
[Page 41]
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
(This item omitted from WebBook edition)
3.1 Visual Basic Controls 42
z Starting a New Visual Basic Program
z A Text Box Walkthrough
z A Button Walkthrough
z A Label Walkthrough
z A List Box Walkthrough
z The Name Property
z A Help Walkthrough
z Fonts
z Auto Hide
z Positioning and Aligning Controls
3.2 Visual Basic Events 60
z An Event Procedure Walkthrough
z Properties and Event Procedures of the Form
z The Header of an Event Procedure
3.3 Numbers 73
z Arithmetic Operations
z Variables
z Incrementing the Value of a Variable
z Built-In Functions: Math.Sqrt, Int, Math.Round
z The Integer Data Type
z Multiple Declarations
Page 1 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

z Parentheses
z Three Types of Errors
3.4 Strings 88
z Variables and Strings
z Using Text Boxes for Input and Output
z Concatenation
z String Properties and Methods: Length Property and ToUpper,
ToLower, Trim, IndexOf, and Substring Methods
z The Empty String
z Initial Value of a String
z Option Strict
z Internal Documentation
z Line-Continuation Character
3.5 Input and Output 105
z Formatting Output with Format Functions
z Formatting Output with Zones
z Reading Data from Files
z Getting Input from an Input Dialog Box
z Using a Message Dialog Box for Output
z Using a Masked Text Box for Input
Summary 127
Programming Projects 128
[Page 42
]
3.1. Visual Basic Controls
Page 2 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Visual Basic programs display a Windows-style screen (called a for
m
) with boxes into which users type
(and in which users edit) information and buttons that they click to initiate actions. The boxes and
buttons are referred to as controls. In this section, we examine forms and four of the most useful Visual
Basic controls.
Starting a New Visual Basic Program
For our purposes, Visual Basic programs are also known as applications, solutions, or projects. Each
p
rogram is saved (as several files and subfolders) in its own folder. Before starting a new program, you
should use Windows Explorer to create a folder to hold the folders for your programs.
The process for invoking Visual Basic varies slightly with the edition of Visual Basic installed on the
computer. To invoke Visual Basic from a computer that has Visual Basic Express installed, click the
Windows Start button, hover over All Programs, and then click on Microsoft Visual Basic 2005 Express
Edition. With the other editions of Visual Basic, hover over All Programs, hover over Microsoft Visual
Studio 2005, and then click on Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 in the short list that is revealed.
The window that appears after Visual Basic is invoked has a menu bar whose first item is "File". Click
on File, and then click on New Project to produce a New Project input dialog box. Figure 3.1 shows the
N
ew Project input dialog box produced by Visual Basic Express. The "Windows Application" icon
should be selected as the installed template. If this is not the case, click on "Windows Application" to
select it. (The other editions of Visual Basic contain a pane identifying a Project type. You should select
"Visual Basic" as the Project type.)
Figure 3.1. The Visual Basic Express New Project input dialog box.
(This item is displayed on page 43 in the print version)
[View full size image]
N
ot
e
: The number of project types and icons showing will vary depending on the version of Visual
Basic you are using. Figure 3.1
was created from the Express Edition.
Page 3 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The name of the program, initially set to WindowsApplication1, can be specified at this time. Since we
will have a chance to change the name later, let's just call the program WindowsApplication1 for now.
Click on the OK button to invoke the Visual Basic programming environment. See Figure 3.2. Note:
Your screen will resemble, but may differ somewhat, from Figure 3.2. The Visual Basic programming
environment is often referred to as the IDE (Integrated Development Environment).
Figure 3.2. The Visual Basic programming environment.
(This item is displayed on page 43 in the print version)
[View full size image]
The Menu bar of the IDE displays the commands you use to work with Visual Basic. Some of the
menus, like File, Edit, View, and Window, are common to most Windows applications. Others, such as
Project, Build, and Debug, provide commands specific to programming in Visual Basic.
The Toolbars hold a collection of icons that carry out standard operations when clicked. For example,
you can use the fifth icon, which looks like a stack of three diskettes, to save the files associated with the
current program. To reveal the purpose of a Toolbar icon, hover the mouse pointer over the icon for a
few seconds. The little information rectangle that pops up is called a tooltip.
In Figure 3.2, the Main area currently holds the Windows Form Designer. The rectangular Form
window, or form for short, becomes a Windows window when a program is executed. Most information
displayed by the program appears on the form. The information usually is displayed in controls that the
p
rogrammer has placed on the form.
[Page 44]
The Solution Explorer window is used to display various parts of a program. The Properties window is
used to change how objects look and react.
The Toolbox holds icons representing controls that can be placed on the form. These controls are
Page 4 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

grouped into categories such as General, Dialogs, Printing, etc. Figure 3.
3
shows the Toolbox after the
p
lus sign to the left of "Common Controls" has been clicked. Nearly all the controls discussed in this
text can be found in the list of common controls. The four controls discussed in this chapter are text
boxes, labels, buttons, and list boxes.
Figure 3.3. The Toolbox's common controls.
N
ote: If your screen does not show the Toolbox, move the mouse over the tab marked Toolbox at the
left side of the screen. The Toolbox will appear. Then click on the pushpin icon in the title bar of the top
of the Toolbox to keep the toolbox from sliding out of the way when the cursor is moved away from the
Toolbox.
Text boxes: You use a text box to get information from the user, referred to as input, or to display
information produced by the program, referred to as output.
Labels: You place a label near a text box to tell the user what type of information is displayed in the text
box.
[Page 45]
Buttons: The user clicks a button to initiate an action.
List boxes: In the first part of the book, we use list boxes to display tables or several lines of output.
Later, we use list boxes to make selections.
Page 5 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

A Text Box Walkthrou
gh
1. Double-click on the text box icon in the Common Controls portion of the Toolbox. A rectangle
with two small squares, called sizing handles, appears at the upper left corner of the form. (You
can alter the width of the text box by dragging one of the sizing handles.) Move the mouse arrow to
any point of the text box other than a sizing handle, hold down the left mouse button, and drag the
text box to the center of the form. See Figure 3.4
. Note: The Tasks button will be discussed later in
this chapter.
Figure 3.4. A text box with sizing handles.
2. Click anywhere on the form outside the rectangle to deselect the text box.
3. Click on the rectangle to restore the handles. An object showing its handles is said to be selected. A
selected text box can have its width altered, location changed, and other properties modified.
4. Move the mouse arrow to the handle in the center of the right side of the text box. The cursor
should change to a double arrow ( ). Hold down the left mouse button, and move the mouse to
the right. The text box is stretched to the right. Similarly, grabbing the text box on the left side and
moving the mouse to the left stretches the text box to the left. You also can use the handles to make
the text box smaller. Steps 1 and 4 allow you to place a text box of any width anywhere on the
form. Note: The text box should now be selected; that is, its sizing handles should be showing. If
not, click anywhere inside the text box to select it.
5. Press the delete key, Del, to remove the text box from the form. Step 6 gives an alternative way to
place a text box of any width at any location on the form.
6. Click on the text box icon in the Toolbox. Then move the mouse pointer to any place on the form.
(When over the form, the mouse pointer becomes a pair of crossed thin lines.) Hold down the left
mouse button, and drag the mouse on a diagonal to generate a rectangle. Release the mouse button
to obtain a selected text box. You can now alter the width and location as before. Note: The text
box should now be selected. If not, click anywhere inside the text box to select it.
7.
Press F4 to activate the Properties window. (You also can activate the Properties window by
clicking on it, clicking on the Properties window icon in the right part of the Toolbar, selecting
Properties Window from the View menu, or clicking on the text box with the right mouse button
and selecting Properties.) See Figure 3.5
. The first line of the Properties window (called the Object
box) reads "TextBox1 etc." TextBox1 is the current name of the text box. The first two buttons
below the Object box permit you to view the list of properties either grouped into categories or
alphabetically. Use the up- and down-arrow keys (or the up- and down-scroll arrows) to move
through the list. The left column gives the property names, and the right column gives the current
settings of the properties. We discuss four properties in this walkthrough.
Page 6 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 46]
Figure 3.5. Text box Properties window.
[View full size image]
Note: If the Description pane is not visible, right-click on the Properties window, and then click on
"Description." The Description pane describes the currently highlighted property.
8. Move to the Text property with the up- and down-arrow keys. (Alternatively, scroll until the
property is visible, and click on the property.) The Text property, which determines the words
displayed in the text box, is now highlighted. Currently, there is no text displayed in the Settings
box on the right.
[Page 47]
9.
Type your first name. Then press the Enter key, or click on another property. Your name now
appears in both the Settings box and the text box. See Figure 3.6
.
Figure 3.6. Setting the Text property to David.
[View full size image]
Page 7 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

10. Click at the beginning of your name in the Text Settings box, and add your title, such as Mr., Ms.,
or The Honorable. (If you mistyped your name, you can easily correct it now.) Then, press Enter.
11. Use the up-arrow key or the mouse to move to the ForeColor property. This property determines
the color of the information displayed in the text box.
12. Click on the down arrow in the right part of the Settings box, and then click on the Custom tab to
display a selection of colors. See Figure 3.7. Click on one of the colors, such as blue or red. Notice
the change in the color of your name.
Figure 3.7. Setting the ForeColor property.
[Page 48]
13. Highlight the Font property with a single click of the mouse. The current font is named Microsoft
Sans Serif.
14.
Click on the ellipsis (...) box in the right part of the Settings box to display a dialog box. See Figure
3.8. The three lists give the current name (Microsoft Sans Serif), current style (Regular), and
current size (8) of the font. You can change any of these attributes by clicking on an item in its list
Page 8 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

or by typing into the box at the top of the list. Click on Bold in the style list, and click on 12 in the
size list. Now click on the OK button to see your name displayed in a larger bold font. The text box
will be longer so that it can accommodate the larger font.
Figure 3.8. The Font dialog box.
[View full size image]
15. Click on the text box and resize it to be about 3 inches wide.
Visual Basic programs consist of three parts: interface, values of properties, and code. Our
interface consists of a form with a single object, a text box. We have set a few properties for the
text boxthe text (namely, your name), the foreground color, the font style, and the font size. In
Section 3.2, we discuss how to place code into a program. Visual Basic endows certain capabilities
to programs that are independent of any code that we will write. We will now run the existing
program without adding any code in order to experience these capabilities.
16. Press F5 to run the program. (Alternatively, a program can be run from the menu by pressing
Alt/D/S or by clicking on the Start Debugging icon, the fourteenth or fifteenth icon on the
Toolbar.) After a brief delay, a copy of the form appears that has neither the form or the text box
selected.
[Page 49]
Note: When a program is run, all the work done so far on the program is automatically saved in a
temporary location with the name listed earlier in the New Project input dialog box.
17.
Your name is highlighted. Press the End key to move the cursor to the end of your name. Now type
Page 9 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

in your last name, and then keep typing. Eventually, the words will scroll to the left.
18. Press Home to return to the beginning of the text. You have a miniature word processor at your
disposal. You can place the cursor anywhere you like to add or delete text. You can drag the cursor
across text to select a block, place a copy of the block in the Clipboard with Ctrl+C, and then
duplicate it elsewhere with Ctrl+V.
19. To end the program, press Alt + F4, Alternatively, you can end a program by clicking on the form's
Close button at the right corner of the title bar.
20. Select the text box, activate the Properties window, select the ReadOnly property, click on the
down-arrow button, and finally click on True. Notice that the background color is now gray.
21. Run the program, and try typing into the text box. You can't. Such a text box is used for output.
Only code can display information in the text box.
Note: In this textbook, whenever a text box will be used only for the purpose of displaying output,
we will always set the ReadOnly property to True.
22. End the program.
23. Let's now save the program on a disk. Click on the Save All icon to save the work done so far.
(The Save All icon is the fifth or sixth icon on the Toolbar. It shows three fanned diskettes.
Alternately, you can press Alt/F/L.) You will be prompted for the name of the program and the
path to the folder where you want the program to be saved. Type a name, such as "VBdemo". You
can either type a path or use Browse to locate a folder. (This folder will automatically be used the
next time you click on the Save All icon while working on this program.) The files for the program
will be held in a subfolder of the selected folder.
Important: If the "Create directory for solution" check box is checked, then click on the check box
to uncheck it. Finally, click on the Save button.
24. Create a new program as before by clicking on "New Project" on the File menu. (Or, you can click
on the New Project icon, the first icon on the Toolbar.) A New Project dialog box will appear.
25. Give a name to the project, such as My Program, and then click on the OK button.
26. Place three text boxes on the form. (If you use the double-click technique, move the text boxes so
that they do not overlap.) Notice that they have the names TextBox1, TextBox2, and TextBox3.
27. Run the program. Notice that the cursor is in TextBox1. We say that TextBox1 has the focus. (This
means that TextBox1 is the currently selected object and any keyboard actions will be sent directly
to this object.) Any text typed will display in that text box.
[Page 50]
28. Press Tab once. Now, TextBox2 has the focus. When you type, the characters appear in TextBox2.
Page 10 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m
A Button Walkthrough
29. Press Tab several times, and then press Shift+Tab a few times. With Tab, the focus cycles through
the objects on the form in the order the objects were created. With Shift+Tab, the focus cycles in
the reverse order.
30. End the program you created.
31. We would now like to reload the first program. Click on "Open Project" from the File menu. An
Open Project dialog box will appear stating that "You must choose to either save or discard
changes in the current project before opening a project." There is no need to save his program, so
click on the Discard button. Then a second Open Project dialog box will appear.
32. Find the folder corresponding to the program you saved earlier, double-click on the folder, and
double-click on the file with extension sln. You have now recovered the first program.
33. If you do not see the Form Designer for the program, double-click on Form1.vb in the Solution
Explorer.
1. Click on the New Project icon to start a new program. (Give a name, such as ButtonProg, to the
program, and click on OK.)
2. Double-click on the Button icon in the Toolbox to place a button on the form. (The Button icon is
the second icon in the Common Controls portion of the Toolbox.)
3. Move the button to the center of the form.
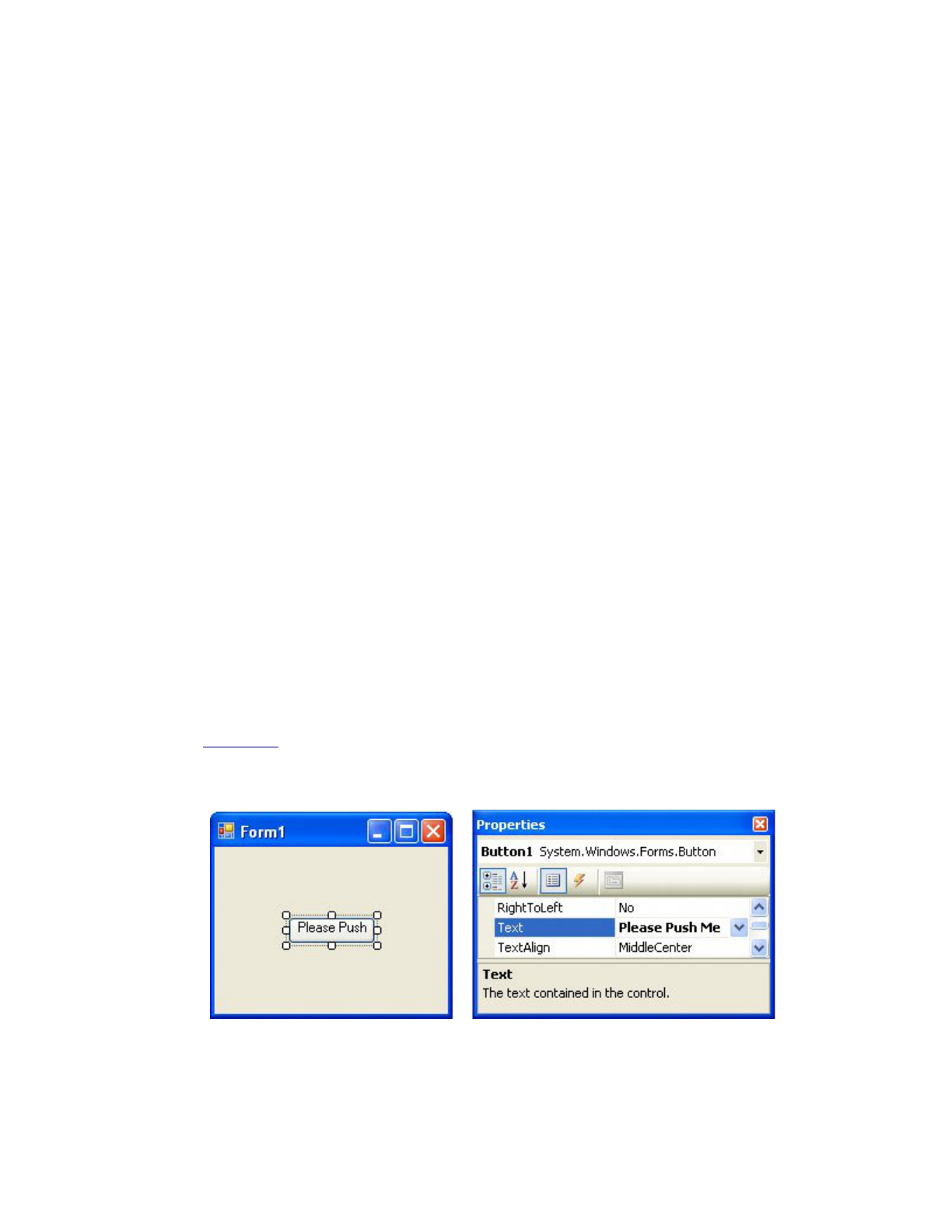
4. Activate the Properties window, highlight the Text property, type "Please Push Me," and press
Enter. See Figure 3.9. The button is too small.
Figure 3.9. Setting the Text property.
5. Click on the button to select it, and then enlarge it to accommodate the phrase "Please Push Me" on
one line.
Page 11 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Figure 3.10. Designating P as an access key.
Label Walkthrough
6. Run the program, and click on the button. The button appears to move in and then out. In Section
3.2, we write code that is executed when a button is pushed.
7. End the program and select the button.
[Page 51]
8. From the Properties window, edit the Text setting by inserting an ampersand (&) before the first
letter, P. Press the Enter key, and notice that the first letter P on the button is now underlined. See
Figure 3.10. Pressing Alt+P while the program is running triggers the same event as clicking the
button. However, the button will not appear to move in and out. Here, P is referred to as the access
key for the button. (The access key is always specified as the character following the ampersand.)
1. Click on the New Project icon to start a new program. Feel free to select the default name, such as
WindowsApplication1.
2. Double-click on the label icon to place a label on the form. (The label icon is a large letter A.)
Move the label to the center of the form.
3. Activate the Properties window, highlight the Text property, type "Enter Your Phone Number:",
and press Enter. (Such a label would be placed next to a text box into which the user will type a
phone number.) Notice that the label widened to accommodate the text. This happened because the
AutoSize property of the label is set to True by default.
4. Change the AutoSize property to False. Press Enter. Notice that the label now has eight sizing
handles when selected.
5. Make the label narrower and longer until the words occupy two lines.
6.
Activate the Properties window, and click on the down arrow to the right of the setting for the
TextAlign property. Experiment by clicking on the various rectangles and observing their effects.
Page 1
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 52]
A List Box Walkthrough
The Name Property
Every control has a Name property. It is used in code to refer to the control. By default, controls are
given names like TextBox1 and TextBox2. You can use the Properties window to change the Name
p
roperty of a control to a more meaningful name. (The Name property is always the third property in the
alphabetized list of properties. A control's name must start with a letter and can be a maximum of 215
characters. It can include numbers and underline (_) characters, but cannot include punctuation or
spaces.) Also, it is good coding practice to have each name begin with a three- or four-letter prefix that
identifies the type of the control. See Table 3.1. The form itself also has a Name property. Beginning
with Section 3.2, we will use suggestive names and these prefixes whenever possible.
The combination of sizing and alignment permits you to design a label easily.
7. Run the program. Nothing happens, even if you click on the label. Labels just sit there. The user
cannot change what a label displays unless you write code to make the change.
8. End the program.
1. Click on the New Project icon to start a new program. Feel free to select the default name, such as
WindowsApplication1.
2. Place a list box on the form. (The list box icon is the ninth icon in the Common Controls group of
the Toolbox.)
3. Press F4 to activate the Properties window and notice that the list box does not have a Text
property. The word ListBox1 is actually the setting for the Name property.
4. Also place a text box, a button and a label on the form.
5. Click on the Object box of the Properties window. The name of the form and the names of the four
controls are displayed. If you click on one of the names, that object will become selected and its
properties displayed in the Properties window.
6. Run the program. Notice that the word ListBox1 has disappeared, but the words Button1 and
Label1 are still visible. The list box is completely blank. In subsequent sections, we will write code
to place information into the list box.
Table 3.1. Some controls and their three-letter prefixes.
Control Prefix Example
form frm frmLottery
Page 1
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The Name property of the form itself also can be changed. Suppose you want to change the name of the
form from Form1 to frmPayroll. The most efficient way to set the name of the form is to change the
name of the file Form1.vb appearing in the Solution Explorer window to frmPayroll.vb. To make the
change, right-click on Form1.vb in the Solution Explorer window, click on Rename, type in the new
name (frmPayroll.vb), and press Enter.
Important: Make sure that the new filename has the extension "vb".
[Page 53]
To display the name of the form, and the names of all the controls on the form, click on the down-arrow
icon at the right of the Property window's Object box. You can make one of these items the selected item
by clicking on its name.
The Name and Text properties of a button are both initially set to something like Button1. However,
changing one of these properties does not affect the setting of the other property, and similarly for the
N
ame and Text properties of forms, text boxes, and labels. The Text property of a form specifies the
words appearing in the form's title bar.
A Help Walkthrough
Visual Basic has an extensive help system. The following walkthrough demonstrates one of its
featuresthe Help Index. The Help Index presents an alphabetized list of all the help topics available for
Visual Basic.
button btn btnComputeTotal
label lbl lblInstructions
listbox lst lstOutput
text box txt txtAddress
1. Press Alt/H/I to invoke the Index window from the Help menu.
2. If the "Filtered by:" box does not say "Visual Basic" or "Visual Basic Express Edition," click on
the down arrow and select one of them from the drop-down list.
3. Type "TextBox class" into the "Look for" box.
4. Click on the last subheading, "Properties." The window that appears contains a list of all the
properties of the textbox control, along with their descriptions.
5. Scroll down the list of properties and read the description of the MaxLength property. The
MaxLength property is used to limit the number of characters that can be typed into a text box.
Think about where this property could be useful.
6.
Type "Windows Forms controls" into the "Look for" box, look down about 27 subheadings of
Page 1
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Fonts
The default font for controls is Microsoft Sans Serif. Two other useful fonts are Courier New and
Wingdings.
Courier New is a fixed-width font; that is, each character has the same width. With such a font, the letter
i occupies the same space as the letter m. Fixed-width fonts are used with tables when information is to
be aligned in columns.
The Wingdings font consists of assorted small pictures and symbols, each corresponding to a character
on the keyboard. For instance if one of the characters %, (, 1, or J is typed into the Text setting of a
control whose Font is Wingdings, the control will display a bell, phone, open folder, or smiling face,
respectively.
To view the character set for a Windows font, click on the Start button in the Windows task bar and
successively select All Programs, Accessories, System Tools, and Character Map. Then click on
Character Map, or press the Enter key. After selecting the font, click on any item to enlarge it. You can
insert the keyboard character for the item into the Clipboard by pressing the Select button and then the
Copy button. To place the character into the Text property of a control having that font, just move the
cursor to the Settings box for the Text property and press Ctrl+V.
[Page 54]
Auto Hide
The Auto Hide feature allows you to make more room for the Main area of the screen by minimizing
tool windows (such as the Toolbox or Index window). Let's illustrate the feature with a walkthrough
using the Toolbox window. We start by discussing the situation where the feature is disabled.
"Windows Forms controls" and then click on "list of."
7. The window that appears contains a long list of underlined links. Click on the first underlined link,
"Windows Form Controls by Function."
8. Read the description of the four controls we have discussed so far. As a preview of coming
attractions, read about some of the controls we will discuss later in the book. They are
MaskedTextBox, ComboBox, OpenFileDialog, GroupBox, CheckBox, RadioButton, PictureBox,
and DataGridView.
1. If the Toolbox window is currently visible and the pushpin icon in the window title is vertical, then
the Auto Hide feature is disabled. (If the Toolbox window is not visible, press Alt/V/X to select
Toolbox from the View menu. If the pushpin icon is horizontal, then click on the icon to make it
vertical.) When the Auto Hide feature is disabled, the Toolbox window stays stationary and is
always ready for use.
2.
Click the mouse cursor somewhere outside of the Toolbox window and note that the window stays
fixed.
Page 1
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Positioning and Aligning Controls
Visual Basic provides several tools for positioning and aligning controls on a form. Proximity lines are
short line segments that help you place controls a comfortable distance from each other and from the
sides of the form. Snap lines are horizontal and vertical line segments that are help you align controls.
The Format menu is used to align controls, center controls horizontally and vertically in a form, and
make a group of selected controls the same size.
A Positioning and Aligning Walkthrough
3. Click on the pushpin icon to make it horizontal. The Auto Hide feature is now enabled.
4. Move the mouse cursor somewhere outside of the Toolbox window and note that the window
slides into a tab on the left side of the screen. The name and icon of the Toolbox window appear on
the tab.
5. Hover the mouse cursor over the tab. The window slides into view and is ready for use.
6. Place a new control on the form, and then move the cursor away from the Toolbox window. The
window automatically slides back to its tab on the edge of the screen.
1. Start a new program.
2. Place a button near the center of the form.
3.
Drag the button toward the upper-right corner of the form until two short line segments appear. See
Figure 3.11(a)
. The button is now a comfortable distance from the two sides of the form.
Figure 3.11. Positioning Controls.
(This item is displayed on page 55 in the print version)
[View full size image]
Page 1
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The most common uses of the submenus of the Format menu are as follows:
Align: Align middles or corresponding sides, of a group of selected controls.
4. Place a second button below the first button and drag it upwards until a proximity line appears
between the two buttons. The buttons are now a comfortable distance apart.
[Page 55]
5. Resize and position the two buttons as shown in Figure 3.11(b).
6. Drag Button2 upwards until a blue line appears along the bottoms of the two buttons. See Figure
3.11(c). This blue line is called a snap line. The bottoms of the two buttons are now aligned.
7. Continue dragging Button2 upwards until a purple snap line appears just underneath the words
Button1 and Button2. See Figure 3.11(d)
. The middles of the two buttons are now aligned. If we
were to continue dragging Button2 upwards, a blue snap line would tell us when the tops are
aligned. Steps 8 and 9 show another way to align the tops.
8. Click on Button1 and then hold down the Ctrl key and click on Button2. After the mouse button is
released, both buttons will be selected.
Note: This process can be repeated to select groups of any number of controls.
9. Open the Format menu in the Menu bar, hover over Align, and click on Tops. The tops of the two
buttons are now aligned. Precisely, Button1 (the first button selected) will stay fixed, and Button2
will move up so that its top is aligned with the top of Button1.
Page 1
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Make Same Size: Make the width and/or height of a group of selected controls the same.
Horizontal Spacing: Equalize the horizontal spacing between a group of three or more selected controls
arranged in a row.
[Page 56]
Vertical Spacing: Equalize the vertical spacing between a group of three or more selected controls
arranged in a column.
Center in Form: Center a selected control either horizontally or vertically in a form.
Comments
1. While you are working on a program, the program resides in memory. Removing a program from
memory is referred to as closing the program. A program is automatically closed then you start a
new program. Also, it can be closed directly with the Close Project command from the File menu.
2. Three useful properties that have not been discussed are the following:
a. BackColor: This property specifies the background color for the form or a control.
b. Visible: Setting the Visible property to False causes an object to disappear when the
program is run. The object can be made to reappear with code.
c. Enabled: Setting the Enabled property of a control to False restricts its use. It appears
grayed and cannot receive the focus. Controls sometimes are disabled temporarily if they do
not apply to the current state of the program.
3. Most properties can be set or altered with code as the program is running instead of being preset
from the Properties window. For instance, a button can be made to disappear with a line such as
Button1.Visible = False. The details are presented in Section 3.2.
4. If you inadvertently double-click on a form, a window containing text will appear. (The first line
begins Public Class Form1.) This is a Code window, which is discussed in the next section. Press
Ctrl+Z to undo the addition of this new code. To return to the Form Designer, click on the page
tab above the Main area labeled "Form1.vb [Design]."
5. We have seen two ways to place a control onto a form. A third method is to drag the control from
the Toolbox to the form.
Practice Problems 3.1
Exercises 3.1
1
.
What is the difference between the Text and the Name
p
ro
p
erties of a button?
2
.
Give a situation where the MaxLength property of a text box is useful.
Page 18 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 3 through 24, carry out the task. Use a new program for each exercise.
1
.
Create a form with two buttons, run the program, and click on each butto
n
. Do you notice
an
y
thin
g
different about a button after it has been clicked?
2. While a program is running, a control is said to lose focus when the focus moves from
that control to another control. In what three ways can the user cause a control to lose
focus?
3
.
Place "CHECKING ACCOUNT" in the title bar of a form.
4
.
Create a text box containin
g
the words "PLAY IT, SAM" in blue letters.
5
.
Create a text box with a yellow background.
[
Pa
g
e 57
]
6. Create a text box named txtGreeting and containing the word "HELLO" in large italic
letters.
7
.
Create a label containing the sentence "After all is said and done, more is said than
done." The sentence should occupy three lines, and each line should be centered
horizontall
y
in the label.
8
.
Create a rea
d
-only text box containing the words "Visual Basic" in bold white letters on a
red back
g
round.
9. Create a text box named txtLanguage and containing the words "Visual Basic 2005" in
Courier New font.
10
.
Create a yellow button named btnPush and containing the word "PUSH".
11
.
Create a white button containin
g
the word "PUSH" in lar
g
e italic letters.
12
.
Create a button containing the word "PUSH" in bold letters in which the letter P is
u
nderlined.
13
.
Create a button containin
g
the word "PUSH" with the letter H as the access ke
y
.
14
.
Create a label containin
g
the word "ALIAS" in white on a blue back
g
round.
15
.
Create a label named lblAKA and containing the centered italicized word "ALIAS".
16
.
Place BALANCE SHEET in the title bar of a form, where the form has a yellow
b
ack
g
round.
17
.
Create a label containing VISUAL on the first line and BASIC on the second line. Each
word should be right justified.
Page 1
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 25 through 30, create the interface shown in that figure. (These exercises give you practice
creating controls and assigning properties. The interfaces do not necessarily correspond to actual
p
rograms.)
18
.
Create a form named frmHello whose title bar reads "Hello World".
19
.
Create a label containing a picture of a diskette.
(
Hint: Use the Wingdings character <)
Make the diskette as lar
g
e as
p
ossible.
20
.
Create a label containing the bold word "ALIAS" in the Courier New font.
21
.
Create a list box with a yellow background.
22
.
Create a list box that will be invisible when the
p
ro
g
ram is run.
23
.
Create a form named frmYellow havin
g
a
y
ellow back
g
round.
24
.
Create a button containing a picture of a red bell.
(
Hint: Use the Wingdings character %.)
Make the bell as lar
g
e as
p
ossible.
25
.
[Page 58]
26
.
27
.
Page 20 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

28
.
29
.
[Page 59]
30
.
Page 21 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The following hands-on exercises develop additional techniques for manipulating and accessing controls
p
laced on a form.
31
.
Create a replica of your bank check on a form. Words common to all checks, such as
"PAY TO THE ORDER OF," should be contained in labels. Items specific to your
checks, such as your name at the top left, should be contained in text boxes. Make the
check on the screen resemble your personal check as much as possible.
32
.
Create a replica of your campus ID on a form. Words that are on all student IDs, such as
the name of the college, should be contained in labels. Information specific to your ID,
such as your name and Social Security number, should be contained in text boxes.
Simulate your picture with a text box containing a smiling facea size 24 Wingdings J.
33.
Place a text box on a form and select the text box. What is the effect of pressing the
various arrow keys?
34
.
Place a text box on a form and select the text box. What is the effect of pressing the
various arrow ke
y
s while holdin
g
down the Shift ke
y
?
35.
Experiment with the Align command on the Format menu to determine the difference
b
etween the center and the middle of a control.
36
.
Place four large buttons vertically on a form. Use the Format menu to make them the
same size and to make the s
p
acin
g
between them uniform.
37
.
Place three buttons vertically on a form. Make them different sizes without their left
sides aligned. Click on the first button. While holding down the Ctrl key, click on the
second button and then the third button. (Notice that the first button has white sizing
handles, and the other two buttons have black sizing handles.) This process is referred to
as selecting multiple controls.
Page 2
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Solutions to Practice Problems 3.1
a
.
What is the effect of pressing the left-arrow key?
b. What is the effect of pressing the left-arrow key while holding down the Shift key?
c. Press F4, set the ForeColor property to Blue, and press Enter. What happens?
d. Open the Format menu and experiment with the Align and Make Same Size
options. What special role does the control with white sizing handles play?
[
Pa
g
e 60
]
38
.
Place a button, a list box, and a text box on a form. Then run the program, and
successively press Tab. Notice that the controls receive the focus in the order in which
they were created. Invoke the Index from the Help menu and type "Tab order" into the
"Look for:" text box. Doubl
e
-click on the subheading "controls on Windows forms" and
read the discussion of how to set the tab order on Windows forms. Then change the tab
order for the three controls you placed on the form.
39
.
Place a text box on a form, select the text box, and open its Properties window. Doubl
e
-
click on the name (not the Settings box) of the ReadOnly property. Doubl
e
-click again.
What is the effect of doubl
e
-clicking on a property whose possible settings are True and
False?
40. Place a button on a form, select the button, and open its Properties window. Doubl
e
-click
on the name (not the Settings box) of the ForeColor property. Doubl
e
-click repeatedly.
Describe what is happening.
1
.
The text is the words appearing on the button, whereas the name is the designation used
to refer to the button. Initially, they have the same value, such as Button1. However, each
can be changed independently of the other.
2
.
If a text box is intended to hold a telephone number, then you might want to set the
MaxLength property to 12. Similarly, text boxes intended for Social Security numbers o
r
state abbreviations might be given maximum lengths of 11 and 2, respectively.
[Page 60 (continued)
]
3.2. Visual Basic Events
When a Visual Basic program runs, the form and its controls appear on the screen. Normally, nothing
happens until the user takes an action, such as clicking a control or pressing a key. We call such an
action an event. The programmer writes code that reacts to an event by performing some functionality.
Page 2
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The three steps in creating a Visual Basic program are as follows:
Section 3.1 covered Steps 1 and 2; this section is devoted to Step 3.
Code consists of statements that carry out tasks. In this section, we limit ourselves to statements that
change properties of a control or the form while a program is running.
Properties of controls are changed in code with statements of the form
controlName.property = setting
where controlName is the name of the control, property is one of the properties of the control, and
setting is a valid setting for that property. Such statements are called assignment statements. They assign
values to properties. Three examples of assignment statements are as follows:
[Page 61]
1. The statement
txtBox.Text = "Hello"
displays the word Hello in the text box.
2. The statement
btnButton.Visible = True
makes the button visible.
3. The statement
txtBox.ForeColor = Color.Red
sets the color of the characters in the text box named txtBox to red.
Most events are associated with controls. The event "click on btnButton" is different from the event
"click on lstBox." These two events are specified btnButton.Click and lstBox.Click. The statements to
be executed when an event occurs are written in a block of code called an event procedure. The first line
of an event procedure (called the header) has the form
Private Sub objectName_event(ByVal sender As System.Object,
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles objectName.event
1. Create the interface; that is, generate, position, and size the objects.
2. Set properties; that is, configure the appearance of the objects.
3. Write the code that executes when events occur.
Page 2
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Since we do not make any use of the lengthy text inside the parentheses in this book, for the sake of
readability we replace it with an ellipsis. However, it will automatically appear in our programs each
time Visual Basic creates the header for an event procedure. The structure of an event procedure is
Private Sub objectName_event(...) Handles objectName.event
statements
End Sub
where the three dots (that is, the ellipsis) represent
ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs
Words such as "Private," "ByVal," "As," "Sub," "Handles," and "End" have special meanings in Visual
Basic and are referred to as keywords or reserved words. The Visual Basic editor automatically
capitalizes the first letter of a keyword and displays the word in blue. The word "Sub" in the first line
signals the beginning of the procedure, and the first line identifies the object and the event occurring to
that object. The last line signals the termination of the event procedure. The statements to be executed
appear between these two lines. (Note: The word "Private" indicates that the event procedure cannot be
invoked by another form. This will not concern us until much later in the book. The expression
following Handles identifies the object and the event happening to that object. The expression
"objectName_event" is the default name of the procedure and can be changed if desired. In this book,
we always use the default name. The word "Sub" is an abbreviation of Subroutine.) For instance, the
event procedure
[Page 62]
Private Sub btnButton_Click(...) Handles btnButton.Click
txtBox.ForeColor = Color.Red
End Sub
changes the color of the words in the text box to red when the button is clicked.
An Event Procedure Walkthrough
The form in Figure 3.12
, which contains two text boxes and a button, will be used to demonstrate what
event procedures are and how they are created. Three event procedures will be used to alter the
appearance of a phrase appearing in the text box. The event procedures are named
txtFirst_TextChanged, btnRed_Click, and txtFirst_Leave.
Figure 3.12. The interface for the event procedure walkthrough.
Page 2
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Object Property Setting
frmDemo Text Demonstration
txtFirst
txtSecond
btnRed Text Change Color to Red
1. Create the interface in Figure 3.12 in the Form Designer. The Name properties of the form, text
boxes, and button should be set as shown in the Object column. The Text property of the form
should be set to Demonstration, the Text property of the text boxes should remain blank, and the
Text property of the button should be set to Change Color to Red.
2.
Click the right mouse button anywhere on the Main area, and select View code. The Form
Designer is replaced by the Code window (also known as the Code view or the Code editor). See
Figure 3.13.
Figure 3.13. The Code window.
[View full size image]
[Page 63]
The page tab, labeled frmDemo.vb, corresponds to the Code window. You press the page tab
labeled frmDemo.vb [Design], when you want to return to the Form Designer window. Just below
the title bar are two drop-down list boxes. The left box is called the Class Name box, and the right
Page 2
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

box is called the Method Name box. (When you hover the mouse pointer over one of these list
boxes, its type appears in a tooltip.) We will place our program code between the two lines shown.
Let's refer to this region as the program region.
3. Click on the tab labeled "frmDemo.vb [Design]" to return to the Form Designer.
4. Double-click on the first text box. The Code window reappears, but now the following two lines of
code have been added to the program region and the cursor is located on the line between them.
Private Sub txtFirst_TextChanged(...) Handles txtFirst.TextChanged
End Sub
The first line is the header for the event procedure named txtFirst_TextChanged. This procedure is
triggered by the event txtFirst.TextChanged. That is, whenever there is a change in the text
displayed in the text box txtFirst, the code between the two lines just shown will be executed.
5. Type the line
txtFirst.ForeColor = Color.Blue
at the cursor location. When you type the first period, a list containing all the properties of text
boxes appears. See Figure 3.14(a). (Each property is preceded by a little Properties window icon.
The list also contains something called methods, which we will discuss later.) At this point, you
can scroll down the list and double-click on ForeColor to automatically enter that property. Or, you
can keep typing. After you have typed "For," the list appears as in Figure 3.14(b). At that point,
you can press the Tab key to enter the highlighted word "ForeColor." This feature, known as
Member Listing, is one of the helpful features of Visual Basic that use a Microsoft technology
called IntelliSense.
Figure 3.14. IntelliSense at work.
Page 2
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 64]
6. Return to the Form Designer and double-click on the button. The Code window reappears, and the
first and last lines of the event procedure btnRed_Click appear in the program region. Type the line
that sets the ForeColor property of txtFirst to Red. The event procedure will now appear as
follows:
Private Sub btnRed_Click(...) Handles btnRed.Click
txtFirst.ForeColor = Color.Red
End Sub
7. Click on the down-arrow button to the right of the Class Name box and on txtFirst in the drop-
down list.
8. Click on the down-arrow button to the right of the Method Name box and on Leave in the drop-
down list box. (The event txtFirst.Leave is triggered when the focus is removed from the text box.)
The first and last lines of the event procedure txtFirst_Leave will be displayed. In this procedure,
type the line that sets the ForeColor property of txtFirst to Black. The Code window will now look
as follows:
Public Class frmDemo
Private Sub txtFirst_Leave(...) Handles txtFirst.Leave
txtFirst.ForeColor = Color.Black
End Sub
Private Sub txtFirst_TextChanged(...) Handles txtFirst.TextChanged
txtFirst.ForeColor = Color.Blue
End Sub
Private Sub btnRed_Click(...) Handles btnRed.Click
txtFirst.ForeColor = Color.Red
End Sub
End Class
9. Place the cursor on the word "ForeColor" and press F1. Visual Basic now displays information
about the foreground color property. This illustrates another help feature of Visual Basic known as
context-sensitive help.
10. Now run the program by pressing F5.
11.
Type something into the text box. In Figure 3.15, the blue word "Hello" has been typed. (Recall
that a text box has the focus whenever it is ready to accept typingthat is, whenever it contains a
blinking cursor.)
Figure 3.15. Text box containing input.
Page 28 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Properties and Event Procedures of the Form
You can assign properties to the Form itself in code. However, a statement such as
frmDemo.Text = "Demonstration"
will not work. The form is referred to by the keyword Me. Therefore, the proper statement is
Me.Text = "Demonstration"
To display a list of the events associated with frmDemo, select "(frmDemo Events)" from the Class
N
ame box and then open the Method Name box.
The Header of an Event Procedure
As mentioned earlier, in a header for an event procedure such as
Private Sub btnOne_Click(...) Handles btnOne.Click
[Page 65]
12. Click on the second text box. The contents of the first text box will become black. When the
second text box was clicked, the first text box lost the focus; that is, the event Leave happened to
txtFirst. Thus, the event procedure txtFirst_Leave was invoked, and the code inside the procedure
was executed.
13. Click on the button. This invokes the event procedure btnRed_Click, which changes the color of
the words in txtFirst to Red.
14. Click on the first text box, and type the word "Friend" after the word "Hello." As soon as typing
begins, the text in the text box is changed and the TextChanged event is triggered. This event
causes the color of the contents of the text box to become blue.
15. You can repeat Steps 11 through 14 as many times as you like. When you are finished, end the
program Alt+F4 by pressing clicking the End icon on the Toolbar, or clicking the Close button (X)
on the form.
Page 2
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

btnOne_Click is the name of the event procedure, and btnOne.Click identifies the event that triggers the
p
rocedure. The name can be changed at will. For instance, the header can be changed t
o
Private Sub ButtonPushed(...) Handles btnOne.Click
Also, an event procedure can be triggered by more than one event. For instance, if the previous line is
changed to
Private Sub ButtonPushed(...) Handles btnOne.Click, btnTwo.Click
the event will be triggered if either btnOne or btnTwo is clicked.
We have been using ellipses (...) as place holders for the phrase
ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs
[Page 66]
In Chapter 4, we will gain a better understanding of this type of phrase. Essentially, the word "sender"
carries a reference to the object that triggered the event, and the letter "e" carries some additional
information that the sending object wants to communicate. We will not make use of either "sender" or
"e".
Comments
1. The Visual Basic editor automatically indents the statements inside procedures. In this book, we
indent by two spaces. To instruct your editor to indent by two spaces, select Options from the
Tools menu, and uncheck the "Show all settings" box in the Options window that appears. Expand
"Text Editor Basic" or "Text Editor," click on "Editor," enter 2 into the "Indent size:" box, and
click on OK.
2. The event control.Leave is triggered when the specified control loses the focus. Its counterpart is
the event control.Enter which is triggered when the specified control gets the focus. A related
statement is
control.Focus()
which moves the focus to the specified control.
3. We have ended our programs by clicking the End icon or pressing Alt + F4 more elegant
technique is to create a button, call it btnQuit, with caption Quit and the following event
procedure:
Private Sub btnQuit_Click(...) Handles btnQuit.Click
End
End Sub
Page 30 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m
4
.
For statements of the for
m
object.Text = setting
the expression for setting must be surrounded by quotes. (For instance, lblName. Text = "Name".)
For properties where the proper setting is one of the words True or False, these words should not
be surrounded by quotation marks.
5. Names of existing event procedures associated with an object are not automatically changed when
you rename the object. You must change them yourself. However, the event that triggers the
procedure (and all other references to the control) will change automatically. For example,
suppose an event procedure is
Private Sub btnOne_Click(...) Handles btnOne.Click
btnOne.Text = "Press Me"
End Sub
and, in the Form Designer, you change the name of btnOne to btnTwo. Then, when you return to
the Code window the procedure will be
Private Sub btnOne_Click(...) Handles btnTwo.Click
btnTwo.Text = "Press Me"
End Sub
[Page 67]
6. Code windows have many features of word processors. For instance, the operations cut, copy,
paste, undo, and redo can be carried out with the sixth through tenth icons from the Toolbar.
These operations, and several others, also can be initiated from the Edit menu.
7. The code editor can detect certain types of errors. For instance, if you type
txtFirst.Text = hello
and then move away from the line, the automatic syntax checker will underline the word "hello"
with a blue squiggle to indicate that something is wrong. When the mouse cursor is hovered over
the offending wording, the editor will display a message explaining what is wrong. If you run the
program without correcting the error, the dialog box in Figure 3.16
will appear.
Figure 3.16. Error dialog box.
8. When you double-click on a control in the Form Designer, the header for the most used event
procedure is placed in the Code window. The event that appears most frequently in this book is
Page 31 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

the Click event for button controls.
9. Font properties, such as the name, style, and size, are usually specified at design time. The setting
of the properties can be displayed in code with statements such as
1stBox.Items.Add(txtBox.Font.Name)
1stBox.Items.Add(txtBox.Font.Bold)
1stBox.Items.Add(txtBox.Font.Size)
However, a font's name, style, and size properties cannot be altered in code with statements of the
form
txtBox.Font.Name = "Courier New"
txtBox.Font.Bold = True
txtBox.Font.Size = 16
10. When you make changes to a program, asterisks appear as superscripts on the page tabs labeled
"frmName.vb [design]" and "frmName.vb." The asterisks disappear when the program is saved or
run.
11. Beginning with the next section, each example contains a program. These programs are on the
companion website for this book. See the discussion on page xv for details. The process of
opening a program stored on a disk is referred to as loading the program. You might want to
prepare for the next section by loading the program 3-3-1 from the subfolder Ch03 of the
Programs folder.
[Page 68]
Note: After you load the program with the Open Project command from the File menu, you should
see the form designer for the program. If not, double-click on the file in the Solution Explorer
with extension "vb", that is, frmArithmetic.vb. If the form designer is still not visible, click on the
View Designer icon at the top of the Solution Explorer window.
Practice Problem 3.2
Exercises 3.2
1
.
What event procedure is displayed when you doubl
e
-click on each of the following
controls in the Form Designer?
a. text box
b. button
c. label
d. list box
2
.
Give a statement that will
p
revent the user from t
yp
in
g
into txtBox.
Page 3
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 1 through 6, describe the contents of the text box after the button is clicked.
[Page 69]
In Exercises 7 through 10, assume that the three objects on the form were created in the order txtFirst,
txtSecond, and lblOne. Determine the output displayed in lblOne when the program is run and the Tab
key is pressed. Note: Initially, txtFirst has the focus.
1.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
2
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.ForeColor = Color.Re
d
txtBox.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
3
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.BackColor = Color.Orang
e
txtBox.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
4
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.Text = "Goodbye
"
txtBox.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
5.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.Text = "Hello
"
txtBox.Visible = Fals
e
E
nd Su
b
6
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.BackColor = Color.Yellow
txtBox.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
7
.
P
rivate Sub txtFirst_Leave(...) Handles txtFirst.Leav
e
Page 3
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 11 through 16, determine the errors.
lblOne.ForeColor = Color.Gree
n
lblOne.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
8
.
P
rivate Sub txtFirst_Leave(...) Handles txtFirst.Leav
e
lblOne.BackColor = Color.Whit
e
lblOne.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
9.
P
rivate Sub txtSecond_Enter(...) Handles txtSecond.Ente
r
lblOne.BackColor = Color.Gol
d
lblOne.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
10
.
P
rivate Sub txtSecond_Enter(...) Handles txtSecond.Ente
r
lblOne.Visible = Fals
e
lblOne.Text = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
11
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
Form1.Text = "Hello
"
End Su
b
12
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.Text = Hello
E
nd Su
b
13.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtFirst.ForeColor = Re
d
E
nd Su
b
14
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox = "Hello
"
E
nd Su
b
Page 3
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 70]
In Exercises 17 through 28, write a line (or lines) of code to carry out the task.
15
.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btnOutput.Clic
k
txtBox.Font.Size = 20
E
nd Su
b
16.
P
rivate Sub btnOutput_Click(...) Handles btn1.Click, btn2.Clic
k
Me.Color = Color.Yellow
E
nd Su
b
17
.
Dis
p
la
y
"E.T.
p
hone home." in lblTwo.
18
.
Display "Play it, Sam." in lblTwo.
19
.
Display "The stuff that dreams are made of." in red letters in txtBox.
20
.
Display "Life is like a box of chocolates." in txtBox with blue letters on a gold
b
ack
g
round.
21
.
Disable txtBox.
22
.
Chan
g
e the words in the form's title bar to "Hello World.
"
23
.
Make lblTwo disa
pp
ear.
24
.
Change the color of the letters in lblName to red.
25
.
Enable the disabled button btnOutcome.
26
.
Give the focus to btnCom
p
ute.
27
.
Change the background color of the form to White.
28
.
Give the focus to txtBoxTwo.
29
.
Describe the Enter event in
y
our own words.
30
.
Describe the Leave event in
y
our own words.
31
.
The label control has an event called DoubleClick that responds to a doubl
e
-clicking of
the left mouse button. Write a simple program to test this event. Determine whether you
Page 3
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 33 through 38, the interface and initial properties are specified. Write the program to carry
out the stated task.
can trigger the DoubleClick event without also triggering the Click event.
32
.
Write a simple program to demonstrate that a button's Click event is triggered when you
p
ress the Enter ke
y
while the button has the focus.
33
.
When one of the three buttons is pressed, the words on the button are displayed in the
text box with the stated alignment. Note: Rely on IntelliSense to provide you with the
p
roper settings for the TextAlign property.
Object Property Setting
frmAlign Text Text Alignment
txtBox ReadOnly True
btnLeft Text Left Justify
btnCenter Text Center
btnRight Text Right Justify
[Page 71]
34
.
When one of the buttons is pressed, the face changes to a smiling face (Wingdings
character "J") or a frowning face (Wingdings character "L").
Page 3
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Object Property Setting
frmFace Text Face
lblFace Font Name Wingdings
Font Size 24
Text K
btnSmile Text Smile
btnFrown Text Frown
35
.
Pressing the buttons alters the background and foreground colors in the text box.
Object Property Setting
frmColors Text Colorful Text
lblBack Text Background
btnRed Text Red
btnBlue Text Blue
txtBox Text Beautiful Day
TextAlign Center
lblFore Text Foreground
Page 3
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

btnWhite Text White
btnYellow Text Yellow
36
.
When one of the three text boxes receives the focus, its text becomes red. When it loses
the focus, the text returns to black. The buttons set the alignment in the text boxes to Left
or Right. Note: Rely on IntelliSense to provide you with the proper settings for the
TextAlign property.
Object Property Setting
frm123 Text One, Two, Three
txtOne Text One
txtTwo Text Two
txtThree Text Three
btnLeft Text Left
btnRight Text Right
[
Pa
g
e 72
]
37
.
When the user moves the focus to one of the three small text boxes at the bottom of the
form, an appropriate saying is displayed in the large text box. Use the sayings "I like life,
it's something to do."; "The future isn't what it used to be."; and "Tell the truth and run.
"
Page 38 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 39 through 44, write a program with a Windows-style interface to carry out the task.
Object Property Setting
frmQuote Text Sayings
txtQuote ReadOnly True
txtLife Text Life
txtFuture Text Future
txtTruth Text Truth
38. The user can disable or enable the text box by clicking on the appropriate button. Afte
r
the user clicks the Enable button, the text box should receive the focus.
Object Property Setting
frmTextBox Text Text Box
txtBox
btnDisable Text Disable Text Box
btnEnable Text Enable Text Box
39
.
The form contains four square buttons arranged in a rectangular array. Each button has
Page 3
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Solutions to Practice Problem 3.2
the caption "Push Me." When the user clicks on a button, the button disappears and the
other three become or remain visible.
40. A form contains two text boxes and one large label between them with no preset caption.
When the first text box receives the focus, the label reads "Enter your full name." When
the second text box receives the focus, the label reads "Enter your phone number,
includin
g
area code.
"
41. Use the same form and properties as in Exercise 34, with the captions for the buttons
replaced with Vanish and Reappear. Clicking a button should produce the stated result.
42
.
Simulate a traffic light with three small square text boxes placed vertically on a form.
Initially, the bottom text box is solid green and the other text boxes are dark gray. When
the Tab key is pressed, the middle text box turns yellow and the bottom text box turns
dark gray. The next time Tab is pressed, the top text box turns red and the middle text
b
ox turns dark gray. Subsequent pressing of the Tab key cycles through the three colors.
Hint: First, place the bottom text box on the form, then the middle text box, and finally
the top text box.
[
Pa
g
e 73
]
43. The form contains a single rea
d
-only text box and two buttons. When the user clicks on
one of the buttons, the sentence "You just clicked on a button." is displayed in the text
b
ox. The program should consist of a single event procedure.
44
.
The form contains two text boxes into which the user types information. When the user
clicks on one of the text boxes, it becomes blank and its contents are displayed in the
other text box. Note: A text box can be cleared with the statement txtBox.Clear() or
the statement txtBox.Text = "".
1
.
a
.
TextChange
d
b. Click
c. Click
d
.
SelectedIndexChan
g
e
d
2. Three possibilities ar
e
t
xtBox.Enabled = Fals
e
t
xtBox.ReadOnly = Tru
e
t
xtBox.Visible = Fals
e
Page 40 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 73 (continued)]
3.3. Numbers
Much of the data processed by computers consist of numbers. In computerese, numbers are called
numeric literals. This section discusses the operations that are performed with numbers and the ways
numbers are displayed.
Arithmetic Operations
The five standard arithmetic operations in Visual Basic are addition, subtraction, multiplication,
division, and exponentiation. Addition, subtraction, and division are denoted in Visual Basic by the
standard symbols +, -, and /, respectively. However, the notations for multiplication and exponentiation
differ from the customary mathematical notations as follows:
(The asterisk [*] is the upper character of the 8 key. The caret [^] is the upper character of the 6 key.)
One way to show a number on the screen is to display it in a list box. If n is a number, then the
instruction
lstBox.Items.Add(n)
displays the number n as the last item in the list box. Add is called a method. (Generally, a method is a
p
rocess that performs a task for a particular object.) If the parentheses contain a combination of numbers
and arithmetic operations, the Add method carries out the operations and displays the result. Another
important method is Clear. The statement
[Page 74]
lstBox.Items.Clear()
erases all the items displayed in the list box lstBox.
Example 1.
Mathematical Notation Visual Basic Notation
a • b or a x b a * b
a
r
a^r
Page 41 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Example 1, the words "lstResults.Items" appear seven times. Visual Basic provides a device for both
reducing the amount of repetitive typing required and making the program appear less cluttered. The
p
rogram can be written as
The following program applies each of the five arithmetic operations. Preceding the
program is the form design and a table showing the names of the objects on the form and
the settings, if any, for properties of these objects. This form design is also used in the
discussion and examples in the remainder of this section.
The word "Run" in the phrasing [Run...] indicates that F5 should be pressed to execute the
program. Notice that in the output 3 / 2 is displayed in decimal form. Visual Basic never
displays numbers as common fractions. In the evaluation of 2*(3 + 4), the operation inside
the parentheses is calculated first.
Note: All programs appearing in examples and case studies are provided on the companion
website for this book. See the discussion on page xv for details.
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
lstResults.Items.Clear()
lstResults.Items.Add(3 + 2)
lstResults.Items.Add(3 - 2)
lstResults.Items.Add(3 * 2)
lstResults.Items.Add(3 / 2)
lstResults.Items.Add(3 ^ 2)
lstResults.Items.Add(2 * (3 + 4))
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The output is shown at the top of the next page.]
Object Property Setting
frmArithmetic Text 3-3-1
lstResults
btnCompute Text Compute
Page 4
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m
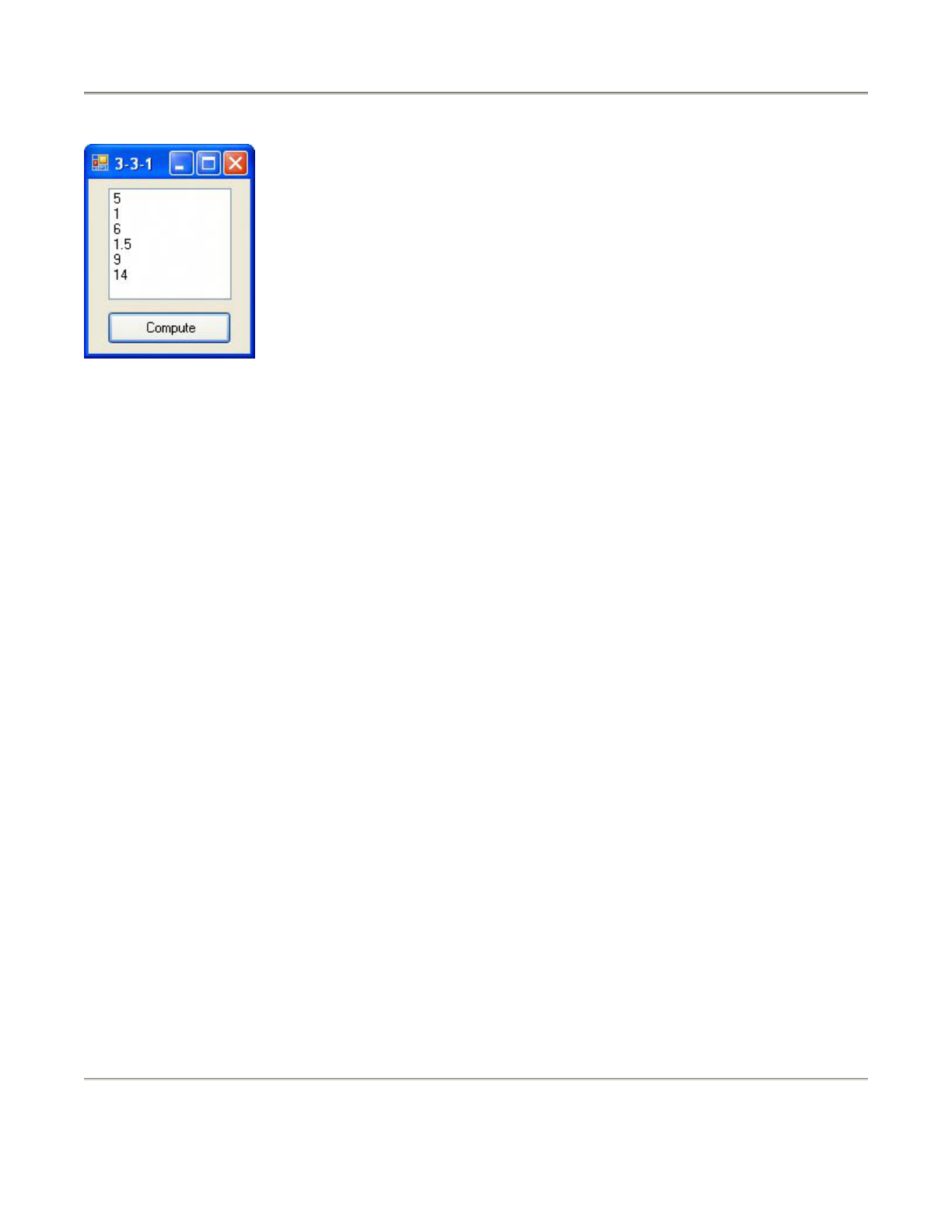
[Page 75]
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
With lstResults.Items
.Clear()
.Add(3 + 2)
.Add(3 - 2)
.Add(3 * 2)
.Add(3 / 2)
.Add(3 ^ 2)
.Add(2 * (3 + 4))
EndWith
End Sub
The nine statements inside the procedure are called a With block. Within the block, each expression
starting with a period is evaluated as if the expression lstResults.Items preceded it.
Variables
In applied mathematics problems, quantities are referred to by names. For instance, consider the
following high school algebra problem: "If a car travels at 50 miles per hour, how far will it travel in 14
hours? Also, how many hours are required to travel 410 miles?" The solution to this problem uses the
well-known formula
distance = speed x time elapsed
Here's how this problem would be solved with a computer program:
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim speed As Double
Dim timeElapsed As Double
Dim distance As Double
lstResults.Items.Clear()
speed = 50
timeElapsed = 14
distance = speed * timeElapsed
lstResults.Items.Add(distance)
[Page 76]
distance = 410
timeElapsed = distance / speed
Page 4
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

lstResults.Items.Add(timeElapsed)
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
700
8.2
Skip the second, third, and fourth lines of the event procedure for now. We will return to them soon. The
sixth line sets the speed to 50, and the seventh line sets the time elapsed to 14. The eighth line multiplies
the value for the speed by the value for the time elapsed and sets the distance to this product. The next
line displays the answer to the distance-traveled question. The three lines before the End Sub statement
answer the time-required question in a similar manner.
The names speed, timeElapsed, and distance, which hold numbers, are referred to as variables. Consider
the variable timeElapsed. In the seventh line, its value was set to 14. In the eleventh line, its value was
changed as the result of a computation. On the other hand, the variable speed had the same value, 50,
throughout the program.
In general, a variable is a name that is used to refer to an item of data. The value assigned to the variable
may change during the execution of the program. In Visual Basic, variable names can be up to 16,383
characters long, must begin with a letter or an underscore, and can consist only of letters, digits, and
underscores. (The shortest variable names consist of a single letter.) Visual Basic does not distinguish
between uppercase and lowercase letters used in variable names. Some examples of variable names are
total, numberOfCars, taxRate_2006, and n. As a convention, we write variable names in lowercase
letters except for the first letters of additional words (as in gradeOnFirstExam).
If var is a variable and n is a literal, then the statement
var = n
assigns the number n to the variable var. (Such a statement is another example of an assignment
statement.)
A variable is declared to be of a certain type depending on the sort of data that can be assigned to it. The
most versatile type for holding numbers is called Double. A variable of type Double can hold whole,
fractional, or mixed numbers between about -1.8 • 10
308
and 1.8 • 10
308
. Dim statements (also called
declaration statements) declare the names and types of the variables to be used in the program. The
second, third, and fourth lines of this event procedure declare three variables of type Double and give
them the names speed, timeElapsed, and distance.
In general, a statement of the form
Dim varName As Double
declares a variable named varName to be of type Double. Actually, the Dim statement causes the
computer to set aside a location in memory with the name varName. Since varName is a numeric
variable, the Dim statement also places the number zero in that memory location. (We say that zero is
Page 4
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

the initial valu
e
or default valu
e
of the variable.) Each subsequent assignment statement having
varName to the left of the equal sign will change the value of the number.
[Page 77]
The initial value can be set to a value other than zero. To specify a nonzero initial value, follow the
declaration statement with an equal sign followed by the initial value. The statement
Dim varName As Double = 50
declares the specified variable as a variable of type Double and gives it the initial value 50.
The statement
lstBox.Items.Add(varName)
looks into this memory location for the current value of the variable and displays the value in the list
box.
A combination of literals, variables, and arithmetic operations that can be evaluated to yield a number is
called a numeric expression. Expressions are evaluated by replacing each variable by its value and
carrying out the arithmetic. Some examples of expressions are 2 * distance + 7, n + 1, and (a + b)/3.
Example 2.
0
3
25
The following program displays the default value of a variable and the value of an
expression:
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim a As Double
Dim b As Double = 3
lstResults.Items.Clear()
lstResults.Items.Add(a)
lstResults.Items.Add(b)
a = 5
lstResults.Items.Add(a * (2 + b))
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
Page 4
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

If va
r
is a variable, then the assignment statement
var = expression
first evaluates the expression on the right and then assigns its value to the variable on the left. For
instance, the event procedure in Example 2
can be written as
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim a As Double
Dim b As Double
Dim c As Double
[Page 78]
lstResults.Items.Clear()
a = 5
b = 3
c = a * (2 + b)
lstResults.Items.Add(c)
End Sub
The expression a*(2 + b) is evaluated to 25, and then this value is assigned to the variable c.
Incrementing the Value of a Variable
Because the expression on the right side of an assignment statement is evaluated before an assignment is
made, a statement such as
var = var + 1
is meaningful. It first evaluates the expression on the right (that is, it adds 1 to the original value of the
variable var) and then assigns this sum to the variable var. The effect is to increase the value of the
variable var by 1. In terms of memory locations, the statement retrieves the value of var from var's
memory location, uses it to compute var + 1, and then places the sum back into var's memory location.
This type of calculation is so common that Visual Basic provides a special operator to carry it out. The
statement
var = var + 1 can be replaced with the statement
var += 1
In general, if n has a numeric value, then the statement
var += n
adds n to the value of var.
Built-In Functions: Math.Sqrt, Int, Math.Round
There are several common operations that we often perform on numbers other than the standard
arithmetic operations. For instance, we may take the square root of a number or round a number. These
Page 4
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

operations are performed by built-in functions. Functions associate with one or more values called the
input, and a single value called the output. The function is said to return the output value. The three
functions considered here have numeric input and output.
The function Math.Sqrt calculates the square root of a number. The function Int finds the greatest integer
less than or equal to a number. Therefore, Int discards the decimal part of positive numbers. The value
of Math.Round(n, r) is the number n rounded to r decimal places. The parameter r can be omitted. If so,
n is rounded to a whole number. Some examples follow:
[Page 79]
The terms inside the parentheses can be numbers (as shown), numeric variables, or numeric expressions.
Expressions are first evaluated to produce the input.
Example 3.
Example 4.
Math.Sqrt(9) is 3. Int(2.7) is 2. Math.Round(2.7) is 3.
Math.Sqrt(0) is 0. Int(3) is 3. Math.Round(2.317, 2) is 2.32.
Math.Sqrt(2) is 1.414214. Int(-2.7) is -3. Math.Round(2.317, 1) is 2.3.
The following program evaluates each of the functions for a specific input given by the
value of the variable n:
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim n As Double
Dim root As Double
n = 6.76
root = Math.Sqrt(n)
With lstResults.Items
.Clear()
.Add(root)
.Add(Int(n))
.Add(Math.Round(n, 1))
End With
End Sub
[Run, and then click the Compute button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
2.6
6
6.8
Page 4
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 80]
The Integer Data Type
In this text, we sometimes need to use variables of type Integer. An Integer variable is declared with a
statement of the form
Dim varName As Integer
and can be assigned only whole numbers from about -2 billion to 2 billion. Integer variables are used
p
rimarily for counting.
Multiple Declarations
Several variables of the same type can be declared with a single Dim statement. For instance, the two
Dim statements in Example 2 can be replaced by the single statement
Dim a, b As Double
Two other types of multiple-declaration statement are
Dim a As Double, b As Integer
Dim c As Double = 2, b As Integer = 5
The following program evaluates each of the preceding functions at an expression:
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim a As Double
Dim b As Double
a = 2
b = 3
With lstResults.Items
.Clear()
.Add(Math.Sqrt(5 * b + 1))
.Add(Int(a ^ b + 0.8))
.Add(Math.Round(a / b, 3))
End With
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
4
8
0.667
Page 48 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Parentheses
Parentheses cannot be used to indicate multiplication, as is commonly done in algebra. For instance, the
expression x(y + z) is not valid. It must be written as x*(y + z).
Parentheses should be used when necessary to clarify the meaning of an expression. When there are no
p
arentheses, the arithmetic operations are performed in the following order: (1) exponentiations; (2)
multiplications and divisions; (3) additions and subtractions. In the event of ties, the leftmost operation
is carried out first. Table 3.2 summarizes these rules. Note: If you use parentheses liberally, you will not
have to remember the precedence table for arithmetic operations.
Three Types of Errors
Grammatical errors, such as misspellings, omissions, or incorrect punctuations, are called syntax errors.
Most syntax errors are spotted by the code editor when they are entered; however, some are not detected
until the program is executed. Some incorrect statements and their errors are as follows:
[Page 81]
Errors that occur while a program is running are called run-time errors. They usually result from the
inability of the computer to carry out the intended task. For instance, if the file DATA.TXT is not in the
root folder of the C drive, then a statement that refers to the file by the filespec "C:\DATA.TXT" will
cause the program to stop executing and produce a message box with the title
FileNotFoundException was unhandled.
Also, a yellow arrow will appear at the left side of the line of code that caused the error. At that point,
you should end the program.
Table 3.2. Level of precedence for arithmetic operations.
() Inner to outer, left to right
^ Left to right in expression
* / Left to right in expression
+- Left to right in expression
Statement Reason for Error
lstBox.Itms.Add(3) The word Items is misspelled.
lstBox.Items.Add(2+) The number following the plus sign is
omitted.
Dim m; n As Integer The semicolon should be a comma.
Page 4
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

A third type of error is the s
o
-called logical erro
r
. Such an error occurs when a program does not
p
erform the way it was intended. For instance, the lin
e
average = firstNum + secondNum / 2
is syntactically correct. However, the missing parentheses in the line of code are responsible for an
incorrect value being generated. Appendix D
discusses debugging tools that can be used to detect and
correct logical errors.
Comments
1. Declaring variables at the beginning of each event procedure is regarded as good programming
practice because it makes programs easier to read and helps prevent certain types of errors.
2. Keywords (reserved words) cannot be used as names of variables. For instance, the statements Dim
private as Double
and Dim sub As Double are not valid. To obtain a complete list of Visual
Basic reserved keywords, look up keywords under Visual Basic in Help's Index.
3. Names given to variables are sometimes referred to as identifiers.
4. In math courses, literals are referred to as constants. However, the word "constant" has a special
meaning in programming languages.
5. Numeric constants used in expressions or assigned to variables must not contain commas, dollar
signs, or percent signs. Also, mixed numbers, such as 8 1/2, are not allowed.
6. Although requesting the square root of a negative number does not terminate the execution of the
program, it can produce unexpected results. For instance, the statement
lstBox.Items.Add(Math.Sqrt(-1))
displays NaN. Note: NaN is an abbreviation for "Not a Number."
7. If the value of numVar is 0 and numVar has type Double, then the statements
numVarInv = 1 / numVar
lstBox.Items.Add(numVarInv)
lstBox.Items.Add(1 / numVarInv)
[Page 82]
cause the following items to be displayed in the list box:
Infinity
0
8. When n is halfway between two successive whole numbers (such as 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, and 4.5), then it
rounds to the nearest even number. For instance, Math.Round (2.5) is 2 and Math.Round(3.5) is 4.
Page 50 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

9
.
In addition to the five arithmetic operators discussed at the beginning of this section, the Mod
operator is another useful operator. If m and n are positive whole numbers, then m Mod n is the
remainder when m is divided by n. For instance, 14 Mod 3 is 2, 18 Mod 5 is 3, and 7 Mod 2 is 1.
10. In scientific notation, numbers are written in the form b•10
r
, where b is a number of magnitude
from 1 up to (but not including) 10, and r is an integer. Visual Basic displays very large numbers
in scientific notation where b•10
r
is written as bEr. (The letter E is an abbreviation for exponent.)
For instance, when the statement lstBox.Items.Add(123 * 10 ^ 15) is executed, 1.23E+17 is
displayed in the list box.
Practice Problems 3.3
1
.
Evaluate 2 + 3*4.
2
.
Explain the difference between the assignment statement
v
ar1 = var
2
and the assignment statement
v
ar2 = var1
3
.
Complete the table by filling in the value of each variable after each line is executed.
a b c
Private Sub btnEvaluate_Click(...) Handles
btnEvaluate.Click
Dim a, b, c As Double 0 0 0
a = 3 3 0 0
b = 4 3 4 0
c = a + b
a = c * a
lstResults.Items.Add(a - b)
b = b * b
End Sub
4
.
Write a statement that increases the value of the numeric variable va
r
b
y
5%.
Page 51 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 83
]
Exercises 3.3
In Exercises 1 through 6, evaluate the numeric expression without the computer, and then use Visual
Basic to check your answer.
In Exercises 7 through 10, evaluate the Mod operation.
In Exercises 11 through 16, determine whether the name is a valid variable name.
In Exercises 17 through 22, evaluate the numeric expression where a = 2, b = 3, and c = 4.
1
.
3*
4
2
.
7^
2
3
.
1/
(
2^3
)
4
.
3 + (4*5)
5
.
(
5 - 3
)
*
4
6
.
3*
((
-2
)
^5
)
7
.
6 Mod
2
8
.
14 Mod
4
9
.
7 Mod
3
10
.
5 Mod
5
11
.
sales.200
6
12
.
room&Boar
d
13
.
fOrM
_
1040
14
.
1040
B
15
.
expenses?
16
.
INCOME 200
6
Page 5
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 23 through 28, write an event procedure to calculate and display the value of the
expression.
In Exercises 29 and 30, complete the table by filling in the value of each variable after each line is
executed.
17
.
(a*b) + c
18
.
a*
(
b + c
)
19
.
(
1 + b
)
*c
20
.
a^c
21
.
b
^(c - a)
22
.
(
c - a
)
^
b
23
.
7•8 +
5
24
.
(
1 +
2
•9
)
3
25
.
5.5% of 20
26
.
15 - 3
(
2 +
3
4
)
27
.
17
(
3 + 162
)
28
.
4 1/2 - 3 5/8
29
.
x y
Private Sub btnEvaluate_Click(...) Handles
btnEvaluate.Click
Dim x, y As Double
x = 2
y = 3 * x
x = y + 5
lstResults.Items.Clear()
lstResults.Items.Add(x + 4)
y = y + 1
End Sub
Page 5
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 31 through 38, determine the output displayed in the list box by the lines of code.
[Page 84]
30
.
bal inter withDr
Private Sub btnEvaluate_Click(...) Handles
btnEvaluate.Click
Dim bal, inter, withDr As Double
bal = 100
inter = 0.05
withDr = 25
bal += inter * bal
bal = bal - withDr
End Sub
31.
D
im amount As Doubl
e
a
mount = 10
l
stOutput.Items.Add(amount - 4)
32
.
D
im a, b As Intege
r
a
= 4
b
= 5 * a
l
stOutput.Items.Add(a + b
)
33
.
D
im n As Integer =
7
n
+= 1
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add(1
)
.Add(n
)
.Add(n + 1
)
E
nd Wit
h
Page 5
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 39 through 44, identify the errors.
34
.
D
im num As Integer =
5
n
um = 2 * nu
m
l
stOutput.Items.Add(num
)
35.
D
im a, b As Intege
r
l
stOutput.Items.Add(a + 1
)
a
= 4
b
= a * a
l
stOutput.Items.Add(a * b
)
36.
D
im tax As Doubl
e
t
ax = 200
t
ax = 25 + ta
x
l
stOutput.Items.Add(tax
)
37
.
D
im x As Double =
3
x
+=
2
l
stOutput.Items.Add(x * x
)
l
stOutput.Items.Add(x + 3 * x
)
[Page 85]
38
.
D
im n As Double = 2, m As Double =
5
l
stOutput.Items.Add(3 * n
)
n
+=
n
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add(n + m
)
.Add(n - m)
E
nd Wit
h
39
.
D
im a, b, c As Doubl
e
a
=
2
b
=
3
a
+ b = c
l
stOutput.Items.Add(c
)
Page 5
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 45 and 46, rewrite the code using one line.
In Exercises 47 through 52, find the value of the given function.
40
.
D
im a, b, c, d As Doubl
e
a
=
2
b
=
3
c
= d = 4
l
stOutput.Items.Add(5((a + b) / (c + d
)
41
.
D
im balance, deposit As Doubl
e
b
alance = 1,234
d
eposit = $100
l
stOutput.Items.Add(balance + deposit
)
42.
D
im interest, balance As Doubl
e
0
.05 = interes
t
b
alance = 800
l
stOutput.Items.Add(interest * balance
)
43
.
D
im 9W As Doubl
e
9
W = 2 * 9
W
l
stOutput.Add(9W
)
44
.
D
im n As Double = 1.234
5
l
stOutput.Items.Add(Round(n, 2)
)
45.
D
im quantity As Intege
r
q
uantity = 1
2
46
.
D
im m As Intege
r
D
im n As Doubl
e
m
=
2
n
=
3
Page 5
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 86]
In Exercises 53 through 58, find the value of the given function where a and b are numeric variables of
type Double, a = 5 and b = 3.
In Exercises 59 through 66, write an event procedure starting with a Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...)
Handles btnCompute.Click statement, ending with an End Sub statement, and having one line for each
step. Lines that display data should use the given variable names.
47
.
Int(10.75)
48
.
Int
(
9 - 2
)
49
.
Math.S
q
rt
(
3*12
)
50
.
Math.Sqrt(64)
51
.
Math.Round(3.1279,3)
52
.
Math.Round
(
-2.6
)
53
.
Int
(
-a/2
)
54
.
Math.Round(a / b)
55
.
Math.S
q
rt
(
a - 5
)
56
.
Math.S
q
rt
(
4 + a
)
57
.
Math.Round(a + .5)
58
.
Int(b * .5)
59
.
The following steps calculate a company's profit:
a. Declare all variables.
b. Assign the value 98456 to the variable revenue.
c. Assign the value 45000 to the variable costs.
d. Assign the difference between the variables revenue and costs to the variable
profit.
e. Display the value of the variable profit in a list box.
Page 5
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

60
.
The following steps calculate the amount of a stock purchase:
a. Declare all variables.
b. Assign the value 25.625 to the variable costPerShare.
c. Assign the value 400 to the variable numberOfShares.
d. Assign the product of costPerShare and numberOfShares to the variable amount.
e. Display the value of the variable amount in a list box.
61
.
The following steps calculate the price of an item after a 30% reduction:
a. Declare all variables.
b. Assign the value 19.95 to the variable price.
c. Assign the value 30 to the variable discountPercent.
d. Assign the value of (discountPercent divided by 100) times price to the variable
markDown.
e. Decrease price by markdown.
f. Display the value of price in a list box.
62
.
The following steps calculate a company's brea
k
-even point, the number of units of
goods the company must manufacture and sell in order to break even:
a. Declare all variables.
b. Assign the value 5000 to the variable fixedCosts.
c. Assign the value 8 to the variable pricePerUnit.
d. Assign the value 6 to the variable costPerUnit.
e. Assign the value fixedCosts divided by (the difference of pricePerUnit and
costPerUnit) to the variable breakEvenPoint.
f. Display the value of the variable breakEvenPoint in a list box.
[Page 87]
Page 58 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

63
.
The following steps calculate the balance after three years when $100 is deposited in a
savings account at 5% interest compounded annually:
a. Declare all variables.
b. Assign the value 100 to the variable balance.
c. Increase the variable balance by 5% of its value.
d. Increase the variable balance by 5% of its value.
e. Increase the variable balance by 5% of its value.
f. Display the value of the variable balance in a list box.
64
.
The following steps calculate the balance at the end of three years when $100 is
deposited at the beginning of each year in a savings account at 5% interest compounded
annually:
a. Declare all variables.
b. Assign the value 100 to the variable balance.
c. Increase the variable balance by 5% of its value, and add 100.
d. Increase the variable balance by 5% of its value, and add 100.
e. Increase the variable balance by 5% of its value.
f. Display the value of the variable balance in a list box.
65
.
The following steps calculate the balance after 10 years when $100 is deposited in a
savings account at 5% interest compounded annually:
a. Declare all variables.
b. Assign the value 100 to the variable balance.
c. Multiply the variable balance by 1.05 raised to the 10th power.
d. Display the value of the variable balance in a list box.
66
.
The following steps calculate the percentage profit from the sale of a stock:
a. Declare all variables.
Page 5
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 67 through 72, write an event procedure to solve the problem and display the answer in a
list box. The program should use variables for each of the quantities.
Solutions to Practice Problems 3.3
b. Assign the value 10 to the variable purchasePrice.
c. Assign the value 15 to the variable sellingPrice.
d. Assign, to the variable percentProfit, 100 times the value of the difference between
sellingPrice and purchasePrice divided by purchasePrice.
e. Display the value of the variable percentProfit in a list box.
67
.
Suppose each acre of farmland produces 18 tons of corn. How many tons of corn can be
p
roduced on a 30-acre farm?
68. Suppose a ball is thrown straight up in the air with an initial velocity of 50 feet per
second and an initial height of 5 feet. How high will the ball be after 3 seconds?
N
ote: The height after t seconds is given by the expression -16t
2
+ v
0
t + h
0
,where v
0
is
the initial velocity and h
0
is the initial height.
69
.
If a car left Washington, D.C., at 2 o'clock and arrived in New York at 7 o'clock, what
was its avera
g
e s
p
eed? Note: New York is 233 miles from Washin
g
ton.
[Page 88]
70
.
A motorist wants to determine her gas mileage. At 23,340 miles (on the odometer), the
tank is filled. At 23,695 miles the tank is filled again with 14.1 gallons. How many miles
p
er gallon did the car average between the two fillings?
71
.
A U.S. geological survey showed that Americans use an average of 1600 gallons of water
p
er person per day, including industrial use. How many gallons of water are used each
year in the United States? Note: The current population of the United States is about 300
million people.
72
.
According to FHA specifications, each room in a house should have a window area equal
to at least 10 percent of the floor area of the room. What is the minimum window area for
a 1
4
-ft by 16-ft room?
1
.
Multiplications are performed before additions. If the intent is for the addition to be
Page 60 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

p
erformed first, the expression should be written (2 + 3)*4.
2
.
The first assignment statement assigns the value of the variable var
2
to the variable var1,
whereas the second assi
g
nment statement assi
g
ns var1's value to var
2
.
3
.
Each time an assignment statement is executed, only one variable (the variable to the left
of the e
q
ual si
g
n
)
has its value chan
g
ed.
a b c
Private Sub btnEvaluate_Click(...) Handles
btnEvaluate.Click
Dim a, b, c As Double 0 0 0
a = 3 3 0 0
b = 4 3 4 0
c = a + b 3 4 7
a = c * a 21 4 7
lstResults.Items.Add(a - b) 21 4 7
b = b * b 21 16 7
End Sub
4. Each of the three following statements increases the value of var by 5%.
v
ar = var + 0.05 * va
r
v
ar = 1.05 * va
r
v
ar += 0.05 * va
r
[Page 88 (continued)]
3.4. Strings
The most common types of data processed by Visual Basic are numbers and strings. Sentences, phrases,
words, letters of the alphabet, names, telephone numbers, addresses, and Social Security numbers are all
examples of strings. Formally, a string literal is a sequence of characters that is treated as a single item.
String literals can be assigned to variables, displayed in text boxes and list boxes, and combined by an
operation called concatenation (denoted by &).
Page 61 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 89]
Variables and Strings
A string variable is a name used to refer to a string. The allowable names of string variables are the same
as those of numeric variables. The value of a string variable is assigned or altered with assignment
statements and displayed in a list box like the value of a numeric variable. String variables are declared
with statements of the form
Dim varName As String
Example 1.
If x, y, ..., z are characters and strVar is a string variable, then the statement
strVar = "xy...z"
assigns the string literal xy...z to the variable and the statement
lstBox.Items.Add("xy...z")
The following code shows how assignment statements and the Add method are used with
strings. The string variable today is assigned a value by the third line and this value is
displayed by the seventh line. The quotation marks surrounding each string literal are not
part of the literal and are not displayed by the Add method. (The form for this example
contains a button and a list box.)
Private Sub btnDisplay_Click(...) Handles btnDisplay.Click
Dim today As String
today = "Monday"
With lstOutput.Items
.Clear()
.Add("today")
.Add(today)
End With
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
today
Monday
Page 6
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

o
r
lstBox.Items.Add(strVar)
displays the string xy...z in a list box. If strVar2 is another string variable, then the statement
strVar2 = strVar
assigns the value of the variable strVar to the variable strVar2. (The value of strVar will remain the
same.) String literals used in assignment or lstBox.Items.Add statements must be surrounded by
quotation marks, but string variables are never surrounded by quotation marks.
[Page 90]
Using Text Boxes for Input and Output
The content of a text box is always a string. Therefore, statements such as
strVar = txtBox.Text
and
txtBox.Text = strVar
can be used to assign the contents of the text box to the string variable strVar and vice versa.
N
umbers typed into text boxes are stored as strings. Such strings must be converted to Double or Integer
numeric values before they can be assigned to numeric variables or used in numeric expressions. The
functions CDbl and CInt convert strings representing numbers into numbers of type Double and Integer,
respectively. Going in the other direction, the function CStr converts a number into a string
representation of the number. Therefore, statements such as
dblVar = CDbl(txtBox.Text)
and
txtBox.Text = CStr(dblVar)
can be used to assign the contents of a text box to the Double variable numVar and vice versa. CDbl,
CInt, and CStr, which stand for "convert to Double," "convert to Integer," and "convert to String," are
referred to as data-conversion or type-casting functions.
Example 2.
(This item is displayed on pages 90 - 91 in the print version)
Page 6
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The following program computes the sum of two numbers supplied by the user:
Private Sub btnCompute_Click() Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim num1, num2, sum As Double
num1 = CDbl(txtFirstNum.Text)
num2 = CDbl(txtSecondNum.Text)
sum = num1 + num2
txtSum.Text = CStr(sum)
End Sub
[Page 91]
[Run, type 45 into the first text box, type 55 into the second text box, and click on the
button.]
Object Property Setting
frmAdd Text Addition
lblFirstNum AutoSize False
Text First Number:
txFirstNum
lblSecondNum AutoSize False
Text Second Number:
btnCompute Text Compute Sum
txtSecondNum
lblSum Text Sum:
txtSum ReadOnly True
Page 6
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Concatenation
Two strings can be combined to form a new string consisting of the strings joined together. The joining
operation is called concatenation and is represented by an ampersand (&). For instance, "good" & "bye"
is "goodbye". A combination of strings and ampersands that can be evaluated to form a string is called a
string expression. The assignment statement and the Add method evaluate expressions before assigning
them or displaying them.
Example 3.
Visual Basic also allows strings to be concatenated with numbers and allows numbers to be
concatenated with numbers. In each case, the result is a string.
Example 4.
(This item is displayed on pages 91 - 92 in the print version)
The following program illustrates concatenation. (The form for this example contains a
button and a text box.) Notice the space at the end of the string assigned to quote1. If that
space weren't present, then the statement that assigns a value to quote would have to be
quote = quotel & " " & quote2.
Private Sub btnDisplay_Click(...) Handles btnDisplay.Click
Dim quote1, quote2, quote As String
quote1 = "The ballgame isn't over, "
quote2 = "until it's over."
quote = quote1 & quote2
txtOutput.Text = quote & " Yogi Berra"
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the text box.]
The ball game isn't over, until it's over. Yogi Berra
Page 6
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The statement
strVar = strVar & strVar2
will append the value of strVar2 to the end of the current value of strVar. The same result can be
accomplished with the statement
strVar &= strVar2
String Properties and Methods: Length Property and ToUpper, ToLower, Trim, IndexOf, and
Substring Methods
We have seen that controls, such as text and list boxes, have properties and methods. A control placed
on a form is an example of an object. A string is also an object, and, like a control, has both properties
and methods that are specified by following the string with a period and the name of the property or
method. The Length property gives the number of characters in a string. The ToUpper and ToLower
methods return an uppercase and lowercase version of the string. The Trim method returns the string
with all leading and trailing spaces deleted. The Substring method returns a sequence of consecutive
characters from the string. The IndexOf method searches for the first occurrence of one string in another
and gives the position at which the string is found.
If str is a string, then
str.Length
The following program concatenates a string with a number. Notice that a space was
inserted after the word "has" and before the word "keys." (The form for this example
contains a button and a text box.)
[Page 92]
Private Sub btnDisplay_Click(...) Handles btnDisplay.Click
Dim str As String, numOfKeys As Double
str = "The piano keyboard has "
numOfKeys = 88
txtOutput.Text = str & numOfKeys & " keys."
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the text box.]
The piano keyboard has 88 keys.
Page 6
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

is the number of characters in the string,
str.ToUpper
is the string with all its letters capitalized,
str.ToLower
is the string with all its letters in lowercase format, and
str.Trim
is the string with all spaces removed from the front and back of the string. For instance,
"Visual".Length is 6. "Visual".ToUpper is VISUAL.
"123 Hike".Length is 8. "123 Hike".ToLower is 123 hike.
"a" & " bcd ".Trim & "efg" is abcdefg.
[Page 93]
In Visual Basic, the position of a character in a string is identified with one of the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3,
....A substring of a string is a sequence of consecutive characters from the string. For instance, consider
the string "Just a moment". The substrings "Jus", "mom", and "nt" begin at positions 0, 7, and 11,
respectively.
If str is a string, then
str.Substring(m, n)
is the substring of str consisting of n characters beginning with the character in position m of str. If the
comma and the number n are omitted, then the substring starts at position m and continues until the end
of str. The value of
str.IndexOf(str2)
is -1 if str2 is not a substring of str, and otherwise is the beginning position of the first occurrence of str2
in str. Some examples using these two methods are as follows:
"fanatic".Substring(0, 3) is "fan". "fanatic".IndexOf("ati") is 3.
"fanatic".Substring(4, 2) is "ti". "fanatic".IndexOf("a") is 1.
"fanatic".Substring(4) is "tic". "fanatic".IndexOf("nt") is -1.
The IndexOf method has a useful extension. The value of str.IndexOf(str2, n), where n is an integer, is
Page 6
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

the position of the first occurrence of str
2
in st
r
in position n or greater. For instance, the value of
"Mississippi".IndexOf("ss", 3) is 5.
Like the numeric functions discussed before, string properties and methods also can be applied to
variables and expressions.
Example 5.
(This item is displayed on pages 93 - 94 in the print version)
N
ote: In Example 5, c is in the third position of str1, and there are three characters of str1 to the left of c.
In general, there are n characters to the left of the character in position n. This fact is used in Example 6.
Example 6.
The following program uses variables and expressions with the property and methods just
discussed:
Private Sub btnEvaluate_Click(...) Handles btnEvaluate.Click
Dim str1, str2 As String
str1 = "Quick as "
str2 = "a wink"
With lstResults.Items
.Clear()
.Add(str1.Substring(0, 7))
.Add(str1.IndexOf("c"))
.Add(str1.Substring(0, 3))
.Add((str1 & str2).Substring(6, 6))
.Add((str1 & str2).ToUpper)
.Add(str1.Trim & str2)
.Add("The average " & str2.Substring(str2.Length 4) & _
" lasts .1 second.")
End With
End Sub
[Page 94]
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
Quick a
3
Qui
as a w
QUICK AS A WINK
Quick asa wink
The average wink lasts .1 second.
Page 68 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 95]
The Empty String
The string "", which contains no characters, is called the empty string or the zero-length string. It is
different from "", the string consisting of a single space.
The statement
lstBox.Items.Add("") skips a line in the list box. The contents of a text box can be
cleared with either the statement
txtBox.Clear()
or the statement
txtBox.Text = ""
Initial Value of a String
The following program parses a name. The fifth line locates the position, call it n, of the
space separating the two names. The first name will contain n characters, and the last name
will consist of all characters to the right of the nth character.
Private Sub btnAnalyze_Click(...) Handles btnAnalyze.Click
Dim fullName, firstName, lastName As String
Dim n As Integer
fullName = txtName.Text
n = fullName.IndexOf(" ")
firstName = fullName.Substring(0, n)
lastName = fullName.Substring(n + 1)
With lstResults.Items
.Clear()
.Add("First name: " & firstName)
.Add("Your last name has " & lastName.Length & " letters.")
End With
End Sub
[Run, type "John Doe" into the text box, and then click the button.]
Page 6
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

When a string variable is declared with a Dim statement, it has the keyword Nothing as its default valu
e
.
To specify a different initial value, follow the declaration statement with an equal sign followed by the
initial value. For instance, the statement
Dim today As String = "Monday"
declares the variable today to be of type String and assigns it the initial value "Monday."
An error occurs whenever an attempt is made to perform an operation on a variable having the value
N
othing or to display it in a list box. Therefore, unless a string variable is guaranteed to be assigned a
value before being used, you should initialize iteven if you just assign the empty string to it.
Option Strict
Visual Basic allows string variables to be assigned to numeric variables and vice versa. However, doing
so is considered poor programming practice, and Visual Basic provides a device, called Option Strict, to
p
revent it. When the statement
Option Strict On
is placed at the very top of the Code window, Visual Basic requires the use of type-casting functions
when assigning string values to numeric variables and assigning numeric values to string variables. In
addition, Option Strict On requires type-casting functions when assigning a Double value to an Integer
variable.
Visual Basic provides a way to enforce Option Strict for all programs. Press Alt/Tools/Options to open
the Options dialog box. In the left pane, click on the + sign to the left of Projects and Solutions to
expand this entry. Then click on the subentry VB Defaults. Three default project settings will appear on
the right. Set the default for Object Strict to On and then click on the OK button. From now on, all new
p
rograms will enforce Object Strict.
When Option Strict is in effect, values of Integer variables can be assigned to Double variables, but not
vice versa. Actually, great care must be taken when computing with Integer variables. For instance, the
value of an expression involving division or exponentiation has type Double and therefore cannot be
assigned to an Integer variable even if the value is a whole number. For instance, none of the four
assignment statements that follow is acceptable with Option Strict in effect:
[Page 96]
Dim m As Integer
Dim n As Double
m = n
m = 2.5
m = 2 ^ 3
m = 6 / 2
Throughout this book, we assume that Option Strict is in effect. Therefore, in order to not have to worry
about the four occurrences just discussed, we restrict the use of the Integer variables primarily to
Page 70 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

counting rather than computation.
Internal Documentation
Program documentation is the inclusion of comments that specify the intent of the program, the purpose
of the variables, and the tasks performed by individual portions of the program. To create a comment
statement, just begin the line with an apostrophe. Such a statement appears green on the screen and is
completely ignored when the program is executed. Comment lines appear whenever the program is
displayed or printed. Also, a line of code can be documented by adding an apostrophe, followed by the
desired information, after the end of the line.
Example 7.
Some of the benefits of documentation are as follows:
1. Other people can easily understand the program.
2. You can understand the program when you read it later.
[Page 97]
3. Long programs are easier to read because the purposes of individual pieces can be determined at a
glance.
Even though Visual Basic code is easy to read, it is difficult to understand the programmer's intentions
without supporting documentation. Good programming practice dictates that developers document their
code at the same time that they are writing it. In fact, many software companies require a certain level of
The following rewrite of Example 6 uses internal documentation. The first comment
describes the entire program, the comment in line 4 gives the meaning of the variable, and
the final comment describes the purpose of the With block.
Private Sub btnAnalyze_Click(...) Handles btnAnalyze.Click
'Determine a person's first name and the length of the second name
Dim fullName, firstName, lastName As String
Dim n As Integer 'location of the space separating the two names
fullName = txtName.Text
n = fullName.IndexOf(" ")
firstName = fullName.Substring(0, n)
lastName = fullName.Substring(n + 1)
'Display the desired information in a list box
With lstResults.Items
.Clear()
.Add("First name: " & firstName)
.Add("Your last name has " & lastName.Length & "letters.")
End With
End Sub
Page 71 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

documentation before they release a version, and some judge their programmers' performances on how
well their code is documented. A rule of thumb is that 10% of the effort developing a software program
is the initial coding, while the remaining 90% is maintenance. Much of the anxiety surrounding the
fixing of the "Year 2000" problem was due to the enormous amount of effort required by programmers
to read and fix old, undocumented code. The challenge was compounded by the fact that most of the
original programmers of the code were retired or could not recall how their code was written.
Line-Continuation Character
Thousands of characters can be typed in a line of code. If you use a statement with more characters than
can fit in the window, Visual Basic scrolls the Code window toward the right as needed. However, most
p
rogrammers prefer having lines that are no longer than the width of the Code window. A long
statement can be split across two or more lines by ending each line (except the last) with the underscore
character (_) preceded by a space. Make sure the underscore doesn't appear inside quotation marks,
though. For instance, the line
msg = "640K ought to be enough for anybody. (Bill Gates, 1981)"
can be written as
msg = "640K ought to be enough for " & _
"anybody. (Bill Gates, 1981)"
The line-continuation character does not work with comment statements. That is, each line of a
comment statement must be preceded by an apostrophe.
Comments
1. From the Code window, you can determine the type of a variable by letting the mouse cursor
hover over the variable name until a tooltip appears.
2. Variable names should describe the role of the variable. Also, some programmers use a prefix,
such as dbl or str, to identify the type of a variable. For example, they would use names like
dblInterestRate and strFirstName. This device is not needed in Visual Basic for the reason
mentioned in Comment 1.
3. The functions CInt and CDbl are user friendly. If the user types a number into a text box, but
types in a comma as the thousands separator, the values of CInt(txtBox.Text) and CDbl
(txtBox.Text) will be the number with the comma removed.
[Page 98]
4. The Trim method is useful when reading data from a text box. Sometimes users type spaces at the
end of the input. Unless the spaces are removed, they can cause havoc elsewhere in the program.
5. There are several alternatives to CStr for casting a value to a string value. For instance, the
statement
strVar = CStr(dblVar)
Page 7
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

can be replaced with any of the following statements:
strVar = CType(dblVar, String)
strVar = convert.ToString(dblVar)
strVar = dblVar.ToString
6. Colorization. You can specify colors for the different elements of a program. For instance, in this
book keywords are colored blue, comment statements are colored green, and strings are colored
maroon. To specify the color for an element, Click on Options in the Tools menu. Then click on
the + sign to the left of Environment to expand this entry, and click on the subentry Fonts and
Colors. At this point, you can select an item from the Display list and specify the items foreground
and background colors.
Practice Problems 3.4
Exercises 3.4
In Exercises 1 through 28, determine the output displayed in the text box or list box by the lines of code.
1
.
What is the value of "Com
p
uter".IndexOf
(
"E"
)
?
2. What is the difference in the output produced by the following two statements? Why is
CStr used in the first statement, but not in the second?
t
xtBox.Text = CStr(8 + 8
)
t
xtBox.Text = 8 &
8
1
.
t
xtBox.Text = "Visual Basic
"
2
.
l
stBox.Items.Add("Hello"
)
3.
D
im var As String
v
ar = "Ernie
"
l
stBox.Items.Add(var
)
4
.
D
im var As String
v
ar = "Bert
"
t
xtBox.Text = va
r
t
xtBox.Text = "f" & "lute
"
Page 7
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

5
.
6.
l
stBox.Items.Add("a" & "cute"
)
[
Pa
g
e 99
]
7.
D
im var As Doubl
e
v
ar = 12
3
t
xtBox.Text = CStr(var
)
8
.
D
im var As Doubl
e
v
ar =
3
t
xtBox.Text = CStr(var + 5
)
9
.
t
xtBox.Text = "Your age is " & 21 & ".
"
10
.
t
xtBox.Text = "Fred has " & 2 & " children.
"
11
.
D
im r, b As String
r
= "A ROSE
"
b
= " IS
"
t
xtBox.Text = r & b & r & b &
r
12
.
D
im s As String, n As Intege
r
s
= "trombones
"
n
= 76
t
xtBox.Text = n & " " &
s
13.
D
im num As Doubl
e
t
xtBox.Text = "5
"
n
um = 0.5 + CDbl(txtBox.Text
)
t
xtBox.Text = CStr(num
)
14
.
D
im num As Integer =
2
Page 7
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

t
xtBox.Text = CStr(num
)
t
xtBox.Text = CStr(1 + CInt(txtBox.Text)
)
15
.
t
xtBox.Text = "good
"
t
xtBox.Text &= "bye
"
16
.
D
im var As String = "eight
"
v
ar &= "h
"
t
xtBox.Text = va
r
17
.
D
im var As String = "WALLA
"
v
ar &= va
r
t
xtBox.Text = va
r
18.
t
xtBox.Text = "mur
"
t
xtBox.Text &= txtBox.Tex
t
19
.
W
ith lstBox.Item
s
.Add("aBc".ToUpper)
.Add("Wallless".IndexOf("lll"))
.Add("five".Length)
.Add(" 55 ".Trim & " mph")
.Add("UNDERSTUDY".Substring(5, 3))
E
nd Wit
h
[Page 100]
20
.
W
ith lstBox.Item
s
.Add("8 Ball".ToLower)
.Add("colonel".IndexOf("k"))
.Add("23.45".Length)
.Add("revolutionary".Substring(1))
.Add("whippersnapper".IndexOf("pp", 5))
E
nd Wit
h
21
.
D
im a As Integer = 4
D
im b As Integer =
2
D
im c As String = "Municipality
"
D
im d As String = "pal
"
Page 7
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 27 through 32, identify any errors.
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add(c.Length)
.Add(c.ToUpper)
.Add(c.Substring(a, b) & c.Substring(5 * b))
.Add(c.IndexOf(d))
E
nd Wit
h
22
.
D
im m As Integer = 4
D
im n As Integer =
3
D
im s As String = "Microsoft
"
D
im t As String = "soft
"
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add(s.Length)
.Add(s.ToLower)
.Add(s.Substring(m, n - 1))
.Add(s.IndexOf(t))
E
nd Wit
h
23
.
How man
y
p
ositions does a strin
g
of ei
g
ht characters have?
24
.
What is the highest numbered position for a string of eight characters?
25
.
(True or False) If n is the length of st
r
, then str.Substring(n - 1) is the string
consisting of the last character of str.
26
.
(True or False) If n is the length of st
r
, then str.Substring(n - 2) is the string
consisting of the last two characters of str.
27
.
D
im phoneNumber As Doubl
e
p
honeNumber = "234-5678"
t
xtBox.Text = "My phone number is " & phoneNumbe
r
28.
D
im quote As String
q
uote = I came to Casablanca for the waters.
t
xtBox.Text = quote & ": " & "Bogart
"
[Page 101]
29
.
D
im end As String
e
nd = "happily ever after.
"
t
xtBox.Text = "They lived " & en
d
Page 7
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m
In Exercises 33 through 34, write an event procedure starting with a Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...)
Handles btnCompute.Click statement, ending with an End Sub statement, and having one line for each
step. Display each result by assigning it to the txtOutput.Text property. Lines that display data should
use the given variable names.
30.
D
im hiyo As String
h
iyo = "Silver
"
t
xtBox = "H
i
-Yo " & hiYo
31
.
D
im num As Double = 1234
t
xtBox.Text = Str(num.IndexOf("2")
)
32
.
D
im num As Integer = 4
5
t
xtBox.Text = Str(num.Length
)
33. The following steps give the name and birth year of a famous inventor:
a. Declare all variables used in steps (b)(e).
b. Assign "Thomas" to the variable firstName.
c. Assign "Alva" to the variable middleName.
d. Assign "Edison" to the variable lastName.
e. Assign 1847 to the variable yearOfBirth.
f. Display the inventor's full name followed by a comma and his year of birth.
34. The following steps compute the price of ketchup:
a. Declare all variables used in steps (b)(d).
b. Assign "ketchup" to the variable item.
c. Assign 1.80 to the variable regularPrice.
d. Assign .27 to the variable discount.
Page 7
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 102]
In Exercises 37 through 40, the interface is specified. Write the code to carry out the stated task.
e. Display the phrase "1.53 is the sale price of ketchup."
35
.
The following steps display a copyright statement:
a. Declare the variable used in step (b).
b. Assign "Prentice Hall, Inc." to the variable publisher.
c. Display the phrase "(c) Prentice Hall, Inc."
36
.
The following steps give advice:
a. Declare the variable used in step (b).
b. Assign "Fore" to the variable prefix.
c. Display the phrase "Forewarned is Forearmed."
37
.
If n is the number of seconds between lightning and thunder, the storm is n/5 miles away.
Write a program that requests the number of seconds between lightning and thunder and
reports the distance of the storm. A sample run is shown in Figure 3.17.
Figure 3.17. Sample output of Exercise 37.
38. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends that you maintain your training
Page 78 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

heart rat
e
during an aerobic workout. Your training heart rate is computed as .7 * (220 -
a) + .3 * r, where a is your age and r is your resting heart rate (your pulse when you first
awaken). Write a program to request a person's age and resting heart rate and then
calculate the training heart rate. (Determine your training heart rate.) A sample run is
shown in Figure 3.18.
Figure 3.18. Sample output of Exercise 38.
[Page 103]
39
.
The number of calories burned per hour by bicycling, jogging, and swimming are 200,
475, and 275, respectively. A person loses 1 pound of weight for each 3500 calories
b
urned. Write a program that allows the user to input the number of hours spent at each
activity and then calculates the number of pounds worked off. A sample run is shown in
Figure 3.1
9
.
Figure 3.19. Sample output of Exercise 39.
Page 7
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 104]
In Exercises 41 through 46, write a program with a Windows-style interface to carry out the task. The
p
rogram should use variables for each of the quantities and display the outcome in a text box with a
label as in Example 6.
40
.
Write a program to request the name of a baseball team, the number of games won, and
the number of games lost as input, and then display the name of the team and the
p
ercentage of games won. A sample run is shown in Figure 3.20.
Figure 3.20. Sample output of Exercise 40.
41
.
Request a company's annual revenue and expenses as input, and display the company's
net income (revenue minus expenses). (Test the program with the amounts $550,000 and
$410,000.
)
42. Request a company's earnings-per-share for the year and the price of one share of stock
as input, and then display the company's pric
e
-to-earnings ratio (that is, price/earnings).
(
Test the
p
ro
g
ram with the amounts $5.25 and $68.25.
)
43. Calculate the amount of a waiter's tip, given the amount of the bill and the percentage tip
as input. (Test the program with $20 and 15 percent.)
44
.
Calculate a baseball player's batting average, given his times at bat and number of hits as
in
p
ut. Not
e
: Battin
g
avera
g
es are dis
p
la
y
ed to three decimal
p
laces.
45
.
Write a program that contains a button and a rea
d
-only text box on the form, with the text
b
ox initially containing 0. Each time the button is pressed, the number in the text box
Page 80 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Solutions to Practice Problems 3.4
should increase by 1.
46
.
Write a program that requests a (complete) phone number in a text box and then displays
the area code in another text box when a button is
p
ressed.
47
.
Write a program that requests a sentence, a word in the sentence, and another word and
then displays the sentence with the first word replaced by the second. For example, if the
u
ser responds by typing "What you don't know won't hurt you." into the first text box and
know and owe into the second and third text boxes, then the message "What you don't
owe won't hurt you." is displayed.
48
.
Write a program that requests a letter, converts it to uppercase, and gives its first position
in the sentence "THE QUICK BROWN FOX JUMPS OVER A LAZY DOG." For
example, if the user responds by typing b into the text box, then the message "B first
occurs in position 10." is displayed.
49
.
The formula gives an estimate of the speed of a car in miles per hour that
skidded d feet on dry concrete when the brakes were applied. Write a program that
requests the distance skidded and then displays the estimated speed of the car. (Try the
p
ro
g
ram for a car that skids 54 feet.
)
50
.
Write a program that requests a positive number containing a decimal point as input and
then displays the number of digits to the left of the decimal point and the number of
di
g
its to the ri
g
ht of the decimal
p
oint.
1. -1.There is no uppercase letter E in the string "Computer". IndexOf distinguishes
b
etween uppercase and lowercase.
2
.
The first statement displays 16 in the text box, whereas the second statement displays 88.
With Option Strict in effect, the first statement would not be valid if CStr were missing,
since 8+8 is a number and txtBox.Text is a string. Visual Basic treats the second
statement as if it wer
e
t
xtBox.Text = CStr(8) & CStr(8
)
[Page 105]
3.5. Input and Output
Page 81 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Formattin
g
Output with Format Functions
The Format functions are used to display numbers in familiar forms and to align numbers. Here are
some examples of how numbers are converted to strings with Format functions:
The value of FormatNumber(n, r) is the string containing the number n rounded to r decimal places and
displayed with commas as thousands separators. The value of FormatCurrency(n, r) is the string
consisting of a dollar sign followed by the value of FormatNumber(n, r). FormatCurrency uses the
accountant's convention of denoting negative amounts with surrounding parentheses. The value of
FormatPercent(n, r) is the string consisting of the number n displayed as a percent and rounded to r
decimal places. With all three functions, r can be omitted. If so, the number is rounded to two decimal
p
laces. Strings corresponding to numbers less than one in magnitude have a zero to the left of the
decimal point. Also, n can be a number, a numeric expression, or even a string corresponding to a
number.
Formatting Output with Zones
Data can be displayed in tabular form in a list box. In order to have the items line up nicely in columns,
you must
a. use a fixed-width font such as Courier New so that each character will have the same width;
b. divide the line into zones with a format string.
Figure 3.21 (on the next page) shows a line of a list box divided into zones of widths 15 characters, 10
characters, and 8 characters. The leftmost zone is referred to as zone 0, the next zone is zone 1, and so
on. These zones are declared in a string with the statement
Dim fmtStr As String = "{0, 15}{1, 10}{2, 8}"
Figure 3.21. Zones.
(This item is displayed on page 106 in the print version)
Function String Value
FormatNumber(12345.628, 1) 12,345.6
FormatCurrency(12345.628, 2) $12,345.63
FormatPercent(0.185, 2) 18.50%
Function String Value
FormatNumber(1 + Math.Sqrt(2), 3) 2.414
FormatCurrency(1000) ($1,000.00)
FormatPercent(".05") 5.00%
Page 8
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

N
ot
e
: The pairs of numbers are surrounded by curly brackets, not parentheses.
[Page 106]
If data0, data1, and data2 are strings or numbers, the statement
lstOutput.Items.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, data0, data1, data2))
displays the pieces of data right justified into the zones. If any of the width numbers 15, 10, or 8 is
p
receded with a minus sign, the data placed into the corresponding zone will be left justified.
Example 1.
The following program displays information about two colleges in the United States. Note:
The endowments are in billions of dollars. The final column tells what fraction of the
student body attended public secondary schools.
Private Sub btnDisplay_Click(...) Handles btnDisplay.Click
Dim fmtStr As String = "{0,-10}{1,12}{2,14}{3,12}"
With lstColleges.Items
.Clear()
Object Property Setting
frmColleges Text College Data
lstColleges Font Courier New
btnDisplay Text Display Table
Page 8
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 107]
There is no limit to the number of zones, and the zones can be of any widths. In addition, by placing a
colon and formatting symbols after the width, you can instruct Visual Basic to specially format numeric
data. (String data are not affected.) The most used formatting symbols consist of a letter (n for number,
C for currency, or P for percent) followed by a digit specifying the number of decimal places. If there is
no digit after the letter, two decimal places are displayed. Here are some examples of such formatting:
If the second line of the program in Example 1 is replaced with
Dim fmtStr As String = "{0,-10}{1,12:N0}{2,14:C}{3,12:P0}"
the output will be as follows.
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "College", "Enrollment", _
"Endowment", "Public SS"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Harvard", 6660, 19.2, 0.659))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Yale", 5278, 10.1, 0.532))
End With
End Sub
[Run, and click on the button.]
Zone Format
Term
Number to Be
Formatted
Number
Displayed
{1, 12:N3} 1234.5679 1,234.568
{1, 12:N0} 34.6 34
{1, 12:C1} 1234.567 $1,234.6
{1, 12:P} 0.569 56.90%
Page 8
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

The format strings considered so far consist of a sequence of pairs of curly brackets. We also can insert
spaces between successive pairs of brackets. If so, the corresponding zones in the output will be
separated by those spaces. The lines of code
Dim fmtStr As String = "{0, 5} {1, -5}" 'Two spaces after the
'first right curly bracket
With lstOutput.Items
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 1, 2))
End With
p
roduce the output
12345678901234567890
1 2
[Page 108]
Reading Data from Files
So far, we have relied on assignment statements and text box controls to assign data to variables. Data
also can be stored in files and accessed with a StreamReader object or supplied by the user with an input
dialog box.
In Chapter 1
, we saw how to create text files with Windows Notepad. We will assume that the files
created with Notepad have one item of information per line. Figure 3.22
shows a sample file giving
p
ayroll information. Each set of three lines gives the name of a person, their hourly wage, and the
number of hours that person worked during the week.
Figure 3.22. Contents of PAYROLL.TXT.
Mike Jones
7.35
35
John Smith
6.75
33
Page 8
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Data stored in a file can be read in order (that is, sequentially) and assigned to variables with the
following steps:
1. Execute a statement of the form
Dim readerVar As IO.StreamReader
A StreamReader is an object from the Input/Output class that can read a stream of characters
coming from a disk or coming over the Internet. The Dim statement declares the variable
readerVar to be of type StreamReader.
2. Execute a statement of the form
readerVar = IO.File.OpenText(filespec)
where filespec identifies the file to be read. This statement establishes a communications link
between the computer and the disk drive for reading data from the disk. Data then can be input
from the specified file and assigned to variables in the program. This assignment statement is said
to "open the file for input."
Just as with other variables, the declaration and assignment statements in Steps 2 and 3 can be
combined into the single statement
Dim readerVar As IO.StreamReader = IO.File.OpenText(filespec)
3. Read items of data in order, one at a time, from the file with the ReadLine method. Each datum is
retrieved as a string. A statement of the form
strVar = readerVar.ReadLine
[Page 109]
causes the program to look in the file for the next unread line of data and assign it to the variable
strVar. The data can be assigned to a numeric variable if it is first converted to a numeric type with
a statement such as
numVar = CDbl(readerVar.ReadLine)
Note: If all the data in a file have been read by ReadLine statements and another item is requested
by a ReadLine statement, the item retrieved will have the value Nothing.
4.
After the desired items have been read from the file, terminate the communications link set in Step
3 with the statement
Page 8
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Example 2.
Let's now rewrite this program so that it uses a file for input and produces the same output. First, use
Windows Notepad to create the file DATA.TXT containing the following two lines:
1600
Pennsylvania Ave.
In the following code, the fifth line of the event procedure reads the first row of data as the string "l600",
converts its type to Double, and assigns it to the variable houseNumber. (Visual Basic records that this
row of data has been used.) The sixth line looks for the next available line of data, "Pennsylvania Ave.",
and assigns it to the string variable street.
N
ot
e
: You will have to alter the information inside the parentheses in the second line to tell Visual Basic
where the file DATA.TXT is located. For instance, if the file is in the root folder of a diskette in drive A,
then the parentheses should contain the string "A:\DATA.TXT". If the file is located in the subfolder My
Programs of the C drive, then the parentheses should contain the string "C:\My Programs\DATA.TXT".
In this book, we will always write just the name of the file and leave it up to you to add an appropriate
p
ath.
[Page 110]
Private Sub btnDisplay_Click(...) Handles btnDisplay.Click
Dim sr As IO.StreamReader = IO.File.OpenText("DATA.TXT")
readerVar.Close()
Consider the following program that displays the address of the White House. (The form
design for all examples in this section consists of a button and a text or list box.)
Private Sub btnDisplay_Click(...) Handles btnDisplay.Click
Dim houseNumber As Double
Dim street, address As String
houseNumber = 1600
street = "Pennsylvania Ave."
address = houseNumber & " " & street
txtAddr.Text = "The White House is located at " & address
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the text box.]
The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave.
Page 8
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Dim houseNumber As Double
Dim street, address As String
houseNumber = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
street = sr.ReadLine
sr.Close()
address = houseNumber & " " & street
txtAddr.Text = "The White House is located at " & address
End Sub
Each Visual Basic program is contained in a folder with the name you specified in the Save Project
window. This folder holds the files for the program and contains three subfolders named bin, My
Project, and obj. The folder bin contains two subfolders named Debug and Release. If no path is
specified for a text file, Visual Basic will look for the file in the Debug subfolder for the program. Every
p
rogram from the companion website for this book that reads a file assumes that the file is located in the
Debug subfolder for the program. Therefore, even after you copy the contents of the Programs folder
onto a hard drive, the programs will continue to execute properly without your having to alter any paths.
Example 3.
(This item is displayed on pages 110 - 111 in the print version)
The following program uses the file PAYROLL.TXT shown in Figure 3.22.
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim sr As IO.StreamReader = IO.File.OpenText("PAYROLL.TXT")
'The file PAYROLL.TXT is in the Debug subfolder
'of the bin subfolder of the folder 3-5-3.
Dim name As String
Dim hourlyWage, hoursWorked, salary As Double
name = sr.ReadLine
hourlyWage = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
hoursWorked = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
salary = hourlyWage * hoursWorked
lstPayroll.Items.Add(name & " " & FormatCurrency(salary))
name = sr.ReadLine
hourlyWage = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
hoursWorked = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
sr.Close()
salary = hourlyWage * hoursWorked
lstPayroll.Items.Add(name & " " & FormatCurrency(salary))
End Sub
[Page 111]
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
Mike Jones $257.25
John Smith $222.75
Page 88 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In certain situations, we must read the data in a file more than once. This is accomplished by reopening
the file with a second assignment statement of the form sr = IO.File.OpenText(filespec). This
statement sets a pointer to the first line of data in the specified file. Each time a ReadLine method is
executed, the line pointed to is read, and the pointer in then moved to the next line. After the last line of
data is read, the pointer is said to be at the end of the file.
Example 4.
(This item is displayed on pages 111 - 112 in the print version)
The following program takes the average annual amounts of money spent by single-person
households for several categories and converts these amounts to percentages. The data are
read once to compute the total amount of money spent and then read again to calculate the
percentage for each category. Note: These figures were compiled for a recent year by the
Bureau of Labor Statistics.
The file COSTS.TXT consists of the following eight lines:
Transportation
4251
Housing
8929
Food
3414
Other
8829
Private Sub btnCompute_Click(...) Handles btnCompute.Click
Dim sr As IO.StreamReader = IO.File.OpenText("COSTS.TXT")
Dim total As Double 'Total annual amount spent
Dim category As String
Dim amount As Double 'Amount spent on category
Dim fmtStr As String = "{0,-15}{1,8:P}"
category = sr.ReadLine 'Read the first category from the file
total += CDbl(sr.ReadLine) 'Increment total by the amount
'associated with the category
category = sr.ReadLine 'Read the next category from the file
total += CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
category = sr.ReadLine
total += CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
category = sr.ReadLine
total += CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
sr.Close()
Page 8
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Getting Input from an Input Dialog Box
N
ormally, a text box is used to obtain input, where the type of information requested is specified in a
label adjacent to the text box. Sometimes, we want just one piece of input and would rather not have a
text box and label stay on the screen forever. The problem can be solved with an input dialog box. When
a statement of the form
stringVar = InputBox(prompt, title)
is executed, an input dialog box similar to the one shown in Figure 3.23 pops up on the screen. After the
user types a response into the text box at the bottom of the screen and presses Enter (or clicks OK), the
response is assigned to the string variable. The title argument is optional and provides the text that
appears in the Title bar. The prompt argument is a string that tells the user what information to type into
the text box.
Figure 3.23. Sample input dialog box.
[Page 112]
sr = IO.File.OpenText("COSTS.TXT") 'Open the file anew
category = sr.ReadLine
amount = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
lstPercent.Items.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, category, amount / total))
category = sr.ReadLine
amount = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
lstPercent.Items.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, category, amount / total))
category = sr.ReadLine
amount = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
lstPercent.Items.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, category, amount / total))
category = sr.ReadLine
amount = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
lstPercent.Items.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, category, amount / total))
sr.Close()
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The following is displayed in the list box.]
Transportation 16.72 %
Housing 34.12 %
Food 13.43 %
Other 34.73 %
Page 90 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 113]
When you type the opening parenthesis following the word InputBox, the editor displays a line
containing the general form of the InputBox statement. See Figure 3.24. This feature of IntelliSense is
called Parameter Info. Optional parameters are surrounded by square brackets. All the parameters in the
general form of the InputBox statement are optional except for prompt.
Figure 3.24. Parameter Info feature of IntelliSense.
[View full size image]
Example 5.
In the following enhancement to Example 2, the file name is provided by the user in an
input dialog box. We assume that the program is contained in the subfolder Debug of the
program folder.
Private Sub btnDisplay_Click(...) Handles btnDisplay.Click
Dim sr As IO.StreamReader
Dim fileName, prompt, title, street As String
Dim houseNumber As Double
prompt = "Enter the name of the file containing the information."
title = "Name of File"
fileName = InputBox(prompt, title)
'We assume the file is located in the subfolder Debug
'of the bin subfolder of the folder 3-5-5.
sr = IO.File.OpenText(fileName)
Page 91 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 114]
The response typed into an input dialog box is treated as a single string value, no matter what is typed.
(Quotation marks are not needed and, if included, are considered as part of the string.) Numeric data
typed into an input dialog box should be converted to a number with CDbl or CInt before being assigned
to a numeric variable or used in a calculation. Just as with a text box or file, the typed data must be a
literal. It cannot be a variable or an expression. For instance, num, 1/2, and 2+3 are not acceptable.
Using a Message Dialog Box for Output
Sometimes you want to grab the user's attention with a brief message such as "Correct" or "Nice try, but
no cigar." You want this message only to appear on the screen until the user has read it. This task is
easily accomplished with a message dialog box such as the one shown in Figure 3.25. When a statement
of the form
Figure 3.25. Sample message dialog box.
MsgBox(prompt, 0, title)
is executed, where prompt and title are strings, a message dialog box appears with prompt displayed and
the Title bar caption title and stays on the screen until the user presses Enter, clicks on the box in the
upper-right corner, or clicks OK. For instance, the statement
MsgBox("Nice try, but no cigar.", 0, "Consolation")
houseNumber = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
street = sr.ReadLine
sr.Close()
txtAddr.Text = "The White House is located at " & _
houseNumber & " " & street & "."
End Sub
[Run, and then click the button. The input dialog box of Figure 3.23 appears on the screen.
Type "DATA.TXT" into the input dialog box, and click on OK. The input dialog box
disappears, and the following appears in the text box.]
The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Ave.
Page 9
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

p
roduces Figure 3.25. You can omit the zero and a value for title and just execute MsgBox(prompt). If
you do, the Title bar will contain the name of the program and the rest of the message dialog box will
appear as before.
Using a Masked Text Box for Input
Problems can arise when the wrong type of data is entered as input into a text box. For instance, if the
user replies to the request for an age by entering "twenty-one" into a text box, the program can easily
crash. Sometimes this type of predicament can be avoided by using a masked text box for input. (In later
chapters, we will consider other ways of insuring the integrity of input.)
In the Toolbox, the icon for the MaskedTextBox control consists of a rectangle containing the two
characters # and _. The most important property of a masked text box is the Mask property that can be
used to restrict the characters entered into the box. Also, the Mask property can be used to show certain
characters in the controlto give users a visual cue that they should be entering a phone number or a
social security number, for example. Some possible settings for the Mask property are shown in Table
3.3. The first two settings can be selected from a list of specified options. The last three settings
generalize to any number of digits, letters, or ampersands. If the Mask property is left blank, then the
MaskedTextBox control is nearly identical to the TextBox control.
[Page 115]
Suppose a form contains a masked text box whose Mask property has the setting 000-00-0000. When
the program is run, the string "___-__-____" will appear in the masked text box. The user will be
allowed to type a digit in place of each of the eight underscore characters. The hyphens cannot be
altered, and no characters can be typed anywhere else in the masked text box.
During run time, the characters 0, L, and & in the setting for a Mask property are replaced by underscore
characters that are place holders for digits, letters, and letters and/or spaces, respectively. When the
characters "-", "(", ")", or "/" appear in a characters for a Mask property, they appear as themselves in the
masked text box and cannot be altered. There are some other mask settings, but these seven will suffice
Table 3.3. Some settings for the Mask property.
Setting Effect
000-00-0000 The user can only enter a social security number.
000-0000 The user can only enter a phone number (without an area
code).
(000)000-0000 The user can only enter a phone number (with an area code).
00/00/0000 The user can only enter a date.
0000000 The user can only enter a positive integer consisting of 7
digits.
LLLLL The user can only enter a string consisting of 5 letters.
&&&&&&&& The user can only enter a string consisting of 8 characters.
Page 9
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

for our purposes.
Figure 3.26 (a) shows a masked text box during design time. It looks like an ordinary text box. However,
the Tasks button for the masked text box is used to set the Mask property rather than the Multiline
p
roperty. Figure 3.26 (b) shows the result of clicking on the Tasks button. Then, clicking on "Set mask"
brings up the Input Mask dialog box shown in Figure 3.27. (This input dialog box is the same input
dialog box that is invoked when you click on the ellipses in the Mask property's setting box.) You can
use this input dialog box to select a commonly used value for the Mask property, such as the social
security number or phone number mask, or set and test a custom-designed mask you create with
characters such as 0, &, and L. We will use the prefix mtxt for the names of masked dialog boxes.
Figure 3.26. The Masked TextBox control.
[Page 116]
Figure 3.27. Input dialog box used to set the Mask property of a masked text box.
Page 9
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Comments
The statement Dim sr As IO.StreamReader = IO.File.OpenText("DATA.TXT") will be used
frequently in this book, albeit with a different file name each time. You can store this line of code (or
any frequently used fragment of code) for later reuse by highlighting it and dragging it from the Code
window into the Toolbox. To reuse the code, just drag it back from the Toolbox to the Code window. A
copy of the code will remain in the Toolbox for further use. Alternately, you can click on the location in
the Code window where you want the code to be inserted, and then double-click on the code in the
Toolbox.
Practice Problems 3.5
Exercises 3.5
In Exercises 1 through 30, determine the output produced by the lines of code.
1
.
Is the statement
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(12345.628, 1
)
correct, or should it be writte
n
t
xtOutput.Text = CStr(FormatNumber(12345.628, 1)
)
[
Pa
g
e 117
]
2
.
What is the difference in the outcomes of the following two sets of code?
s
trVar = InputBox("How old are you?", "Age"
)
n
umVar = CDbl(strVar
)
t
xtOutput.Text = numVa
r
n
umVar = CDbl(InputBox("How old are you?", "Age"
)
t
xtOutput.Text = numVa
r
1
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(1234.56, 0
)
2
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(-12.3456, 3)
Page 9
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

3
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(1234, 1
)
4.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(12345
)
5
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(0.012, 1
)
6.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(5 * (10 ^ -2), 1)
7
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(-2/3)
8.
D
im numVar As Double = Math.Round(1.2345, 1
)
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(numVar
)
9
.
D
im numVar As Double = Math.Round(12345.9
)
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(numVar, 3
)
10.
D
im numVar As Double = Math.Round(12.5
)
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(numVar, 0
)
11
.
D
im numVar As Double = Math.Round(11.5
)
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatNumber(numVar, 0
)
12
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatCurrency(1234.5
)
13
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatCurrency(12345.67, 0
)
14
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatCurrency(-1234567)
Page 9
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

15
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatCurrency(-0.225)
16.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatCurrency(32 * (10 ^ 2)
)
17
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatCurrency(4 / 5
)
18.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(0.04, 0
)
19
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(0.075
)
20.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(-.05, 3)
21
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(1
)
22.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(0.01
)
23
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(2 / 3
)
24
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(3 / 4, 1
)
25
.
t
xtOutput.Text = "Pay to France " & FormatCurrency(27267622
)
26
.
t
xtOutput.Text = "Manhattan was purchased for " & FormatCurrency(24
)
[
Pa
g
e 118
]
27.
D
im popUSover24 As Double = 177.6 'Millio
n
Page 9
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 31 through 40, determine the output produced by the lines of code. Assume that Courier
N
ew is the font for the list box.
D
im collegeGrads As Double = 45.5 'Millio
n
'45.5/177.6 = 0.2561937
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatPercent(collegeGrads / popUSover24, 1) &
_
" of the U.S. population 25+ years old are college graduates."
28
.
D
im degrees As String = FormatNumber(1711500, 0
)
t
xtOutput.Text = degrees & " degrees were conferred.
"
29.
t
xtOutput.Text = "The likelihood of Heads is " &
_
FormatPercent(1 / 2, 0)
30
.
t
xtOutput.Text = "Pi = " & FormatNumber(3.1415926536, 4
)
31
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0
,
-5}{1,5}"
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 1, 2))
E
nd Wit
h
32
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0,5}{1,5}
"
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 1, 2))
E
nd Wit
h
33
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0,5}{1
,
-5}"
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 1, 2))
E
nd Wit
h
34
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0
,
-5}{1,-5}"
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add("12345678901234567890")
Page 98 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 1, 2))
E
nd Wit
h
35
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0,3}{1,10}
"
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "A", "Alice"))
E
nd Wit
h
[
Pa
g
e 119
]
36
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0
,
-13}{1,-10}{2,-7:N0}"
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add("123456789012345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Mountain", "Place", "Ht (ft)"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "K2", "Kashmir", 28250))
E
nd Wit
h
37
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0,11} {1
,
-11}" 'Three spaces
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "College", "Mascot"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Univ. of MD", "Terrapins"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Duke", "Blue Devils"))
E
nd Wit
h
38
.
'
Toss coin twic
e
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0,8} {1
,
-7:P0}" 'Two spaces
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Clear()
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Number", "Percent"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "of Heads", "of time"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 0, 1 / 4))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 1, 1 / 2))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, 2, 1 / 4))
E
nd Wit
h
39
.
'
Elements in a 150 Pound Perso
n
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0
,
-7} {1,-7:N1} {2,-7:P1}" '2 spaces
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Clear()
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Element", "Weight", "Percent"))
Page 9
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 120]
In Exercises 41 through 52, assume that the file DATA.TXT (shown to the right of the code) has been
accessed with the statement Dim sr As IO.StreamReader = IO.File.OpenText("DATA.TXT") and
closed afterwards with the statement sr.Close(). Determine the output displayed by the lines of code.
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Oxygen", 97.5, 97.5 / 150))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Carbon", 27, 27 / 150))
E
nd Wit
h
40
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0,10} {1
,
-10:C0}" 'Three spaces
W
ith lstOutput.Item
s
.Clear()
.Add("12345678901234567890")
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "", "Tuition"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "College", "& Fees"))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Stanford", 24441))
.Add(String.Format(fmtStr, "Harvard", 25128))
E
nd Wit
h
41
.
D
im num As Double DATA.TX
T
n
um = CDbl(sr.ReadLine) 4
t
xtOutput.Text = CStr(num * num
)
42
.
D
im word As String DATA.TX
T
w
ord = sr.ReadLine speakabl
e
t
xtOutput.Text = "un" & wor
d
43.
D
im strl, str2 As String DATA.TX
T
s
tr1 = sr.ReadLine bas
e
s
tr2 = sr.ReadLine bal
l
t
xtOutput.Text = strl & str
2
44
.
D
im numl, num2, num3 As Double DATA.TX
T
n
um1 = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
3
n
um2 = CDbl(sr.ReadLine) 4
n
um3 = CDbl(sr.ReadLine)
5
t
xtOutput.Text = CStr((numl + num2) * num3
)
Page 100 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

45
.
D
im yrOfBirth, curYr As Double DATA.TX
T
y
rOfBirth = CDbl(sr.ReadLine) 1986
c
urYr = CDbl(sr.ReadLine) 'Current year 2006
t
xtOutput.Text = "Age: " & curYr - yrOfBirth
46.
D
im strl, str2 As String DATA.TX
T
s
trl = sr.ReadLine A, my name i
s
s
tr2 = sr.ReadLine Alic
e
t
xtOutput.Text = strl & " " & str
2
47
.
D
im building As String DATA.TX
T
D
im numRooms As Double White Hous
e
b
uilding = sr.ReadLine 13
2
n
umRooms = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
t
xtOutput.Text = "The " & building " has " & numRooms & " rooms.
"
48
.
D
im major As String DATA.TX
T
D
im percent As Double Computer Scienc
e
m
ajor = sr.ReadLine 1.4
p
ercent = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
t
xtOutput.Text = "In 2004, " & percent &
_
"% of entering college freshmen majored in " & major & "."
49
.
D
im num, sum As Doubl
e
DATA.TXT
s
um = 0 12
3
n
um = CDbl(sr.ReadLine) 321
s
um += nu
m
n
um = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
s
um += nu
m
t
xtOutput.Text = "Sum: "& su
m
[Page 121]
50
.
D
im grade, total, average As Doubl
e
DATA.TXT
D
im numGrades As Intege
r
85
t
otal = 0 95
n
umGrades = 0
g
rade = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
t
otal += grad
e
'Increase value of total by value of grade
n
umGrades += 1 'Increase value of numGrades by 1
g
rade = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
t
otal += grade 'Increase value of total by value of grad
e
Page 101 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 53 through 58, determine the output displayed.
n
umGrades += 1 'Increase value of numGrades by 1
a
verage = total / numGrade
s
t
xtOutput.Text = "Average grade: " & averag
e
51
.
D
im college As String DATA.TXT
c
ollege = sr.ReadLin
e
Harvard
l
stOutput.Items.Add(college
)
Yale
s
r.Close(
)
s
r = IO.File.OpenText("DATA.TXT"
)
c
ollege = sr.ReadLin
e
l
stOutput.Items.Add(college
)
52
.
D
im num As Integer, str As String DATA.TXT
n
um = CInt(sr.ReadLine
)
4
s
tr = sr.ReadLin
e
calling birds
l
stOutput.Items.Add(num & " " & str
)
3
s
r.Close(
)
French hens
s
r = IO.File.OpenText("DATA.TXT"
)
n
um = CInt(sr.ReadLine
)
s
tr = sr.ReadLin
e
l
stOutput.Items.Add(num & " " & str
)
53
.
Dim bet As Double 'Amount bet at roulette
bet = CDbl(InputBox("How much do you want to bet?", "Wager"))
txtOutput.Text = "You might win " & 36 * bet & " dollars."
(
Assume that the res
p
onse is 10.
)
54.
Dim word As String
word = InputBox("Word to negate:", "Negatives")
txtOutput.Text = "un" & word
(Assume that the response is "tied".)
55
.
Dim lastName, message, firstName As String
lastName = "Jones"
message = "What is your first name Mr. " & lastName & "?"
firstName = InputBox(message, "Name")
txtOutput.Text = "Hello " & firstName & " " & lastName
(
Assume that the res
p
onse is "John".
)
Page 10
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m
In Exercises 57 and 58, write a line of code to carry out the task.
In Exercises 59 through 66, identify any errors. If the code refers to a file, assume that DATA.TXT (on
the right of the code) already has been opened for input.
[Page 122]
56
.
Dim intRate, doublingTime As Double 'Current interest rate, time to double
intRate = CDbl(InputBox("Current interest rate?", "Interest"))
doublingTime = 72 / intRate
lstOutput.Items.Add("At the current interest rate, money will")
lstOutput.Items.Add("double in " & doublingTime & " years.")
(
Assume that the res
p
onse is 4.
)
57. Pop up a message dialog box with "Good Advice" in the title bar and the message "Keep
cool, but don't freeze.
"
58
.
Pop up a message dialog box with "Taking Risks Proverb" in the title bar and the
messa
g
e "You can't steal second base and kee
p
one foot on first.
"
59
.
D
im num As Doubl
e
DATA.TXT
n
um = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
1 + 2
t
xtOutput.Text = CStr(3 * num
)
60
.
'
Each line triplet of DATA.TXT contain
s
DATA.TXT
'
building, height, # of storie
s
Sears Tower
D
im building As String 1454
D
im ht As Doubl
e
110
D
im numStories As Intege
r
Empire State Building
l
stOutput.Items.Clear(
)
1250
b
uilding = sr.ReadLin
e
102
h
t = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
l
stOutput.Items.Add(building & " is " & ht & " feet tall."
)
b
uilding = sr.ReadLin
e
h
t = CDbl(sr.ReadLine
)
l
stOutput.Items.Add(building & " is " & ht & " feet tall."
)
61
.
D
im num As Doubl
e
n
um = InputBox("Pick a number from 1 to 10."
)
t
xtOutput.Text = "Your number is " & nu
m
Page 10
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 123]
In Exercises 67 through 70, write an event procedure starting with a Private Sub btnCompute_Click
(. . .) Handles btnCompute.Click
statement, ending with an End Sub statement, and having one,
two, or three lines for each step. Lines that display data should use the given variable names.
62
.
i
nfo = InputBox(
)
63.
D
im num As Double = FormatNumber(123456
)
lstOutput.Items.Add(num)
64
.
t
xtOutput.Text = FormatCurrency($1234
)
65
.
D
im fmtStr As String = "{0,20}{1,10}
"
l
stOutput.Items.Add(fmtStr, "Washington", "George"
)
66
.
M
sgBox("Proof", "Pulitzer Prize for Drama"
)
67. The following steps display information about Americans' eating habits. Assume that the
three lines of the file SODA.TXT contain the following data: soft drinks, million gallons,
23.
a. Declare all variables used in step (c).
b. Open the file SODA.TXT for input.
c. Use ReadLine statements to assign values to the variables food, units, and
quantityPerDay.
d. Display a sentence giving the quantity of a food item consumed by Americans in
one day.
68. The following steps display the changes in majors for first-year college students from
2003 to 2004. Assume that file MAJORS.TXT consists of six lines containing the
following data: Elementary Education, 4.9, 4.6, Psychology, 4.7, 4.6.
Page 10
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 124]
In Exercises 71 through 76, give a setting for the Mask property of a masked text box used to input the
stated information.
a
.
Declare all variables used in the steps that follow.
b. Open the file MAJORS.TXT for input.
c. Use ReadLine statements to assign values to the variables major, percent03, and
percent04.
d. Display a sentence giving the change in the percentage of students majoring in a
certain subject.
e. Repeat steps (c) and (d).
69
.
The following steps calculate the percent increase in a typical grocery basket of goods:
a. Declare all variables used in the steps that follow.
b. Assign 200 to the variable begOfYearPrice.
c. Request the price at the end of the year with an input dialog box, and assign it to
the variable endOfYearPrice.
d. Assign 100
*
(endOfYearPrice begOfYearPrice) / begOfYearPrice to the variable
percentIncrease.
e. Display a sentence giving the percent increase for the year.
(Test the program with a $215 en
d
-of-year price.)
70
.
The following steps calculate the amount of money earned in a wal
k
-a-thon:
a. Declare all variables used in the steps that follow.
b. Request the amount pledged per mile from an input dialog box, and assign it to the
variable pledge.
c. Request the number of miles walked from an input dialog box, and assign it to the
variable miles.
d. Display a sentence giving the amount to be paid.
(
Test the
p
ro
g
ram with a
p
led
g
e of $2.00 and a 1
5
-mile walk.
)
Page 10
5
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

71
.
A number from 100 to 999.
72
.
A word of ten letters.
73. A Maryland license plate consisting of three letters followed by three digits.
(
Example:
BHC365)
74
.
A California license plate consisting of a digit followed by three letters and then three
di
g
its.
(
Exam
p
l
e
: 7BHC365
)
75. An ISBN number. [Every book is identified by a te
n
-character International Standard
Book Number (ISBN). The first nine characters are digits and the last character is either a
di
g
it or the letter X.
]
(
Exam
p
l
e
: 0-3
2
-10859
9
-X
)
.
76
.
A tw
o
-letter state abbreviation.
(
Exam
p
l
e
: CA
)
77
.
Table 3.
4
summarizes the month's activity of three checking accounts. Write a program
that displays the account number and the en
d
-of-month balance for each account and
then displays the total amount of money in the three accounts. Assume that the data are
stored in a text file.
Table 3.4. Checking account activity.
Account
Number
Beginning
of Month
Balance
Deposits Withdrawals
AB4057 1234.56 345.67 100.00
XY4321 789.00 120.00 350.00
GH2222 321.45 143.65 0.00
78
.
Table 3.
5
contains a list of colleges with their student enrollments and faculty sizes.
Write a program to display the names of the colleges and their student/faculty ratios, and
the ratio for the total collection of students and faculty. Assume that the data for the
colleges are stored in a text file.
Source: The World Almanac, 2005.
Table 3.5. Colleges.
Enrollment Faculty
Ohio State 50721 3657
Univ. of MD, College Park 35262 2087
Princeton 6849 1015
Page 10
6
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

79
.
Write a program to compute semester averages. Each set of five lines in a text file should
contain a student's Social Security number and the grades for three hourly exams and the
final exam. (The final exam counts as two hourly exams.) The program should display
each student's Social Security number and semester average, and then the class average.
Use the data in Table 3.6.
[Page 125]
Table 3.6. Student grades.
Soc. Sec. No. Exam 1 Exam 2 Exam 3 Final Exam
123-45-6789 67 85 90 88
111-11-1111 93 76 82 80
123-32-1234 85 82 89 84
80
.
Table 3.
7
gives the year 2003 populations of three New England states. Write a program
that calculates the average population and then displays the name of each state and the
difference between its population and the average population. The states and their
p
opulations should be stored in a text file.
Table 3.7. 2003 population (in thousands) of three New England
states.
State Population
Maine 1305
Massachusetts 6433
Connecticut 3483
81. Design a form with two text boxes labeled "Name" and "Phone number". Then write an
event procedure that shows a message dialog box stating "Be sure to include the area
code!" when the second text box receives the focus.
82. Write a program to calculate the amount of a waiter's tip given the amount of the bill and
the percentage tip obtained via input dialog boxes. The output should be a complete
sentence that reiterates the inputs and gives the resulting tip, as shown in Figure 3.28
.
Figure 3.28. Sample output for Exercise 82.
Page 10
7
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

In Exercises 84 and 85, write lines of code corresponding to the given flowchart. Assume that the data
needed are contained in a file.
83. When P dollars are deposited in a savings account at interest rate r compounded
annually, the balance after n years is P(1 + r)
n
. Write a program to request the principal P
and the interest rate r as input, and compute the balance after 10 years, as shown in
Figure 3.2
9
(on the next page).
[Page 126]
Figure 3.29. Sample output for Exercise 83.
84
.
Page 108 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

85
.
Page 10
9
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 127]
Solutions to Practice Problems 3.5
1. The first statement is correct, since FormatNumber evaluates to a string. Although the
second statement is not incorrect, the use of CStr is redundant.
2
.
The outcomes are identical. In this text, we primarily use the second style.
Page 110 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 127 (continued)
]
Chapter 3 Summary
1. The Visual Basic window consists of a form holding a collection of controls for which various
properties can be set. Some examples of controls are text boxes, labels, buttons, and list boxes.
Some useful properties are Text (sets the text displayed in a control), Name (used to give a
meaningful name to a control), Font.Name (selects the name of the font used), Font.Size (sets the
size of the characters displayed), Font.Bold (displays boldface text), Font.Italic (displays italic
text), BackColor (sets the background color), ForeColor (sets the color of the text), ReadOnly
(determines whether text can be typed into the text box), TextAlign (sets the type of alignment for
the text in a control), and Visible (shows or hides an object). The With block is a useful device for
setting properties at run time.
2. An event procedure is executed when something happens to a specified object. Some events are
object.Click (object is clicked), object.TextChanged (a change occurred in the value of the object's
Text property), object.Leave (object loses the focus), and object.Enter (object receives the focus).
Note: The statement object.Focus() moves the focus to the specified object.
3. Two types of literals that can be stored and processed by Visual Basic are numbers and strings.
4. Many Visual Basic tasks are carried out by methods such as Clear (erases the contents of a text
box or list box), Add (places an item into a list box), ToUpper (converts a string to uppercase),
ToLower (converts a string to lowercase), Trim (removes leading and trailing spaces from a
string), IndexOf (searches for a specified character in a string and gives its position if found), and
SubString (returns a sequence of consecutive characters from a string).
5. The standard arithmetic operations are +,-,*,/, and ^. The only string operation is &,
concatenation. An expression is a combination of literals, variables, functions, and operations that
can be evaluated.
6. A variable is a name used to refer to data. Variable names must begin with a letter or an
underscore and may contain letters, digits, and underscores. Dim statements explicitly declare
variables, specify the data types of the variables, and assign initial values to the variables. In this
book, most variables have data types Double, Integer, or String.
7. Values are assigned to variables by assignment statements. The values appearing in assignment
statements can be literals, variables, or expressions. String literals used in assignment statements
must be surrounded by quotation marks.
8. Comment statements are used to explain formulas, state the purposes of variables, and articulate
the purposes of various parts of a program.
[Page 128]
9. Format strings can be used to line up data in tables uniformly and display them with dollar signs,
commas, percent signs, and a specified number of decimal places.
10. A StreamReader object allows us to read data from a file that is specified with an OpenText
method. The ReadLine method reads the next unread line from a file.
Page 111 of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

11
.
Functions can be thought of as accepting numbers or strings as input and returning numbers o
r
strings as output.
12. Masked text boxes are useful for input since they have a Mask property that specifies the type of
data that can be typed into them.
Function Input Output
CDbl string or number number
CInt string or number number
CStr number string
FormatCurrency number string
FormatNumber number string
FormatPercent number string
InputBox string, string string
Int number number
Math.Round number, number number
Math.Sqrt number number
[Page 128 (continued)
]
Chapter 3 Programming Projects
1. Write a program that allows the user to specify two numbers and then adds, subtracts, or
multiplies them when the user clicks on the appropriate button. The output should give the type of
arithmetic performed and the result.
2. Suppose automobile repair customers are billed at the rate of $35 per hour for labor. Also, costs
for parts and supplies are subject to a 5% sales tax. Write a program to display a simplified bill.
The customer's name, the number of hours of labor, and the cost of parts and supplies should be
entered into the program via text boxes. When a button is clicked, the customer's name (indented)
and the three costs should be displayed in a list box, as shown in the sample run in Figure 3.30
.
Figure 3.30. Sample run for Programming Project 2.
Page 11
2
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

[Page 129]
3. At the end of each month, a credit card company constructs the table in Figure 3.31 to summarize
the status of the accounts. Write a program to produce this table. The first four pieces of
information for each account should be read from a text file. The program should compute the
finance charges (1.5% of the unpaid past due amount) and the current amount due.
Figure 3.31. Status of credit card accounts.
[View full size image]
4. Table 3.8 gives the projected 2005 distribution of the U.S. population (in thousands) by age group
and sex. Write a program to produce the table shown in Figure 3.32. For each age group, the
column labeled "%Males" gives the percentage of the people in that age group who are male, and
the column labeled "%Females" gives this information about the female population. The last
column gives the percentage of the total population in each age group. Note: Store the information
in Table 3.8
in a text file. For instance, the first three lines in the file should contain the following
data: Under 25, 51210, 48905. Read and add up the data once to obtain the total population, and
then read the data again to produce the table.
Table 3.8. Projected U.S.population (2005).
Age Group Males Females
Under 25 51,210 48,905
2564 74,169 77,059
Page 11
3
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m

Figure 3.32. Output of Programming Project 4.
[View full size image]
[Page 130]
5. Write a program to convert a U.S. Customary System length in miles, yards, feet, and inches to a
Metric System length in kilometers, meters, and centimeters. A sample run is shown in Figure
3.33. After the numbers of miles, yards, feet, and inches are read from the text boxes, the length
should be converted entirely to inches and then divided by 39.37 to obtain the value in meters.
The Int function should be used to break the total number of meters into a whole number of
kilometers and meters. The number of centimeters should be displayed to one decimal place.
Some of the needed formulas are as follows:
Figure 3.33. Sample run for Programming Project 5.
total inches = 63360 * miles + 36 * yards + 12 * feet + inches
total meters = total inches/39.37
kilometers = Int
(
meters/1000
)
65+ 15,319 21,051
Page 11
4
of 11
4
Chapter 3. Fundamentals of Programming in Visual Basic
9
/
11
/
201
3
file:///C:/Users/CTESORIERO14/A
pp
Data/Local/Tem
p
/~hh50C3.ht
m
