
Syntax Description
Number of seconds in the interval at which LSAs are grouped and refreshed, checksummed, or
aged. The range is from 10 to 1800 seconds. The default value is 240 seconds.
seconds
Command Default
The default interval for this command is 240 seconds. OSPF LSA group pacing is enabled by default.
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.11.3AA
The syntax of this command was changed from timers lsa-group-pacing to timers pacing
lsa-group.
12.2(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S.12.2(14)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
This command allows you to control the rate at which LSA updates occur so that high CPU or buffer utilization
that can occur when an area is flooded with a very large number of LSAs can be reduced. The default settings
for OSPF packet pacing timers are suitable for the majority of OSPF deployments. Do not change the packet
pacing timers unless all other options to meet OSPF packet flooding requirements have been exhausted.
Specifically, network operators should prefer summarization, stub area usage, queue tuning, and buffer tuning
before changing the default flooding timers. Furthermore, there are no guidelines for changing timer values;
each OSPF deployment is unique and should be considered on a case-by-case basis. The network operator
assumes the risks associated with changing the default timer values.
Cisco IOS software groups the periodic refresh of LSAs to improve the LSA packing density for the refreshes
in large topologies. The group timer controls the interval used for group refreshment of LSAs; however, this
timer does not change the frequency that individual LSAs are refreshed (the default refresh rate is every 30
minutes).
The duration of the LSA group pacing is inversely proportional to the number of LSAs the router is handling.
For example, if you have about 10,000 LSAs, decreasing the pacing interval would benefit you. If you have
a very small database (40 to 100 LSAs), increasing the pacing interval to 10 to 20 minutes might benefit you
slightly.
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
272
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers pacing lsa-group

Examples
The following example configures OSPF group packet-pacing updates between LSA groups to occur
in 60-second intervals for OSPF routing process 1:
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# timers pacing lsa-group 60
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays general information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Configures LSA flood packet pacing.timers pacing flood
Configures LSA retransmission packet pacing.timers pacing retransmission
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
273
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers pacing lsa-group

timers pacing retransmission
To configure link-state adv ertisement (LSA) retransmission packet pacing, use the timers pacing retransmission
command in router configuration mode. To restore the default retransmission packet pacing value, use the no
form of this command.
timers pacing retransmission milliseconds
no timers pacing retransmission
Syntax Description
The time (in milliseconds) at which LSAs in the retransmission queue are paced. The
configurable range is from 5 milliseconds to 200 milliseconds. The default value is 66
milliseconds.
milliseconds
Command Default
66 milliseconds
Command Modes
Router configuration
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(4)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S.12.2(14)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific
12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
Configuring Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) retransmission pacing timers allow you to control interpacket
spacing between consecutive link-state update packets in the OSPF retransmission queue. This command
allows you to control the rate at which LSA updates occur so that high CPU or buffer utilization that can occur
when an area is flooded with a very large number of LSAs can be reduced. The default settings for OSPF
packet retransmission pacing timers are suitable for the majority of OSPF deployments. Do not change the
packet retransmission pacing timers unless all other options to meet OSPF packet flooding requirements have
been exhausted. Specifically, network operators should prefer summarization, stub area usage, queue tuning,
and buffer tuning before changing the default flooding timers. Furthermore, there are no guidelines for changing
timer values; each OSPF deployment is unique and should be considered on a case-by-case basis. The network
operator assumes risks associated with changing the default packet retransmission pacing timer values.
Examples
The following example configures LSA flood pacing updates to occur in 55-millisecond intervals
for OSPF routing process 1:
Router(config)# router ospf 1
Router(config-router)# timers pacing retransmission 55
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays general information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
274
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers pacing retransmission

DescriptionCommand
Configures LSA flood packet pacing.timers pacing flood
Changes the interval at which OSPF LSAs are collected into a group and
refreshed, checksummed, or aged.
timers pacing lsa-group
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
275
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers pacing retransmission

timers throttle lsa all
To set rate-limiting values for all types of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) link-state advertisement (LSA)
generation, use the timers throttle lsa allcommand in router configuration mode. To restore the default values,
use the no form of this command.
timers throttle lsa all start-interval hold-interval max-interval
no timers throttle lsa all
Syntax Description
Minimum delay in milliseconds for the generation of LSAs. The first instance of LSA is
always generated immediately upon a local OSPF topology change. The generation of the
next LSA is not before the start interval. The range is 0 to 600,000 milliseconds. The default
is 0 milliseconds, which means no delay; the LSA is sent immediately.
start-interval
Incremental time in milliseconds. This value is used to calculate the subsequent rate limiting
times for LSA generation. The range is 1 to 600,000 milliseconds. The default value is 5000
milliseconds.
hold-interval
Maximum wait time in milliseconds between generation of the same LSA. The range is 1
to 600,000 milliseconds. The default value is 5000 milliseconds.
max-interval
Command Default
start-interval : 0 millisecondshold-interval:5000 millisecondsmax-interval: 5000 milliseconds
Command Modes
Router configuration (config router)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.0(25)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)T.12.3(2)T
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in a specific 12.2SX
release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and platform hardware.
12.2SX
Usage Guidelines
The “same LSA” is defined as an LSA instance that contains the same LSA ID number, LSA type, and
advertising router ID. We suggest you keep the millisecondsvalue of the timers lsa arrivalcommand less
than or equal to the hold-interval value of the timers throttle lsa all command.
Examples
This example customizes OSPF LSA throttling so that the start interval is 200 milliseconds, the hold
interval is 10,000 milliseconds, and the maximum interval is 45,000 milliseconds. The minimum
interval between instances of receiving the same LSA is 2000 milliseconds.
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
timers throttle lsa all 200 10000 45000
timers lsa arrival 2000
network 10.10.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 24
network 10.10.24.0 0.0.0.255 area 24
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
276
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers throttle lsa all

Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Displays information about OSPF routing processes.show ip ospf
Sets the minimum interval at which the software accepts the same LSA from OSPF
neighbors.
timers lsa arrival
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
277
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers throttle lsa all

timers throttle spf
To turn on Open Shortest Path First ( OSPF) shortest path first (SPF) throttling, use the timers throttle spf
command in the appropriate configuration mode. To turn off OSPF SPF throttling, use the no form of this
command.
timers throttle spf spf-start spf-hold spf-max-wait
no timers throttle spf spf-start spf-hold spf-max-wait
Syntax Description
Initial delay to schedule an SPF calculation after a change, in milliseconds. Range is from
1 to 600000. In OSPF for IPv6, the default value is 5000.
spf-start
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPF calculations, in milliseconds. Range is
from 1 to 600000. In OSPF for IPv6, the default value is 10,000.
spf-hold
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPF calculations, in milliseconds. Range is
from 1 to 600000. In OSPF for IPv6, the default value is 10,000.
spf-max-wait
Command Default
SPF throttling is not set.
Command Modes
Address family configuration (config-router-af) Router address family topology configuration
(config-router-af-topology) Router configuration (config-router) OSPF for IPv6 router configuration (config-rtr)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced. This command replaces the timers spf-interval
command.
12.2(14)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(23)S.12.0(23)S
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)T.12.2(15)T
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA.12.2(33)SRA
This command was made available in router address family configuration mode.12.2(33)SRB
This command is supported in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX train. Support in
a specific 12.2SX release of this train depends on your feature set, platform, and
platform hardware.
12.2SX
Support for IPv6 was added.12.2(33)SRC
Support for IPv6 was added and this command was integrated into Cisco IOS
Release 12.2(33)SB.
12.2(33)SB
This command was introduced on Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.5(1)M.15.0(1)M
This command was modified. It was integrated into Cisco IOS Release
12.2(33)XNE.
12.2(33)XNE
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
278
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers throttle spf

ModificationRelease
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.1(1)SY.15.1(1)SY
Usage Guidelines
The first wait interval between SPF calculations is the amount of time in milliseconds specified by the
spf-startargument. Each consecutive wait interval is two times the current hold level in milliseconds until the
wait time reaches the maximum time in milliseconds as specified by the spf-max-wait argument. Subsequent
wait times remain at the maximum until the values are reset or a link-state advertisement (LSA) is received
between SPF calculations.
Release 12.2(33)SRB
If you plan to configure the Multi-Topology Routing (MTR) feature, you need to enter the timers throttle
spf command in router address family topology configuration mode in order to make this OSPF router
configuration command become topology-aware.
Release 15.2(1)T
When you configure the ospfv3 network manet command on any interface attached to the OSPFv3 process,
the default values for the spf-start, spf-hold, and the spf-max-wait arguments are reduced to 1000 milliseconds,
1000 milliseconds, and 2000 milliseconds respectively.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure a router with the delay, hold, and maximum interval
values for the timers throttle spf command set at 5, 1000, and 90,000 milliseconds, respectively.
router ospf 1
router-id 10.10.10.2
log-adjacency-changes
timers throttle spf 5 1000 90000
redistribute static subnets
network 10.21.21.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 10.22.22.0 0.0.0.255 area 00
The following example shows how to configure a router using IPv6 with the delay, hold, and maximum
interval values for the timers throttle spf command set at 500, 1000, and 10,000 milliseconds,
respectively.
ipv6 router ospf 1
event-log size 10000 one-shot
log-adjacency-changes
timers throttle spf 500 1000 10000
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Sets the network type to Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET).ospfv3 network manet
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
279
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
timers throttle spf

ttl-security all-interfaces
To enable Time-to-Live (TTL) security check on all OSPF interfaces, use the ttl-security
all-interfacescommand in interface configuration mode. To disable TTL security check, use the noform of
this command.
ttl-security all-interfaces [hops hop-count]
no ttl-security all-interfaces
Syntax Description
(Optional) Configures the maximum number of IP hops allowed. The hop-countargument
range is from 1 to 254.
hops hop-count
Command Default
TTL security check is disabled on OSPF interfaces.
Command Modes
Interface configuration (config-if)
Command History
ModificationRelease
This command was introduced.12.2(33)SRC
This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M.15.0(1)M
Usage Guidelines
Use the ttl-security all-interfaces command to enable TTL security check on all OSPF interfaces.
This command applies only to normal OSPF interfaces. It does not apply to virtual or sham links that require
TTL security protection. Virtual and sham links must be configured independently.
As a convenience, this command can be used to globally enable TTL security check on all OSPF interfaces.
Then the ip ospf ttl-security disable command ininterface configuration mode can be used to disable TTL
security on an interface-by-interface basis.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable TTL security check on all OSPF interfaces:
Router(config
)
# router ospf 1
Router(config-router
)
# ttl-security all-interfaces
Related Commands
DescriptionCommand
Configures TTL security check on a specific interface.ip ospf ttl-security
Cisco IOS IP Routing: OSPF Command Reference
280
OSPF Commands: show ip ospf through T
ttl-security all-interfaces
